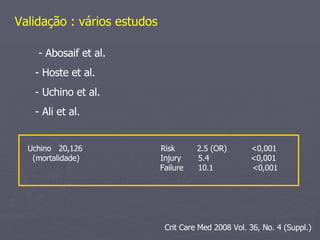
1) O documento discute critérios para diagnóstico de lesão renal aguda (AKI), incluindo os critérios RIFLE. 2) A incidência de AKI em unidades de terapia intensiva é alta, variando de 60-70% dos pacientes, e está associada a maior mortalidade. 3) Marcadores biológicos como cistatina C e lipocalina associada a neutrófilos podem diagnosticar AKI mais precocemente do que a creatinina.






















![NECROSE TUBULAR AGUDA APOPTOSE TUBULAR Crit Care Med 2008; 36[Suppl.]:S198–S203](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acute-kidney-injury-1215216635223310-9/85/Acute-Kidney-Injury-24-320.jpg)










