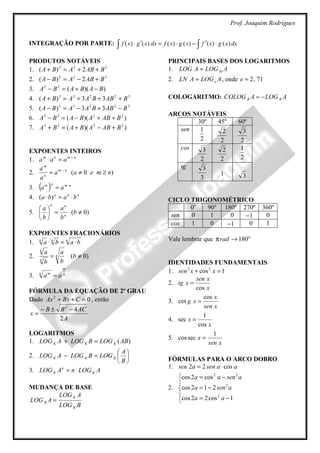
1) O documento fornece uma tabela de derivadas e integrais comuns, incluindo fórmulas para derivadas de funções exponenciais, trigonométricas e logarítmicas.
2) Também apresenta regras úteis como a regra da cadeia, do produto, do quociente e L'Hospital, além de fórmulas para produtos notáveis, expoentes inteiros e fracionários, logaritmos, mudança de base e arco trigonométrico.
3) Por fim, lista identidades trigonométricas fundament
()]([)( xhxhgxfxhgxf ′⋅′=′⇒=
Regra de L’Hospital
Seja 0)(lim =
→
xf
ax
e 0)(lim =
→
xg
ax
e se existe
)(
)(
lim
xg
xf
ax ′
′
→
, então existe
)(
)(
lim
xg
xf
ax →
e daí temos:
)(
)(
lim
)(
)(
lim
xg
xf
xg
xf
axax ′
′
=
→→](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tabeladerivadaseintegrais-1-151022191408-lva1-app6891/75/Tabela-derivadas-e-integrais-1-1-2048.jpg)