Indifference Curve
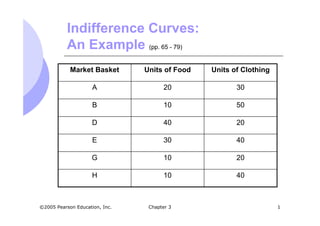
- 1. Chapter 3 1©2005 Pearson Education, Inc. Indifference Curves: An Example (pp. 65 - 79) 4010H 2010G 4030E 2040D 5010B 3020A Units of ClothingUnits of FoodMarket Basket
- 2. Chapter 3 2©2005 Pearson Education, Inc. Indifference Curves: An Example (pp. 65 - 79) Graph the points with one good on the x- axis and one good on the y-axis Plotting the points, we can make some immediate observations about preferences The more, the better
- 3. Chapter 3 3©2005 Pearson Education, Inc. The consumer prefers A to all combinations in the yellow box, while all those in the pink box are preferred to A. Indifference Curves: An Example (pp. 65 - 79) Food 10 20 30 40 10 20 30 40 Clothing 50 G A EH B D
- 4. Chapter 3 4©2005 Pearson Education, Inc. Indifference Curves: An Example (pp. 65 - 79) Points such as B & D have more of one good but less of another compared to A Need more information about consumer ranking Consumer may decide they are indifferent between B, A and D We can then connect those points with an indifference curve
- 5. Chapter 3 5©2005 Pearson Education, Inc. •Indifferent between points B, A, & D •E is preferred to any points on the indifference curve U1 •Points on U1 are preferred to H & G Indifference Curves: An Example (pp. 65 - 79) Food 10 20 30 40 10 20 30 40 Clothing 50 U1G D A E H B
- 6. Chapter 3 6©2005 Pearson Education, Inc. Indifference Curves (pp. 65 - 79) Any market basket lying northeast of an indifference curve is preferred to any market basket that lies on the indifference curve Points on the curve are preferred to points southwest of the curve
- 7. Chapter 3 7©2005 Pearson Education, Inc. Indifference Curves (pp. 65 - 79) Indifference curves slope downward to the right If they sloped upward, they would violate the assumption that more is preferred to less
- 8. Chapter 3 8©2005 Pearson Education, Inc. Indifference Curves (pp. 65 - 79) To describe preferences for all combinations of goods/services, we have a set of indifference curves – an indifference map Each indifference curve in the map shows the market baskets among which the person is indifferent
- 9. Chapter 3 9©2005 Pearson Education, Inc. U2 U3 Indifference Map (pp. 65 - 79) Food Clothing U1 AB D Market basket A is preferred to B. Market basket B is preferred to D.
- 10. Chapter 3 10©2005 Pearson Education, Inc. Indifference Maps (pp. 65 - 79) Indifference maps give more information about shapes of indifference curves Indifference curves cannot cross Violates assumption that more is better Why? What if we assume they can cross?
- 11. Chapter 3 11©2005 Pearson Education, Inc. Indifference Maps (pp. 65 - 79) Food Clothing •B is preferred to D •A is indifferent to B & D •B must be indifferent to D but that can’t be if B is preferred to D. A contradiction •Other example: On a map, two contours never cross each other. U1 U1 U2 U2 A B D
- 12. Chapter 3 12©2005 Pearson Education, Inc. Indifference Curves (pp. 65 - 79) The shapes of indifference curves describe how a consumer is willing to substitute one good for another A to B, give up 6 clothing to get 1 food D to E, give up 2 clothing to get 1 food The more clothing and less food a person has, the more clothing they will give up to get more food
- 13. Chapter 3 13©2005 Pearson Education, Inc. A B D E G -1 -6 1 1 -4 -2 1 1 Observation: The amount of clothing given up for 1 unit of food decreases from 6 to 1 Indifference Curves (pp. 65 - 79) Food Clothing 2 3 4 51 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16
- 14. Chapter 3 14©2005 Pearson Education, Inc. Indifference Curves (pp. 65 - 79) We measure how a person trades one good for another using the marginal rate of substitution (MRS) It quantifies the amount of one good a consumer will give up to obtain more of another good, or the individual terms of trade From a geometric viewpoint, it is measured by the slope of the indifference curve
- 15. Chapter 3 15©2005 Pearson Education, Inc. Marginal Rate of Substitution (pp. 65 - 79) Food 2 3 4 51 Clothing 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 A B D E G -6 1 1 1 1 -4 -2 -1 MRS = 6 MRS = 2 F CMRS Δ Δ−=
- 16. Chapter 3 16©2005 Pearson Education, Inc. Marginal Rate of Substitution (pp. 65 - 79) From A to B, give up 6 clothing to get 1 food. That is, ΔF=2-1=1, ΔC=10-16 =-6; MRS=- ΔC / ΔF=6 From D to E, , give up 2 clothing to get 1 food; ΔF=4-3=1, ΔC=4-6 =-2; MRS =- ΔC / ΔF= 2
- 17. Chapter 3 17©2005 Pearson Education, Inc. Marginal Rate of Substitution (pp. 65 - 79) Indifference curves are convex As more of one good is consumed, a consumer would prefer to give up fewer units of a second good to get additional units of the first one. As food becomes less scarce, he/she would give up less of clothing for an additional food. Consumers generally prefer a balanced market basket (preference for varieties; the Doctrine of the Mean in a Chinese classic)
- 18. Chapter 3 18©2005 Pearson Education, Inc. Marginal Rate of Substitution (pp. 65 - 79) The MRS decreases as we move down the indifference curve Along an indifference curve there is a diminishing marginal rate of substitution. The MRS went from 6 to 4 to 1
- 19. Chapter 3 19©2005 Pearson Education, Inc. Marginal Rate of Substitution (pp. 65 - 79) Indifference curves with different shapes imply a different willingness to substitute [That is, an indifference map is a concept to represent one’s preference for market baskets.] Two polar cases are of interest Perfect substitutes Perfect complements
- 20. Chapter 3 20©2005 Pearson Education, Inc. Marginal Rate of Substitution (pp. 65 - 79) Perfect Substitutes Two goods are perfect substitutes when the marginal rate of substitution of one good for the other is constant Example: a person might consider apple juice and orange juice perfect substitutes They would always trade 1 glass of OJ for 1 glass of Apple Juice Find your own examples.
- 21. Chapter 3 21©2005 Pearson Education, Inc. Consumer Preferences (pp. 65 - 79) Orange Juice (glasses) Apple Juice (glasses) 2 3 41 1 2 3 4 0 Perfect Substitutes
- 22. Chapter 3 22©2005 Pearson Education, Inc. Consumer Preferences (pp. 65 - 79) Perfect Complements Two goods are perfect complements when the indifference curves for the goods are shaped as right angles Example: If you have 1 left shoe and 1 right shoe, you are indifferent between having more left shoes only Must have one right for one left. That’s why we always get a pair of shoes, not one by one. Find your own examples.
- 23. Chapter 3 23©2005 Pearson Education, Inc. Consumer Preferences (pp. 65 - 79) Right Shoes Left Shoes 2 3 41 1 2 3 4 0 Perfect Complements
- 24. Chapter 3 24©2005 Pearson Education, Inc. Consumer Preferences: An Application (pp. 65 - 79) In designing new cars, automobile executives must determine how much time and money to invest in restyling versus increased performance Higher demand for car with better styling and performance Both cost more to improve
- 25. Chapter 3 25©2005 Pearson Education, Inc. Consumer Preferences: An Application (pp. 65 - 79) An analysis of consumer preferences would help to determine where to spend more on change: performance or styling Some consumers will prefer better styling and some will prefer better performance In recent years we have seen more and more SUVs on our roads. Certainly more owners/drivers prefer SUVs to other styles.
- 26. Chapter 3 26©2005 Pearson Education, Inc. Consumer Preferences (pp. 65 - 79) The theory of consumer behavior does not required assigning a numerical value to the level of satisfaction. Can you tell the level of satisfaction from your monthly basket? Although ranking of market baskets is good, sometimes numerical value is useful
- 27. Chapter 3 27©2005 Pearson Education, Inc. Consumer Preferences (pp. 65 - 79) Utility A numerical score (concept) representing the satisfaction that a consumer gets from a given market basket. The concept of utility was born before that of consumer preference. If buying 3 copies of Microeconomics makes you happier than buying one shirt, then we say that the books give you more utility than the shirt
- 28. Chapter 3 28©2005 Pearson Education, Inc. Utility (pp. 65 - 79) Utility function Formula that assigns a level of utility to individual market baskets If the utility function is U(F,C) = F + 2C A market basket with 8 units of food and 3 units of clothing gives a utility of 14 = 8 + 2(3)
- 29. Chapter 3 29©2005 Pearson Education, Inc. Utility - Example (pp. 65 - 79) 4 + 2(4) = 1244C 6 + 2(4) = 1446B 8 + 2(3) = 1438A UtilityClothingFoodMarket Basket Consumer is indifferent between A & B and prefers both to C.
- 30. Chapter 3 30©2005 Pearson Education, Inc. Utility - Example (pp. 65 - 79) Baskets for each level of utility can be plotted to get an indifference curve To find the indifference curve for a utility of 14, we can change the combinations of food and clothing that give us a utility of 14
- 31. Chapter 3 31©2005 Pearson Education, Inc. Utility - Another Example (pp. 65 - 79) Food 10 155 5 10 15 0 Clothing U1 = 25 U2 = 50 U3 = 100A B C Basket U = FC C 25 = 2.5(10) A 25 = 5(5) B 25 = 10(2.5)
- 32. Chapter 3 32©2005 Pearson Education, Inc. Utility (pp. 65 - 79) Although we numerically rank baskets and indifference curves, numbers are ONLY for ranking A utility of 4 is not necessarily twice as good as a utility of 2. A umber assigned to a utility level DOES NOT have any meaning. There are two types of rankings Ordinal ranking; Ordinal Utility Function Think of a number on your ticket when you are in a waiting line. Cardinal ranking; Cardinal Utility Function Think of the total number of students in this class.
- 33. Chapter 3 33©2005 Pearson Education, Inc. Budget Constraints (pp. 79 - 83) Preferences do not explain all of consumer behavior Budget constraints limit an individual’s ability to consume in light of the prices they must pay for various goods and services
- 34. Chapter 3 34©2005 Pearson Education, Inc. Budget Constraints (pp. 79 - 83) The Budget Line (Constraint) Indicates all combinations of two commodities for which total money spent equals total income We assume only 2 goods are consumed, so we do not consider savings
- 35. Chapter 3 35©2005 Pearson Education, Inc. The Budget Line (pp. 79 - 83) Let F equal the amount of food purchased, and C is the amount of clothing Price of food = PF and price of clothing = PC Then PFF is the amount of money spent on food, and PCC is the amount of money spent on clothing
- 36. Chapter 3 36©2005 Pearson Education, Inc. ICPFP CF =+ The Budget Line (pp. 79 - 83) The budget line then can be written: All income is allocated to food (F) and/or clothing (C)
- 37. Chapter 3 37©2005 Pearson Education, Inc. The Budget Line (pp. 79 - 83) Different choices of food and clothing can be calculated that use all income These choices can be graphed as the budget line Example: Assume income of $80/week, PF = $1 and PC = $2
- 38. Chapter 3 38©2005 Pearson Education, Inc. Budget Constraints (pp. 79 - 83) $80080G $801060E $802040D $803020B $80400A Income I = PFF + PCC Clothing PC = $2 Food PF = $1 Market Basket
- 39. Chapter 3 39©2005 Pearson Education, Inc. C F P P F C Slope - 2 1 - == Δ Δ = The Budget Line (pp. 79 - 83) 10 20 A B D E G (I/PC) = 40 Food 40 60 80 = (I/PF)20 10 20 30 0 Clothing
- 40. Chapter 3 40©2005 Pearson Education, Inc. The Budget Line (pp. 79 - 83) As consumption moves along a budget line from the intercept, the consumer spends less on one item and more on the other The slope of the line measures the relative cost of food and clothing The slope is the negative of the ratio of the prices of the two goods
- 41. Chapter 3 41©2005 Pearson Education, Inc. The Budget Line (pp. 79 - 83) The slope indicates the rate at which the two goods can be substituted without changing the amount of money spent It represents exchange ratio or terms of trade in market places. We can rearrange the budget line equation to make this more clear
- 42. Chapter 3 42©2005 Pearson Education, Inc. The Budget Line (pp. 79 - 83) YX P P P I YPXPI YPXPI Y X Y YX YX =− =− +=
