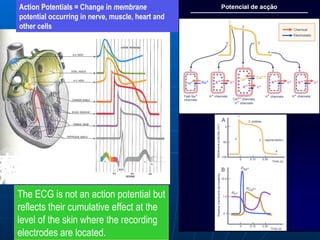
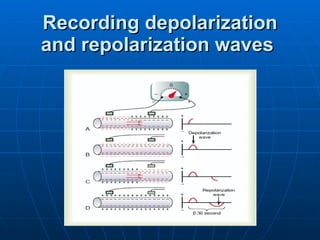
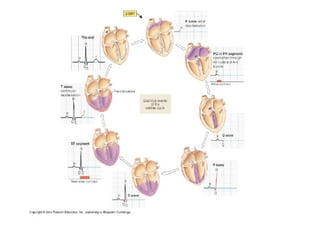
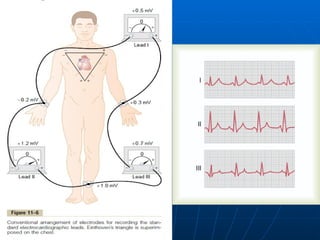
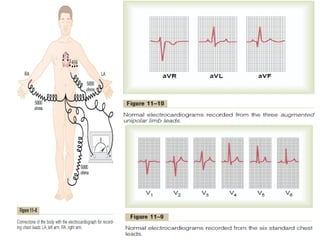
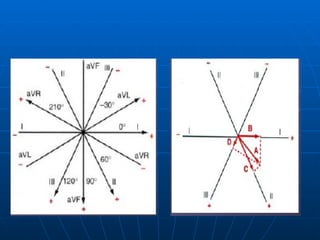
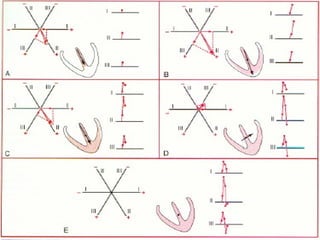
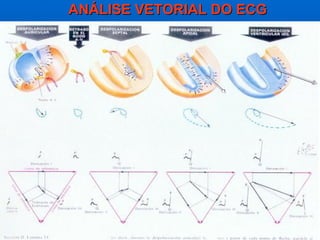
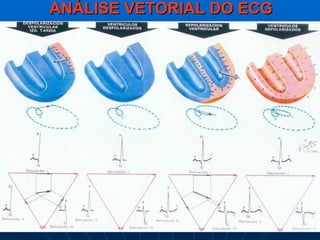
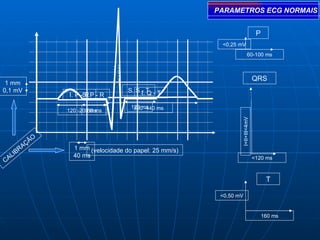
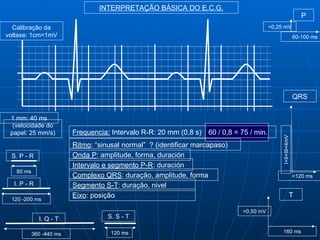
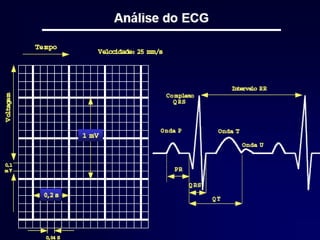
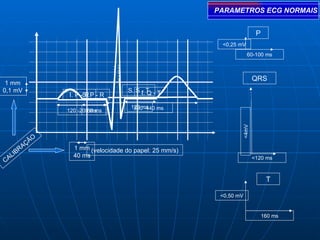
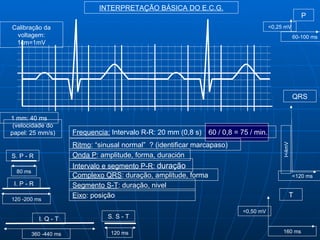
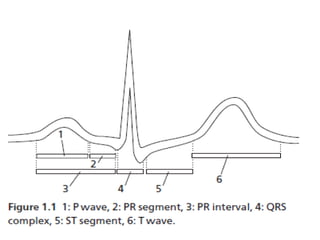
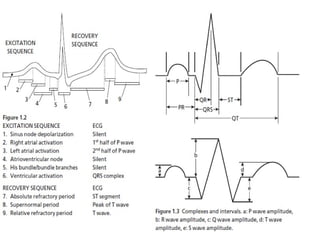
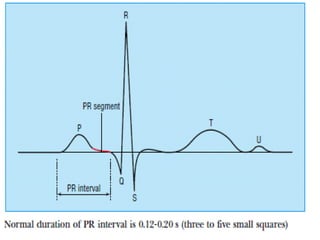
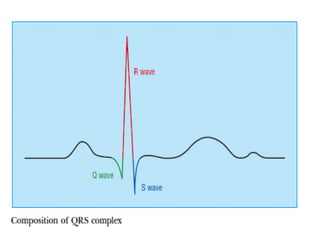
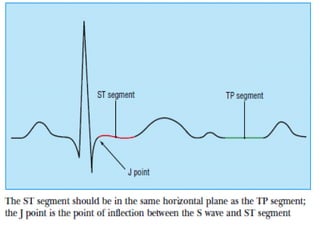
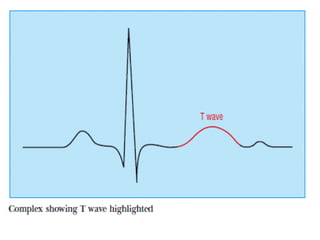
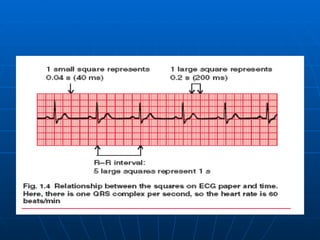
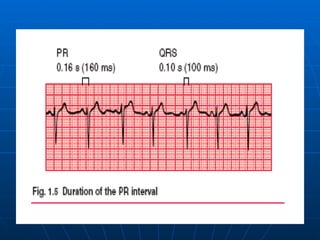
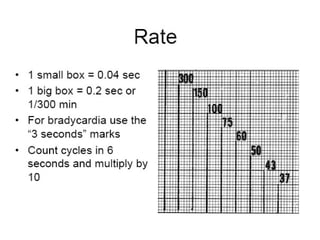
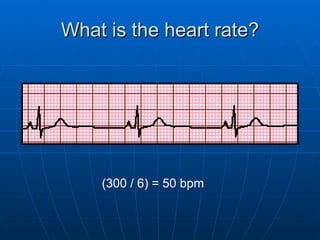
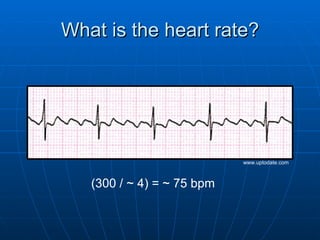
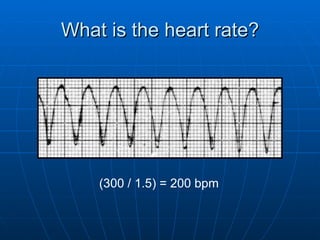
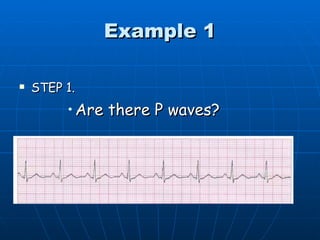
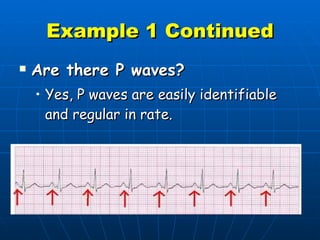
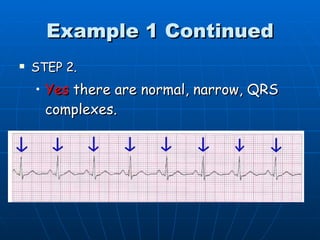
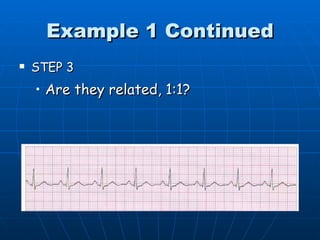
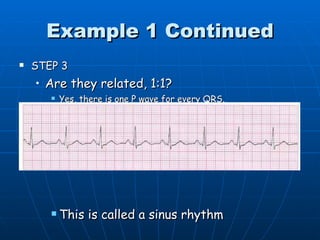
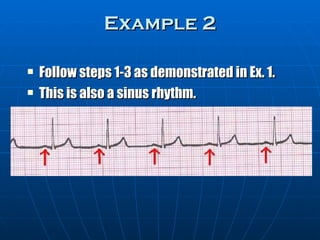
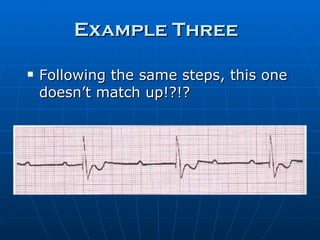
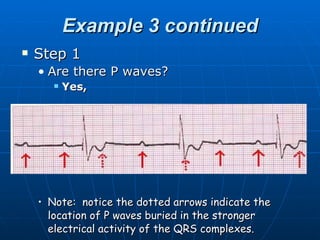
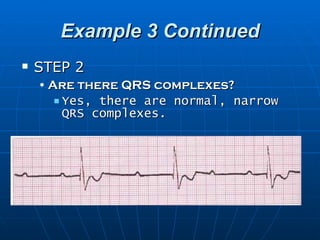
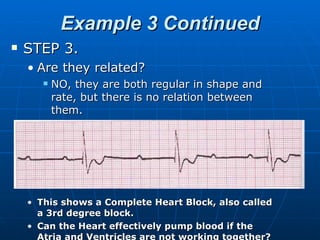
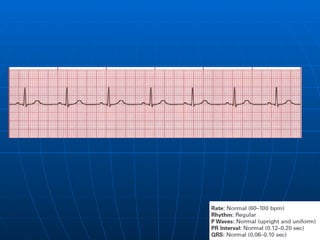
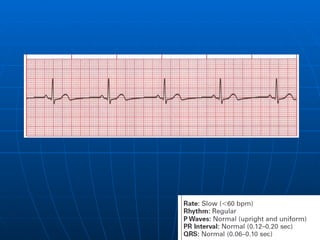
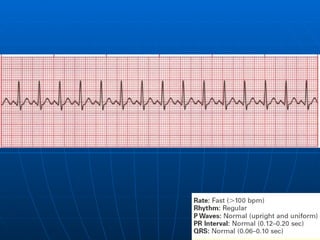
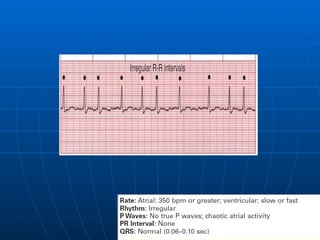
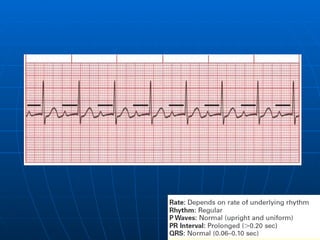
This document outlines the content of a course on electrocardiography (ECG), covering normal ECG parameters and patterns, vectorial analysis of the ECG, basic ECG interpretation, and beginning recognition of rhythms such as sinus rhythm and heart block. The course is divided into modules that cover topics including normal ECG features, abnormalities, arrhythmias, antiarrhythmic drugs, and a test with 20 ECG strips.