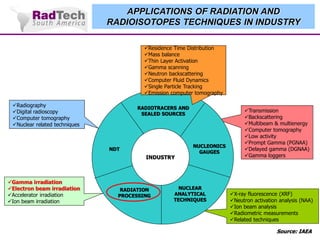
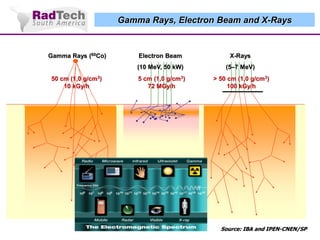
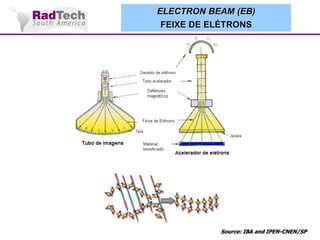
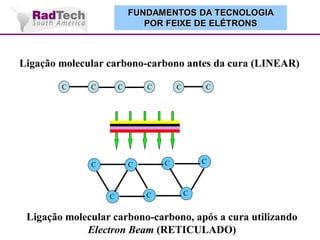
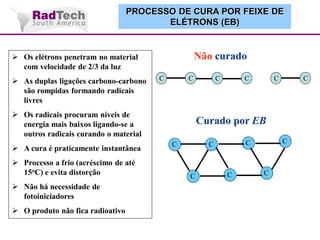
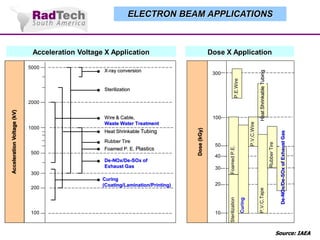
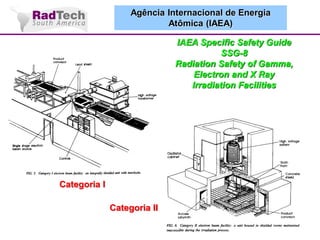
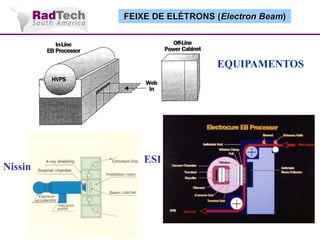
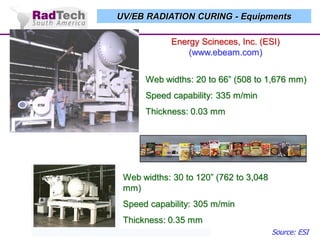
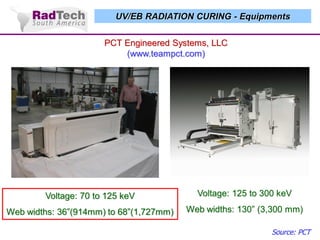
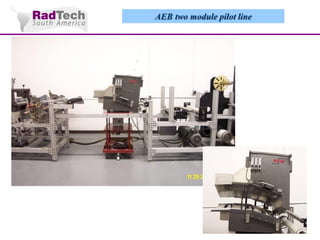
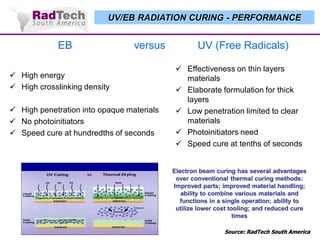
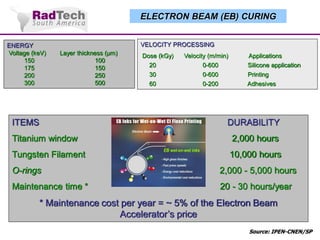
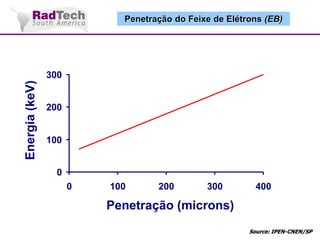
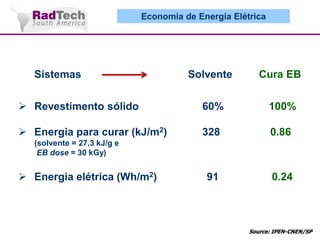
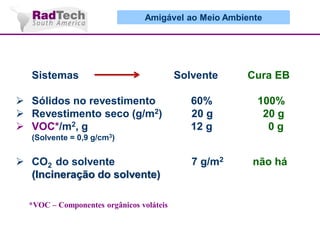
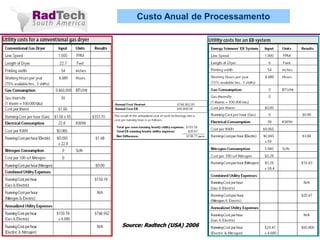
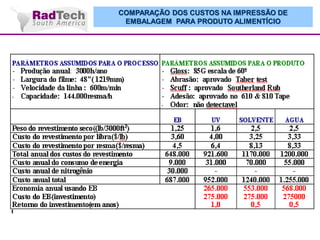
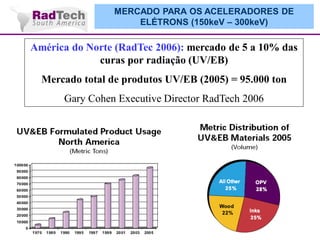
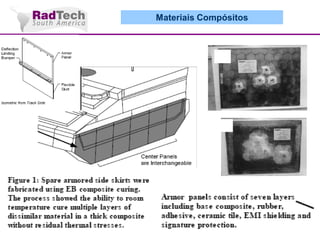
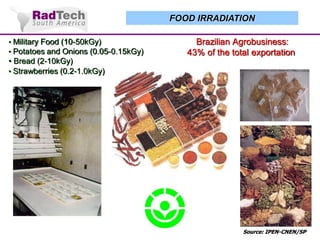
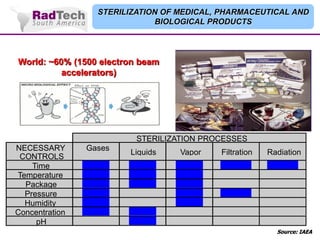
O documento discute a aplicação de feixes de elétrons na cura por radiação e suas aplicações industriais. Apresenta os principais tipos de aceleradores de elétrons usados e exemplos de aplicações como cura de revestimentos, silicones, adesivos, materiais compósitos, esterilização de produtos médicos e alimentícios. A cura por feixe de elétrons oferece vantagens como alta velocidade de processamento e sustentabilidade ambiental.