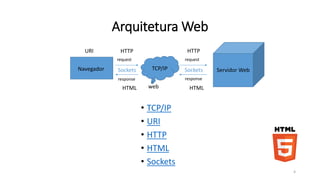
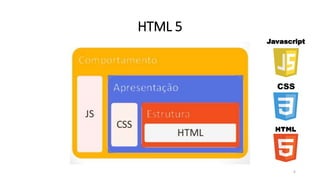
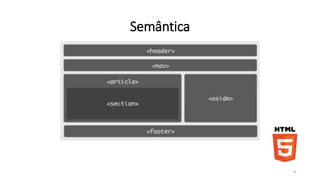
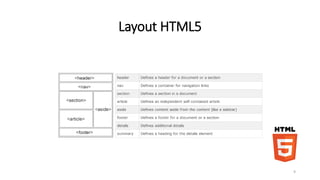
1. O documento discute HTML5, apresentando sua história, arquitetura, elementos e semântica. Também aborda CSS3 e JavaScript.
2. São apresentados diversos elementos HTML5 como vídeo, áudio, listas e formulários, além de CSS como fontes, cores e bordas.
3. O documento fornece links e exemplos para auxiliar no aprendizado de HTML5, CSS3 e JavaScript.






























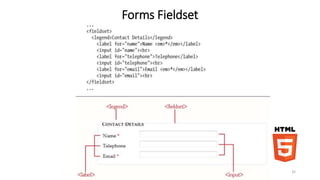
![FORMS
<style>
input[ required] { border: 1px red solid; }
<style>
<FORM name=“Contact” action=“contact.cgi”>
<FIELDSET>
<LEGEND>Contato</LEGEND>
<LABEL for=“nome”>Nome:</LABEL><INPUT id=“nome” required></br>
<LABEL for=“nome”>Telefone:</LABEL><INPUT id=“telefone” type=“tel” required></br>
<LABEL for=“email”>Email:</LABEL><INPUT id=“email” type=“email”></br>
</FIELDSET>
<INPUT type="submit" value=“Enviar“ >
</FORM>
36
http://www.w3schools.com/html/html_forms.asp
http://www.w3schools.com/tags/tag_input.asp](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aulahtml5-141009110435-conversion-gate02/85/Aula-html5-36-320.jpg)

![Atributo Pattern do elemento <INPUT>
<form action="demo_form.asp">
Country code: <input type="text" name="country_code"
pattern="[A-Za-z]{3}" title="Three letter country code“ required>
<input type="submit">
</form>
38
http://www.w3schools.com/tags/att_input_pattern.asp](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aulahtml5-141009110435-conversion-gate02/85/Aula-html5-38-320.jpg)



