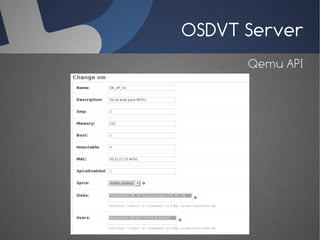
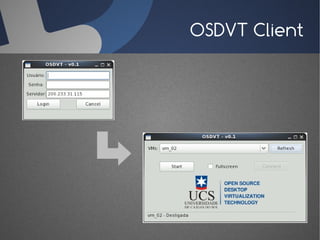
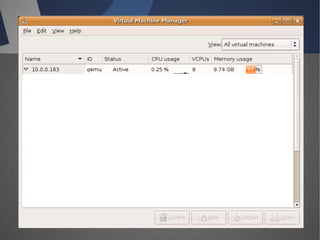
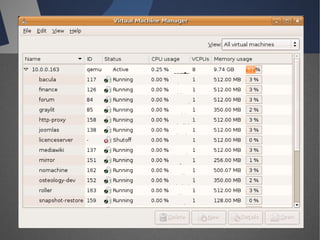
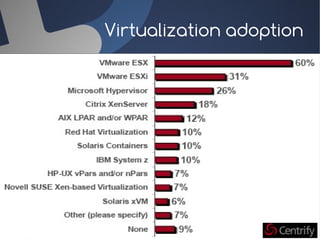
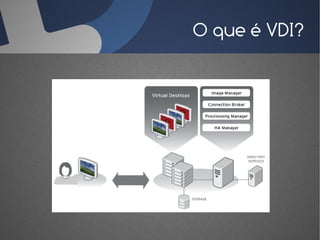
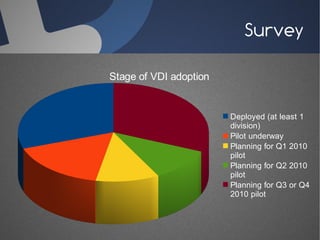
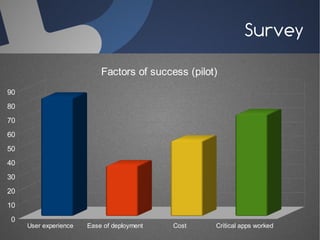
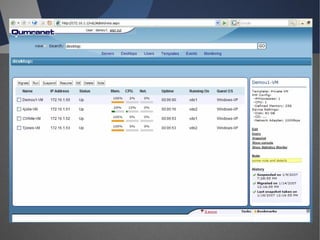
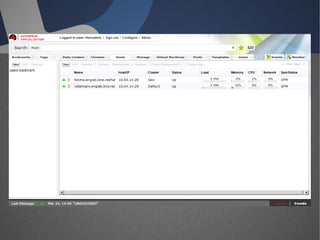
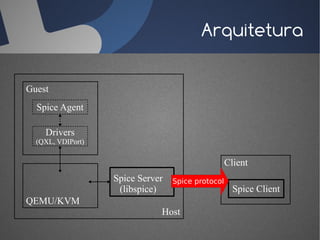
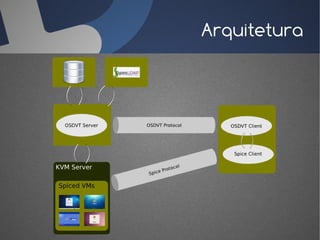
O documento discute a infraestrutura de desktop virtual (VDI) e fornece detalhes sobre o projeto Open Source Desktop Virtualization Technology (OSDVT). O OSDVT visa criar uma estrutura de VDI totalmente de código aberto usando tecnologias como Qemu, libvirt, OpenLDAP e MySQL para gerenciar desktops virtuais.

























![OSDVT Server
osdvt-server.conf
[Main] [SSL]
# Port to listen client connections # Version - SSLv1, SSLv2, SSLv23 or TLSv1
Port = 6970 Version = SSLv23
# Root directory of daemon files # Public cert file (full path)
MainDir = /usr/local/osdvt/server CertFile = /etc/openssl/cert.pem
# Private cert file (full path)
[Database] KeyFile = /etc/openssl/private/key.pem
# Type – MySQL, Oracle or Postgres
Type = MySQL [LDAP]
# Database server # Enable SSL (LDAPS) - True or False
Host = localhost SSL = True
# Database name # LDAP host
Name = vdesktop Host = ldap.com.br
# Table name #CA cert file (full path)
Table = vms CACert = /etc/openssl/cacert.pem
# Database user # Bae DN seach to authenticate users
User = osdvtuser BaseDN = ou=people,dc=foo,dc=bar
# Database password # Search filter
Password = osdvtpass Filter = uid](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vdi-osdvt-110412145718-phpapp01/85/VDI-e-Projeto-OSDVT-39-320.jpg)