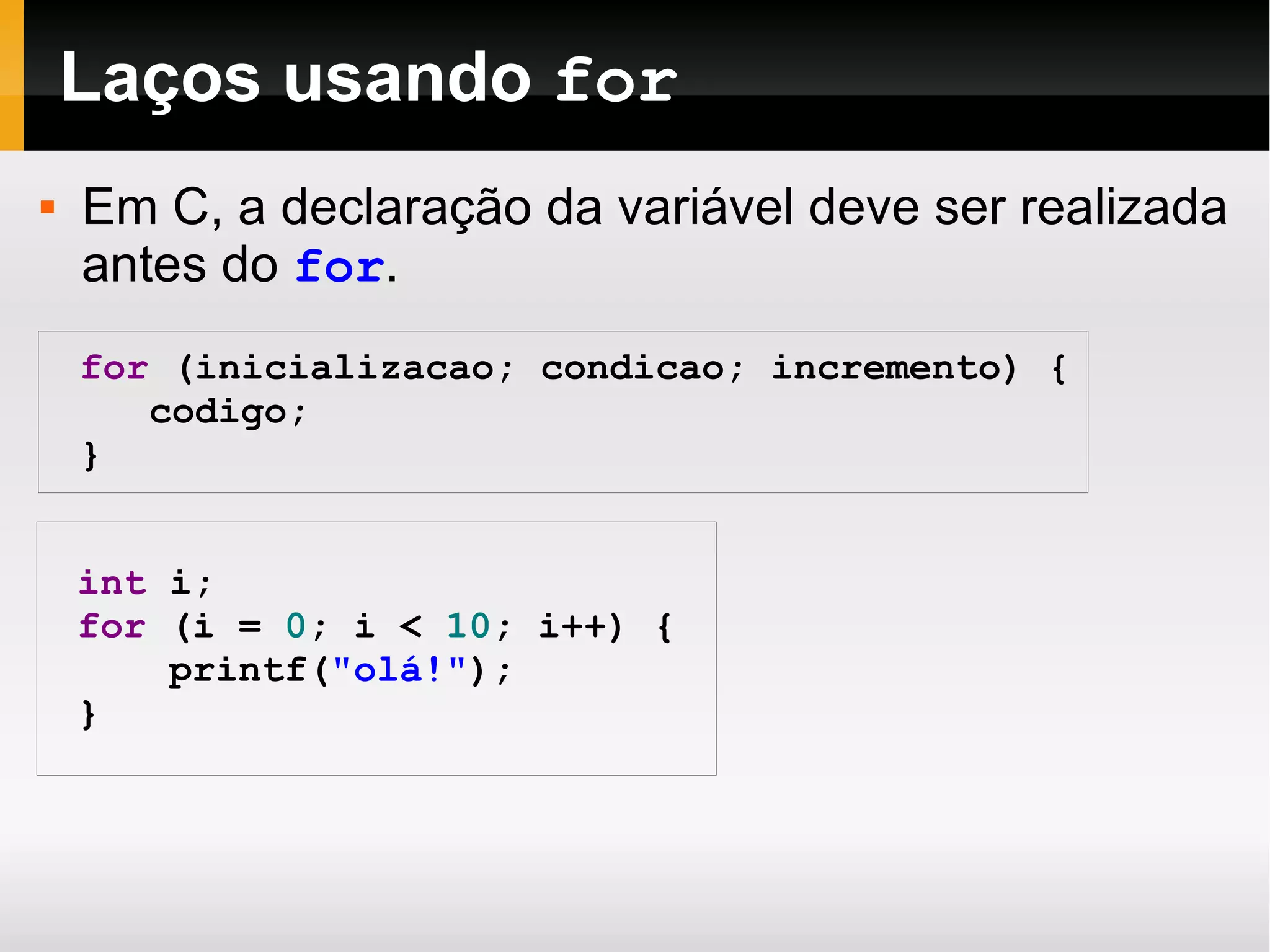
O documento descreve diferentes estruturas de repetição em linguagem C, incluindo laços while, for e como controlá-los com break e continue. Exemplos mostram como imprimir linhas, quadrados e laços aninhados de asteriscos, além de como usar múltiplas condições e incrementos em laços for.
![Linguagem C Estruturas de Controle Repetição Regis Pires Magalhães [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linguagemc04estruturasderepeticao-1228390453406961-9/75/Linguagem-C-04-Estruturas-De-Repeticao-1-2048.jpg)