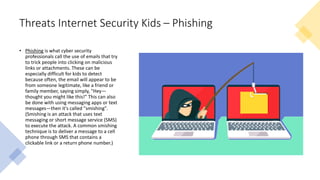
O documento discute as principais ameaças à segurança da internet para crianças, incluindo predadores online, cyberbullying e como ensinar crianças a se manterem seguras online. Ele fornece diretrizes como evitar conversas pessoais com estranhos, não enviar fotos ou se encontrar pessoalmente com alguém conhecido online.