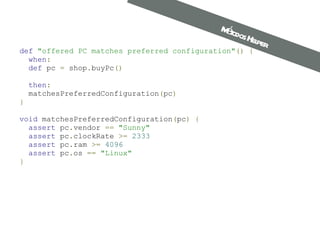
O documento apresenta o framework Spock para testes de software. Discute os principais recursos como blocos expect, then, where e cleanup para validar comportamentos. Também mostra como usar métodos helper para isolar validações e melhorar a legibilidade dos testes.


![// valor de retorno único, repetido indefinidamente subscriber . isAlive () >> true // valores de retorno múltiplos (qualquer coisa que o Groovy pode iterar). O último é repetido indefinidamente subscriber . isAlive () >>> [ true , false , true ] // valor de retorno personalizado def random = new Random () subscriber . isAlive () >> { random . nextBoolean () } // Ações personalizadas subscriber . isAlive () >> { throw new TimeoutException () } subscriberDao.get (_) >> { args -> new Subscriber(args[0]) } Valores de retorno](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spock2-110128054721-phpapp01/85/Spock-Framework-2-3-320.jpg)




![def "computing the maximum of two numbers" () { expect : Math . max ( a , b ) == c where : a << [ 5 , 3 ] b << [ 1 , 9 ] c << [ 5 , 9 ] } Bloco Where](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spock2-110128054721-phpapp01/85/Spock-Framework-2-8-320.jpg)


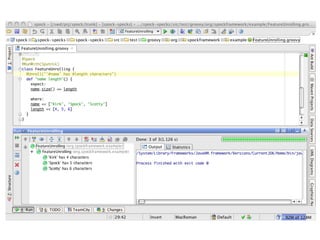
![Melhorando a visualização no console @Unroll def "name length" () { expect : name.size() == length where : name << ["Kirk", "Spock", "Scotty"] length << [4, 5, 6] }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spock2-110128054721-phpapp01/85/Spock-Framework-2-12-320.jpg)