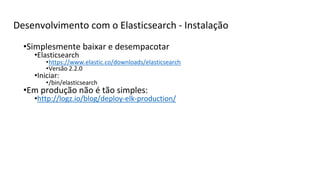
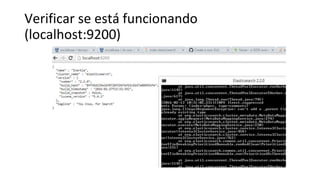
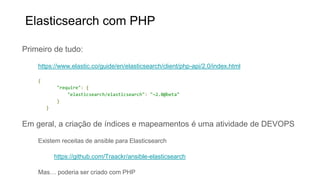
O documento apresenta uma visão geral do Elasticsearch 2.0 e como usá-lo com PHP. As principais seções incluem: (1) visão geral do Elasticsearch, sua arquitetura e uso, (2) desenvolvimento com o Elasticsearch, incluindo indexação, busca e agregações, (3) uso do cliente PHP para interagir com o Elasticsearch, realizando operações como indexação, busca e sugestão.



















![Busca - bool, boost e agregações
GET /phpsc/post,comment
/_search
{
"sort": [
{
"author": {
"order": "desc"
}
}
],
"size": 100,
"query": {
"bool": {
"should": [{
"match": {
"author": "anônimo"
}}, {
"match": {
"local": "Florianópolis"
}
}
]
} ,
"aggs" : {
"hashtags" : {
"terms" : { "field" : "author.raw"
}
}
https://gist.github.com/lhzsantana/f552751d
a153741657](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/novidades-do-elasticsearch-20-e0b-como-uslo-com-php-160213150140/85/Novidades-do-elasticsearch-2-0-e-como-usa-lo-com-PHP-29-320.jpg)

![Elasticsearch com PHP - Criar o cliente
$hosts = [
'192.168.1.1:9200', // IP + Port
'192.168.1.2', // Just IP
'mydomain.server.com:9201', // Domain + Port
'mydomain2.server.com', // Just Domain
'https://localhost', // SSL to localhost
'https://192.168.1.3:9200' // SSL to IP + Port
];
$client = ClientBuilder::create() // Instantiate a new ClientBuilder
->setHosts($hosts) // Set the hosts
->build(); // Build the client object
Num cluster, todos IPs
devem estar entre os
hosts. O cliente irá
acessar em round-
robin.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/novidades-do-elasticsearch-20-e0b-como-uslo-com-php-160213150140/85/Novidades-do-elasticsearch-2-0-e-como-usa-lo-com-PHP-32-320.jpg)
![Elasticsearch com PHP - Indexação
$params = [
'index' => phpsc,
'type' => 'post',
'body' =>
[
'author' => 'Luiz',
'text' => 'Ufaaa finalmente PHP :)'
]
];
$response = $client->index($params);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/novidades-do-elasticsearch-20-e0b-como-uslo-com-php-160213150140/85/Novidades-do-elasticsearch-2-0-e-como-usa-lo-com-PHP-33-320.jpg)
![Elasticsearch com PHP - Recuperar com ID
$params = [
'index' => 'phpsc',
'type' => 'post',
'id' => '1'
];
$response = $client->get($params);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/novidades-do-elasticsearch-20-e0b-como-uslo-com-php-160213150140/85/Novidades-do-elasticsearch-2-0-e-como-usa-lo-com-PHP-34-320.jpg)
![Elasticsearch com PHP - Buscar
$params = [
'index' => phpsc,
'type' => 'post',
'body' => [
'query' => [
'match' => [
'author' => 'Luiz'
]
]
]
];
$results = $client->search($params);
//resultados
$milliseconds = $results['took'];
$maxScore = $results['hits']['max_score'];
$score = $results['hits']['hits'][0]['_score'];
$docs = $results['hits']['hits'];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/novidades-do-elasticsearch-20-e0b-como-uslo-com-php-160213150140/85/Novidades-do-elasticsearch-2-0-e-como-usa-lo-com-PHP-35-320.jpg)
![Elasticsearch com PHP - Filtros já não existem no ES 2.0!
$params = [
'index' => phpsc,
'type' => 'post',
'body' => [
'query' => [
'match' => [
'author' => 'Luiz'
]
],
'filter' => [
'match' => [
'local' => 'Florianópolis'
]
]
]
];
$results = $client->search($params);
USE
QUERY](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/novidades-do-elasticsearch-20-e0b-como-uslo-com-php-160213150140/85/Novidades-do-elasticsearch-2-0-e-como-usa-lo-com-PHP-36-320.jpg)
![Elasticsearch com PHP - Boolean
$params = [
'index' => 'phpsc',
'type' => 'post',
'body' => [
'query' => [
'bool' => [
'should' => [
[ 'match' => [ 'author' => 'luiz' ] ],
[ 'match' => [ 'local' => 'florianópolis' ] ],
]
]
]
]
];
$results = $client->search($params);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/novidades-do-elasticsearch-20-e0b-como-uslo-com-php-160213150140/85/Novidades-do-elasticsearch-2-0-e-como-usa-lo-com-PHP-37-320.jpg)
![Elasticsearch com PHP - Desafio
$params = [
'index' => 'phpsc',
'type' => 'post',
//sort
'body' => [
'query' => [
],
//aggregations
]
];
$results = $client->search($params);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/novidades-do-elasticsearch-20-e0b-como-uslo-com-php-160213150140/85/Novidades-do-elasticsearch-2-0-e-como-usa-lo-com-PHP-38-320.jpg)
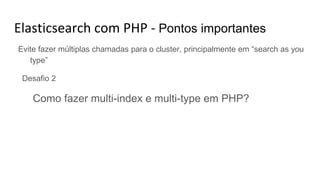
![Elasticsearch com PHP - Pontos importantes
MSearch
$params = [
'index' => 'phpsc',
'body' => [
['type' => 'post'],
['query' => ['match_all' => []]],
['type' => 'comment'],
['query' => ['match_all' => []]]
]
];
$results = $client->msearch($params);
//resultados
$responses = $results['responses']['hits']['hits'];
$posts = $responses[0]['hits']['hits'];
$comments = $responses[1]['hits']['hits'];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/novidades-do-elasticsearch-20-e0b-como-uslo-com-php-160213150140/85/Novidades-do-elasticsearch-2-0-e-como-usa-lo-com-PHP-40-320.jpg)
![Elasticsearch com PHP
Bulk no lugar de Rivers para o ES 2.0!
if (!is_string($type) || !is_string($operation)) {
throw new InvalidArgumentException();
}
$response = [];
if (!empty($json)) {
$params = [];
for ($i = 0; $i < count($json); $i++) {
$params['body'][] = [
'index' => $index,
'type' => $type
];
$params['body'][] = [
$json [$i]
];
}
$response = $this->elasticsearchClient->bulk($params);
{ "index" : { "_index" : "test", "_type" : "type1", "_id" : "1" }
}
{ "field1" : "value1" }
{ "delete" : { "_index" : "test", "_type" : "type1", "_id" : "2" }
}
{ "create" : { "_index" : "test", "_type" : "type1", "_id" : "3" }
}
{ "field1" : "value3" }
{ "update" : {"_id" : "1", "_type" : "type1", "_index" : "index1"}
}
{ "doc" : {"field2" : "value2"} }
$ curl -s -XPOST localhost:9200/_bulk --data-binary "@requests";
echo
{"took":7,"items":[
{"create":{"_index":"test","_type":"type1","_id":"1","_version":1}
}]}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/novidades-do-elasticsearch-20-e0b-como-uslo-com-php-160213150140/85/Novidades-do-elasticsearch-2-0-e-como-usa-lo-com-PHP-41-320.jpg)
![Elasticsearch com PHP - Suggestion
params = [
'hashtag-suggest' => [
"text" => “#qu”,
"completion" => [
"field" =>
"hashtags.suggest"
]
]
];
$response = $this->client-
>suggest(params);
//resultados
if (!isset($response['hashtag-suggest'])) {
return ['items' => []];
}
$items = [];
foreach ($response['hashtag-suggest'] as $item) {
foreach ($item['options'] as $option) {
$items[] = $option['text'];
}
}
return ['items' => $items];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/novidades-do-elasticsearch-20-e0b-como-uslo-com-php-160213150140/85/Novidades-do-elasticsearch-2-0-e-como-usa-lo-com-PHP-42-320.jpg)

![Elasticsearch com PHP - Array x JSON
$json = '{
"query" : {
"match" : {
"author" : "Luiz"
}
}
}';
$params = [
'index' => 'phpsc',
'type' => 'post',
'body' => $json
];
$results = $client->search($params);
$params = [
'index' =>'phpsc',
'type' => 'post',
'body' => [
'query' => [
'match' => [
'author' => 'Luiz'
]
]
]
];
$results = $client->search($params);
$params = ['index'] = 'phpsc';
$params = ['my_type'] = 'post';
$params = ['body']['query']['match']
['author' ] = 'Luiz';
$results = $client->search($params);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/novidades-do-elasticsearch-20-e0b-como-uslo-com-php-160213150140/85/Novidades-do-elasticsearch-2-0-e-como-usa-lo-com-PHP-44-320.jpg)