cloud computing
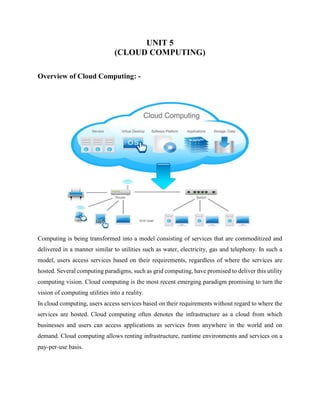
- 1. UNIT 5 (CLOUD COMPUTING) Overview of Cloud Computing: - Computing is being transformed into a model consisting of services that are commoditized and delivered in a manner similar to utilities such as water, electricity, gas and telephony. In such a model, users access services based on their requirements, regardless of where the services are hosted. Several computing paradigms, such as grid computing, have promised to deliver this utility computing vision. Cloud computing is the most recent emerging paradigm promising to turn the vision of computing utilities into a reality. In cloud computing, users access services based on their requirements without regard to where the services are hosted. Cloud computing often denotes the infrastructure as a cloud from which businesses and users can access applications as services from anywhere in the world and on demand. Cloud computing allows renting infrastructure, runtime environments and services on a pay-per-use basis.
- 2. This principle finds several practical applications and then gives different images of cloud computing to different people. Chief information and technology officers of large enterprises see opportunities for scaling their infrastructure on demand and sizing it according to their business needs. End users leveraging cloud computing services can access their documents and data anytime, anywhere and from any device connected to the Internet. The most diffuse views of cloud computing can be summarized as follows: I don’t care where my servers are, who manages them, where my documents are stored or where my applications are hosted. I just want them always available and access them from any device connected through Internet. And I am willing to pay for this service for as a long as I need it. The definition proposed by the U. S. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST): Cloud computing is a model for enabling ubiquitous, convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources (e.g., networks, servers, storage, applications, and services) that can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal management effort or service provider interaction. Cloud computing enables companies to consume a compute resource, such as a virtual machine (VM), storage or an application, as a utility -- just like electricity -- rather than having to build and maintain computing infrastructures in house. Cloud computing characteristics and benefits Cloud computing boasts several attractive benefits for businesses and end users. Five of the main benefits of cloud computing are: • Self-service provisioning: End users can spin up compute resources for almost any type of workload on demand. This eliminates the traditional need for IT administrators to provision and manage compute resources. • Elasticity: Companies can scale up as computing needs increase and scale down again as demands decrease. This eliminates the need for massive investments in local infrastructure, which may or may not remain active. • Pay per use: Compute resources are measured at a granular level, enabling users to pay only for the resources and workloads they use.
- 3. • Workload resilience: Cloud service providers often implement redundant resources to ensure resilient storage and to keep users' important workloads running -- often across multiple global regions. • Migration flexibility: Organizations can move certain workloads to or from the cloud -- or to different cloud platforms -- as desired or automatically for better cost savings or to use new services as they emerge. Cloud Types Most people separate cloud computing into two distinct sets of models: • Deployment models: This refers to the location and management of the cloud's infrastructure. • Service models: This consists of the particular types of services that you can access on a cloud computing platform. Deployment Models A deployment model defines the purpose of the cloud and the nature of how the cloud is located. The NIST definition for the four deployment models is as follows: 1. Public cloud: The public cloud infrastructure is available for public use alternatively for a large industry group and is owned by an organization selling cloud services. In the public cloud model, a third-party cloud service provider delivers the cloud service over the internet. Public cloud services are sold on demand, typically by the minute or hour, though long-term commitments are available for many services. Customers only pay for the CPU cycles, storage or bandwidth they consume. Leading public cloud service providers include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, IBM and Google Cloud Platform.
- 4. 2. Private cloud: The private cloud infrastructure is operated for the exclusive use of an organization. The cloud may be managed by that organization or a third party. Private clouds may be either on- or off-premises. Private cloud services are delivered from a business's data center to internal users. This model offers the versatility and convenience of the cloud, while preserving the management, control and security common to local data centers. Internal users may or may not be billed for services through IT chargeback. Common private cloud technologies and vendors include VMware and OpenStack. 3. Hybrid cloud: A hybrid cloud combines multiple clouds (private, community of public) where those clouds retain their unique identities but are bound together as a unit. A hybrid cloud may offer standardized or proprietary access to data and applications, as well as application portability. A hybrid cloud is a combination of public cloud services and an on-premises private cloud, with orchestration and automation between the two. Companies can run mission-critical workloads or sensitive applications on the private cloud and use the public cloud to handle workload bursts or spikes in demand. The goal of a hybrid cloud is to create a unified, automated, scalable environment that takes advantage of all that a public cloud infrastructure can provide, while still maintaining control over mission-critical data. 4. Community cloud: A community cloud is one where the cloud has been organized to serve a common function or purpose. It may be for one organization or for several organizations, but they share common concerns such as their mission, policies, security, regulatory compliance needs, and so on. A community cloud may be managed by the constituent organization(s) or by a third party.
- 5. Service Models Although cloud computing has changed over time, it has been divided into three broad service categories: infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS) and software as a service (SaaS). In the deployment model, different cloud types are an expression of the manner in which infrastructure is deployed. You can think of the cloud as the boundary between where a client's network, management and responsibilities ends and the cloud service provider's begins. As cloud computing has developed, different vendors offer clouds that have different services associated with them. Three service types have been universally accepted: 1. Infrastructure as a Service: IaaS provides virtual machines, virtual storage, virtual infrastructure and other hardware assets as resources that clients can provision. The IaaS service provider manages all the infrastructure, while the client is responsible for all other aspects of the deployment. This can include the operating system, applications, and user interactions with the system.
- 6. IaaS providers, such as AWS, supply a virtual server instance and storage, as well as APIs that enable users to migrate workloads to a VM. Users have an allocated storage capacity and can start, stop, access and configure the VM and storage as desired. IaaS providers offer small, medium, large, extra-large and memory- or compute-optimized instances, in addition to customized instances, for various workload needs. 2. Platform as a Service: PaaS provides virtual machines, operating systems, applications, services, development frameworks, transactions, and control structures. The client can deploy its applications on the cloud infrastructure or use applications that were programmed using languages and tools that are supported by the PaaS service provider. The service provider manages the cloud infrastructure, the operating systems, and the enabling software. The client is responsible for installing and managing the application that it is deploying. In the PaaS model, cloud providers host development tools on their infrastructures. Users access these tools over the internet using APIs, web portals or gateway software. PaaS is used for general software development, and many PaaS providers host the software after it's developed. Common PaaS providers include Salesforce's Force.com, AWS Elastic Beanstalk and Google App Engine. 3. Software as a Service: SaaS is a complete operating environment with applications, management and the user interface. In the SaaS model, the application is provided to the client through a thin client interface (a browser, usually), and the customer's responsibility begins and ends with entering and managing its data and user interaction. Everything from the application down to the infrastructure is the vendor's responsibility. SaaS is a distribution model that delivers software applications over the internet; these applications are often called web services. Users can access SaaS applications and services from any location using a computer or mobile device that has internet access. One common example of a SaaS application is Microsoft Office 365 for productivity and email services.
- 7. Cyber infrastructure Cyberinfrastructure consists of computing systems, data storage systems, advanced instruments and data repositories, visualization environments, and people, all linked together by software and high-performance networks to improve research productivity and enable breakthroughs not otherwise possible. Cloud computing is a new computing paradigm, involving data and/or computation outsourcing, with Infinite and elastic resource scalability , On demand “just-in-time” provisioning and No upfront cost … pay-as-you-go That is, use as much or as less you need, use only when you want, and pay only what you use. Cloud computing will be based on virtualized resources. web based computing resources that deliver on demand information services to users from any location in the world. It is essential to state that this form of computing is very different from utility and grid computing. Cloud hosting, also referred to as clustered hosting, is an online hosting service that is delivered to users from a network of linked servers. These servers are usually located in data centers scattered all over the world. The cloud consists of two main components: the back-end and the front-end. Everything ends with the client. The hardware components, the application and everything else developed for cloud
- 8. computing will be used in the client. Without the client, nothing will be possible. Cloud computing promises to cut operational and capital costs and, more importantly, let IT departments focus on strategic projects instead of keeping the datacenter running. A cloud is used in network diagrams to depict the internet. Many users or clients share public cloud facilities. The economics of sharing a virtualized cloud web hosting in public is to cut the service cost by distributing the facility’s cost among its users. With this arrangement, users only get to pay for what they actually use. This model is also referred to as pay-per-use model. In a public cloud set up, users also share the same security configurations. Therefore, if you intend to use this service in your business, you need to ensure that it complies with your business’ security measures. Cyber Infrastructure, "CIS" We at CIS work hard every day and provide our clients, quality solutions in the areas of Custom Software Development, ITeS Services, Outsourcing Services, Offsite/ Onsite Staff Augmentation, for industries such as engineering, communications, software and systems development etc Today, almost any business or major activity uses, or relies in some form, on IT and IT services. IT is the primary business of an organization, less than 20% of its efforts not directly connected to its primary business should have to do with IT overhead, even though 80% of its business might be conducted using electronic means. m hardware and platforms to application components, software
- 9. services, and whole applications, as shown in Figure 1. The commercial cloud marketplace offers a wide range of cloud services that vary in complexity and value. The common thread in cloud computing offerings across all levels of the stack is the consumer/provider relationship and a dependence on the network to connect the two parties. A cloud is used in network diagrams to depict the internet. Cloud Clients Presentation Layer Example: browsers, mobile devices Cloud Applications Software as a Service Example: Google docs or calendar Cloud Services Components as a Service Example: SOA via Web Service standards Cloud Platform Platform as a Service Example: web server, app server Cloud Storage Storage as a Service Note: formerly utility computing Cloud Infrastructure Distributed Multi-site Physical Infrastructure Note: enabled by server virtualization Note: formerly utility computing Cloud Infrastructure Distributed Multi-site Physical Infrastructure Note: enabled by server virtualization
- 10. Many users or clients share public cloud facilities. The economics of sharing a virtualized cloud web hosting in public is to cut the service cost by distributing the facility’s cost among its users. With this arrangement, users only get to pay for what they actually use. This model is also referred to as pay-per-use model. In a public cloud set up, users also share the same security configurations. Therefore, if you intend to use this service in your business, you need to ensure that it complies with your business’ security measures. Service Oriented Architecture Oriented Architecture (SOA): is a flexible set of design principles used during the phases of systems development and integration. A deployed SOA-based architecture will provide a loosely- integrated suite of services that can be used within multiple business domains. Cloud Computing: is Internet-based computing, whereby shared resources, software and information are provided to computers and other devices on-demand, like a public utility.
- 11. SOA is for application architecture. The dividing of different components is based on their roles in the SOA applications. More often than not, you start with a business problem and then abstract out the services. These services can be re-used by other applications in the future. Cloud Computing is for IT delivery. The dividing of different services is based on their roles in a software stack that is mostly well defined. You don’t need a problem before defining the cloud services. The services can be easily re-used by all applications. Virtualization Virtualization is a technology that allows a physical server to appear to applications as multiple "logical servers." SOA facilitates cloud computing by making software easier to distribute in the cloud. It can be an alternative to virtualization in server-sharing, or it can use virtualization to improve performance and reliability. Finally, SOA makes everything a service and thus supports the SaaS model, not only for complete applications but also for components of applications. As SOA principles remake applications, SOA will transform all three technologies. SOA may be transforming, but from the user's perspective, cloud computing is harmonizing. Many would argue that cloud computing is the unification of virtualization and SaaS, but it's more complicated than that. There will be applications of virtualization that are not "cloud computing" for years to come, and there will also be SaaS applications that do not use virtualization in application hosting. All three technologies have their place in managing capital and operations costs for IT. But it does seem likely that cloud computing will become the overarching framework in which most virtualization is applied and that the majority of SaaS providers will employ cloud computing to serve their users most economically and reliably. Using the advanced virtualization and management capabilities of System Center along with partner solutions, you can implement business continuity solutions to minimize downtime and improve service reliability.
- 12. “SOA: Principles of Service Design” Cloud Computing Components: Client: Clients are the device that the end user interact to manage their information on cloud. They generally divide into 3 categories: Service A Capability A Service C Capability A Capability B Service B Capability A Capability B Service D Capability A Capability B
- 13. MOBILE CLIENTS Mobile device includes (PDA, SMARTPHONE, or IPHONE) now these devices are portable and work on wireless access of network, through Internet. THIN CLIENT Now thin computers are that do not have internal hard drives, but rather the server do all their work and then display the information. THICK CLIENTS Now these are regular computer that do contain internal hard disk, and use web browser (Firefox, opera, internet explorer)to connect to the cloud. NOTE: (Now thin computer are becoming relatively popular solution for the cloud because of its price or effect on environment) Some benefits of using Thin Clients are -> Lower Hardware cost -> Lower IT cost -> Security -> Less power consumption -> Less noise -> Ease of replacement of hardware
- 14. Datacenter Now datacenter is collection of server where application to which you subscribe is housed, it could be a large room in basement, or room full of server which you access through internet. Now the growing trend in IT sector is using visualization i.e. (using virtual server) in this software can be installed allowing multiple instances of virtual server to be used in this way we can have half dozens of virtual servers running on one physical server. NOTE: (The number of virtual server that can exist on a physical server depend on the SIZE & SPEED of the physical server which runs the application of the virtual server). Distributed Client Now the server doesn’t have to be housed in same location often server is in dispersed geographically location but to you the cloud subscriber, these server acts if they are humming right away next to each other. This gives the service provider more flexibility in option and security. FOR EXAMPLE: Amazon has there cloud solution in servers all the world, if something goes wrong for instance causing a failure on one site, the service will not be stopped it would be accessed through another site also if the cloud needs more hardware they did not need throw more server in the safe room they can add them at another site and simply make it as part of the cloud Facebook ·Google Apps ·SalesForce ·Microsoft Online Browser(Chrome) ·Firefox ·Cloud ·Mobile (Android ·iPhone) ·Netbook (EeePC ·MSI Wind) ·Nettop (CherryPal ·Zonbu) BitTorrent ·EC2 ·GoGrid ·Sun Grid ·3tera Applications Client Infrastructure
- 15. App Engine ·Azure ·Mosso ·SalesForce Alexa ·FPS ·MTurk ·SQS S3 ·SimpleDB ·SQL Services Ajax ·Atom ·HTML 5 ·REST Application A cloud application leverages the Cloud in software architecture, often eliminating the need to install and run the application on the customer's own computer, thus alleviating the burden of software maintenance, ongoing operation, and support. For example: Peer-to-peer / volunteer computing (Bittorrent, BOINC Projects, Skype) Web application (Facebook) Software as a service (Google Apps, SAP and Salesforce) Software plus services (Microsoft Online Services) Platforms Services Storage Standards
- 16. Client A cloud client consists of computer hardware and/or computer software which relies on cloud computing for application delivery, or which is specifically designed for delivery of cloud services and which, in either case, is essentially useless without it. For example: Mobile (Android, iPhone, Windows Mobile) Thin client (CherryPal, Zonbu, gOS-based systems) Thick client / Web browser (Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox) Infrastructure Cloud infrastructure, such as Infrastructure as a service, is the delivery of computer infrastructure, typically a platform virtualization environment, as a service. For example: Full virtualization (GoGrid, Skytap) Management (RightScale) Compute (Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud) Platform (Force.com) Platform A cloud platform, such as Platform as a service, the delivery of a computing platform, and/or solution stack as a service, facilitates deployment of applications without the cost and complexity of buying and managing the underlying hardware and software layers. For example: Web application frameworks o Python Django (Google App Engine) o Ruby on Rails (Heroku) o .NET (Azure Services Platform) Web hosting (Mosso) Proprietary (Force.com)
- 17. Service A cloud service includes "products, services and solutions that are delivered and consumed in real-time over the Internet". For example, Web Services ("software system[s] designed to support interoperable machine-to-machine interaction over a network") which may be accessed by other cloud computing components, software, e.g., Software plus service, or end users directly. Specific examples include: Identity (OAuth, OpenID) Integration (Amazon Simple Queue Service) Payments (Amazon Flexible Payments Service, Google Checkout, PayPal) Mapping (Google Maps, Yahoo! Maps) Search (Alexa, Google Custom Search, Yahoo! BOSS) Others (Amazon Mechanical Turk) Storage Cloud storage involves the delivery of data storage as a service, including database-like services, often billed on a utility computing basis, e.g., per gigabyte per month. For example: Database (Amazon SimpleDB, Google App Engine's BigTable datastore) Network attached storage (MobileMe iDisk, Nirvanix CloudNAS) Synchronization (Live Mesh Live Desktop component, MobileMe push functions) Web service (Amazon Simple Storage Service, Nirvanix SDN) Cloud computing architecture Cloud computing architecture refers to the components and subcomponents required for cloud computing. These components typically consist of a front end platform (fat client, thin client, mobile device), back end platforms (servers, storage), a cloud based delivery, and a network
- 18. (Internet, Intranet, Intercloud). Combined, these components make up cloud computing architecture. Cloud computing architectures consist of front-end platforms called clients or cloud clients. These clients are servers, fat (or thick) clients, thin clients, zero clients, tablets and mobile devices. These client platforms interact with the cloud data storage via an application (middleware), via a web browser, or through a virtual session. The zero or ultra-thin client initializes the network to gather required configuration files that then tell it where its OS binaries are stored. The entire zero client device runs via the network. This creates a single point of failure, in that, if the network goes down, the device is rendered useless. Front-End Platform A visible interface that can be accessed on mobile or desktop devices, the front-end platform is the component that can be seen by users and clients. This front-end platform interacts with cloud data storage networks and servers through an application, commonly Middleware, a web browser (Chrome, Firefox, etc.) or a virtual session. Each cloud computing system or architecture may have a different interface to meet specific user or client demands. Sometimes the platform is a desktop computer or a mobile smartphone, other times it is a thin client or virtual terminal. Back-End Platform The back-end platform component of cloud architecture is comprised of millions of servers and data storage systems and software that is accessed securely over the public network, or via private connections. The size and usage growth of the largest platforms in place today is staggering. To put the magnitude of the back-end platform into perspective, Amazon AWS and Microsoft together have more than 4 million servers in hundreds of cloud data centers around the world, and Google’s cloud offering likely has at least 2 million servers. A single AWS data cenhttp://Link to http://www.cloudcruiser.com/aws-azure-google-cloudter will conservatively contain 50,000 – 80,000 servers and cover an area the size of 10 football fields.
- 19. Internet / Network Without the network, there would be no cloud. The Internet and other private or public networks connect user to data, and data platforms to each other. This cloud network layer should provide users with uninterrupted access to data and applications, agile movement between servers and other clouds and effective security protocols. Cloud Storage An online network storage where data is stored and accessible to multiple clients. Cloud storage is generally deployed in the following configurations: public cloud, private cloud, community cloud, or some combination of the three also known as hybrid cloud. In order to be effective, the cloud storage needs to be agile, flexible, scalable, multi-tenancy, and secure. Cloud Based Delivery Software as a service (SaaS) The software-as-a-service (SaaS) service-model involves the cloud provider installing and maintaining software in the cloud and users running the software from their cloud clients over the Internet (or Intranet). The users' client machines require no installation of any application-specific software - cloud applications run on the server (in the cloud). SaaS is scalable, and system administrators may load the applications on several servers. In the past, each customer would purchase and load their own copy of the application to each of their own servers, but with the SaaS the customer can access the application without installing the software locally. SaaS typically involves a monthly or annual fee. Software as a service provides the equivalent of installed applications in the traditional (non-cloud computing) delivery of applications. Software as a service has four common approaches: 1. single instance 2. multi instance 3. multi-tenant
- 20. 4. flex tenancy Of these, flex tenancy is considered the most user adaptive SaaS paradigm in designated multi- input four way manifold models.[8] Such systems are based on simplified encryption methods that target listed data sequences over multiple passes.[9] The simplicity of this concept makes flex tenancy SaaS popular among those without informatics processing experience, such as basic maintenance and custodial staff in franchise businesses. Development as a service (DaaS) Development as a service is web based, community shared development tools. This is the equivalent to locally installed development tools in the traditional (non-cloud computing) delivery of development tools. Data as a service (DaaS) Data as a service is web-based design construct where by cloud data is accessed through some defined API layer. DaaS services are often considered as a specialized subset of a Software as a service offering. Platform as a service (PaaS) Platform as a service is cloud computing service which provides the users with application platforms and databases as a service. This is equivalent to middleware in the traditional (non-cloud computing) delivery of application platforms and databases. Infrastructure as a service (IaaS) Infrastructure as a service is taking the physical hardware and going completely virtual (e.g. all servers, networks, storage, and system management all existing in the cloud). This is the equivalent to infrastructure and hardware in the traditional (non-cloud computing) method running in the cloud. In other words, businesses pay a fee (monthly or annually) to run virtual servers, networks, storage from the cloud. This will mitigate the need for a data center, heating, cooling, and maintaining hardware at the local level