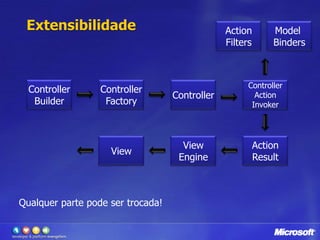
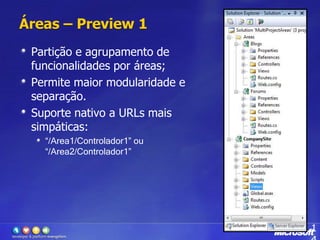
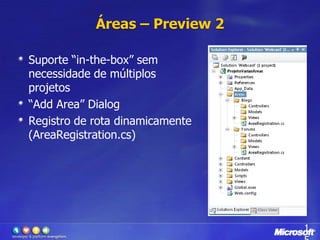
O documento apresenta o framework ASP.NET MVC 2.0, discutindo suas principais funcionalidades como áreas, helpers HTML, templates, validação com DataAnnotations, atributos como HttpPost e RequireHttps e provedores extensíveis. O ASP.NET MVC é uma opção para desenvolvimento web que separa apresentação, lógica e dados de forma mais clara comparado aos WebForms.





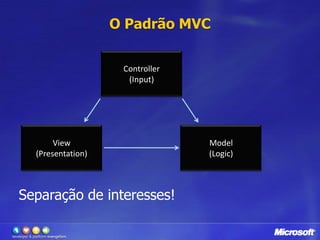






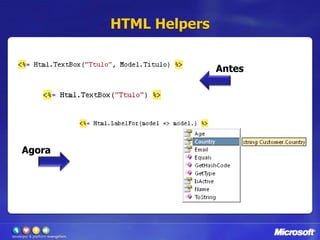

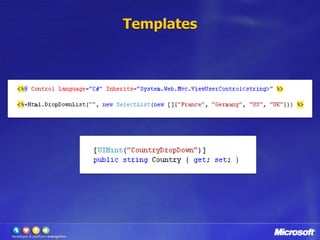


![Validação com DataAnnotationspublic classCustomer{[Required]public stringName{get; set; }[Range(1, 120, ErrorMessage="Invalid age")]public intAge{ get; set; }[RegularExpression(@"^(([a-zA-Z0-9_\-\.]+)@([a-zA-Z0-9_\-\.]+)\.([a-zA-Z]{2,5}){1,25})+([;.](([a-zA-Z0-9_\-\.]+)@([a-zA-Z0-9_\-\.]+)\.([a-zA-Z]{2,5}){1,25})+)*$", ErrorMessage="Invalid email")]public string Email{get; set; }[UIHint("CountryDropDown")]public string Country {get; set;}[DisplayName("Is Active Customer:")]public bool IsActive{get; set; }}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/novidadesdoasp-netmvc2-100420113101-phpapp01/85/CLPE-Novidades-do-Asp-net-mvc-2-24-320.jpg)
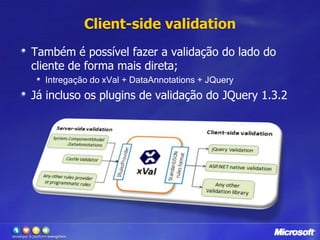
![HttpPostAttributeAntes:Agora:[AcceptVerbs(HttpVerbs.Post)] publicActionResult Create(Post post) [HttpPost]publicActionResultCreate(Postpost)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/novidadesdoasp-netmvc2-100420113101-phpapp01/85/CLPE-Novidades-do-Asp-net-mvc-2-26-320.jpg)
![DefaultValueAttributeAgora as ações podem ter valores default, o que antes só era possível com a implementação de diferentes rotas:Agora basta declarar antes do atributoroutes.MapRoute("Default", "{controller}/{action}/{id}", new { controller = "Home", action = "Index", id = "" });publicActionResultCreate([DefaultValueAttribute(5)] int pagina)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/novidadesdoasp-netmvc2-100420113101-phpapp01/85/CLPE-Novidades-do-Asp-net-mvc-2-27-320.jpg)