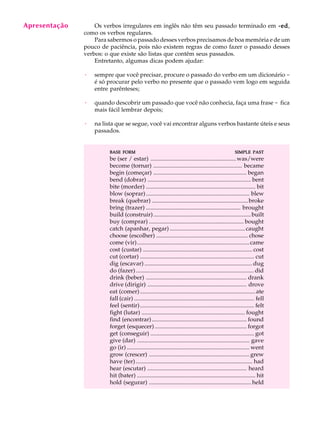
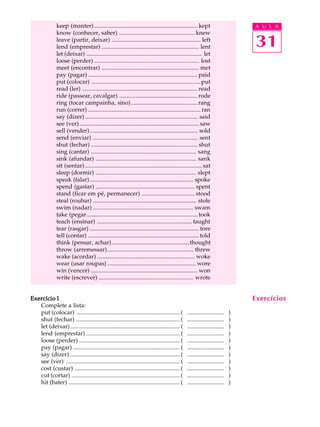
1) O documento discute verbos irregulares em inglês e fornece exemplos de verbos comuns e suas formas no passado.
2) É fornecida uma lista de mais de 50 verbos irregulares em inglês com suas formas no presente e passado.
3) Exemplos são dados para ajudar a praticar a conjugação de verbos irregulares no passado.