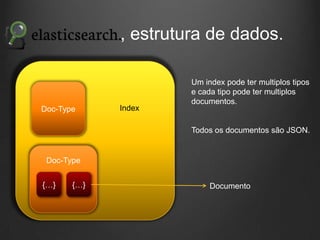
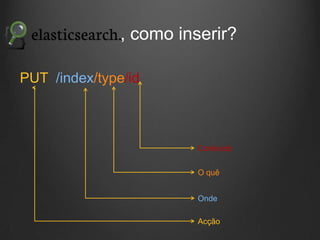
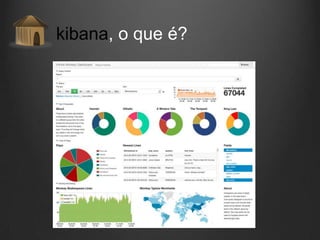
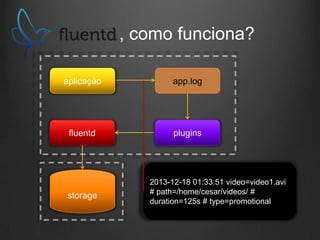
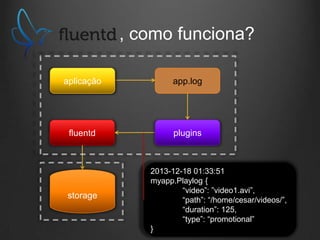
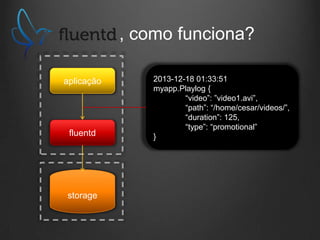
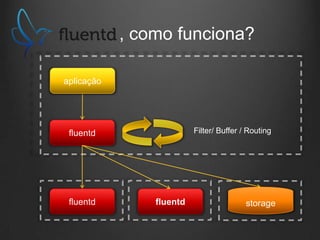
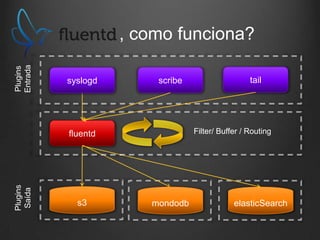
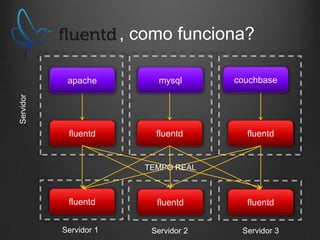
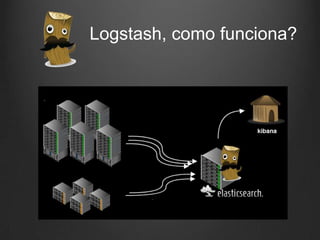
O documento descreve como Fluentd, Logstash, Elasticsearch e Kibana podem ser usados juntos para análise de logs em tempo real. Fluentd coleta logs de aplicações e os envia para Logstash ou diretamente para Elasticsearch. Logstash filtra e transforma os dados antes de enviá-los para Elasticsearch. Elasticsearch armazena os dados de forma a permitir pesquisas rápidas. Kibana fornece uma interface para visualização e análise dos dados armazenados no Elasticsearch.

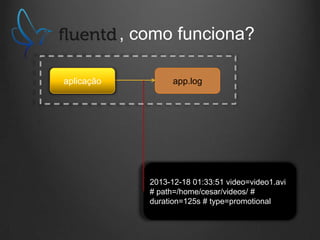
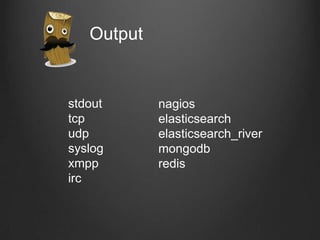
![, como funciona?
<source>
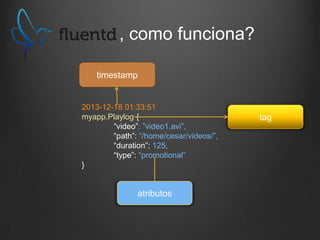
type tail
path /var/log/application/terminal.log # Localização do ficheiro do playlog
pos_file /var/log/td-agent/terminal.log.pos # Ficheiro que guarda posição do log
tag xp.terminal # Tag do fluentd para identificação!
format /^(?<time>[^ ]* [^ ]*) ?(?<Thread>[^ ]*) ?(?<TypeOfAlert>[^ ]*)
?(?<Machine>[XP]*[0-9a-fA-F]{12})-?(?<Player>[^ ]*).*filename=
"(?<Filename>[0-9]*.[^"]*).*/
</source>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fluentd-1-131109112520-phpapp02/85/Fluentd-LogStash-elastic-search-kibana-11-320.jpg)


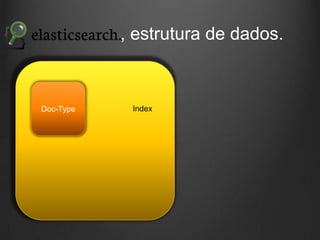
![Input - Exemplos
input {
file {
type => "syslog"
path => [ "/var/log/messages", "/var/log/syslog", "/var/log/*.log" ]
}
}
input {
redis {
host => "127.0.0.1"
type => "redis-input"
key => "logstash“
message_format => "json_event"
}
}
# “index”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fluentd-1-131109112520-phpapp02/85/Fluentd-LogStash-elastic-search-kibana-16-320.jpg)