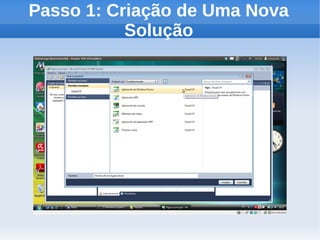
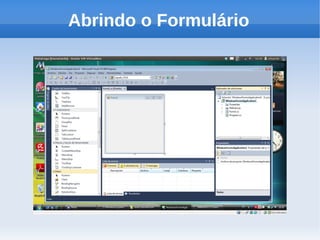
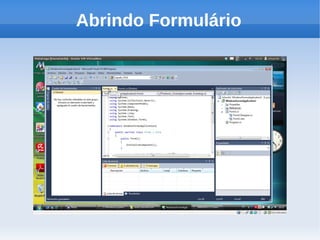
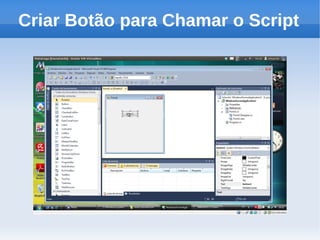
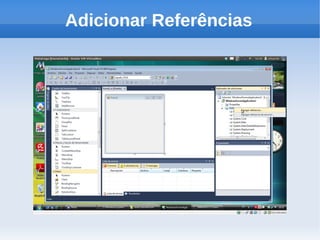
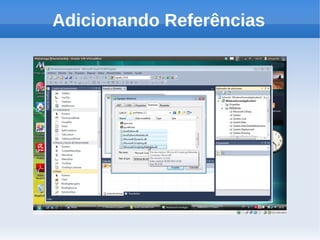
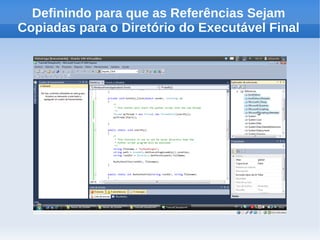
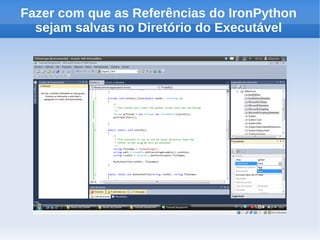
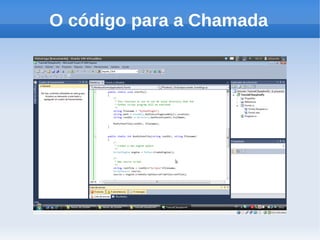
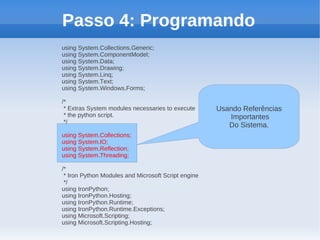
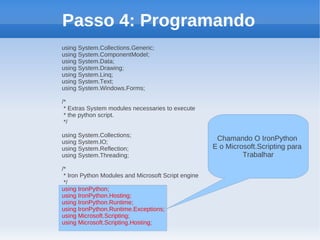
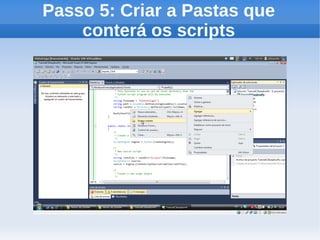
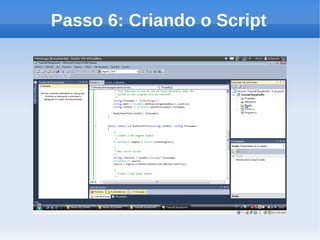
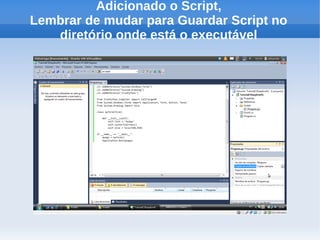
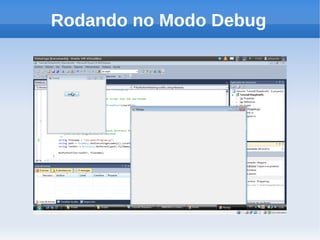
O documento apresenta um tutorial introdutório sobre como criar plugins em IronPython para projetos escritos originalmente em C#. O tutorial explica os 4 passos principais: 1) Criar uma nova solução no Visual Studio; 2) Adicionar um botão para chamar o script; 3) Adicionar referências do IronPython; 4) Programar a chamada do script em uma nova thread.
![Tutorial [Introdutório]: Criando
Pluging IronPython para c#
Por: Eduardo dos Santos Pereira
Dr. em Astrofísica
pereira.somoza@gmail.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tutorialcsharpitonpython-120830124126-phpapp01/75/Tutorial-Rodando-Python-no-C-1-2048.jpg)
![Tutorial [Introdutório]: Criando
Pluging IronPython para c#
Instituto Nacional de Pesquisas Espaciais/DEA
Apresentado uma breve introdução de como
rodar um script IronPython dentro do C#, isso
permitiria a criação de plugins em IronPython
para projetos que originalmente forma escritos
em c#.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tutorialcsharpitonpython-120830124126-phpapp01/85/Tutorial-Rodando-Python-no-C-2-320.jpg)