Evolution presentation I & II.
- 1. Evolution I & II
- 2. Evolution I Several types of evolution: A. Cosmic --- the stars, planets, universe B. Chemical --- development of life C. Organic --- biological D. Cultural --- social / societies We'll be dealing with organic evolution
- 3. Evolution I Evolution is the gradual development of life . It is the descent of organisms with modification (Darwinian). Put simply: Evolution is change over time . Fitness is the ability to live to reproduce .
- 4. Evolution I Adaptation is any trait that is determined genetically and enhances an organism's fitness. Adaptation a. behavioral changes (adaptations) b. morphological changes (adaptations) c. physiological changes (adaptations) Evolution is a slow and gradual process. Shorter the generation time, faster evolution occurs. Micro evolution special kind occuring in few generations (2-3 hours in some bacteria) in a given population.
- 5. Evolution I Evolution is: a. Opportunistic --- new adaptation do not arise out of thin air, they arise from something already present -- mutations b. Undirected changes --- cannot tell what will happen next -- random
- 6. Evolution I Rapid change in terms of evolution is 10,000 years. This equals 1/2 mm of in a rock layer, brief to a geologist.
- 7. Evolution I James Hutton in 1795 rejected previous ideas and state the present is the key to the past. He looked at sediments and determined it would take a vast amount of time to accumulate. He advance the idea that the earth was millions of years old. Charles Lyell made Hutton's work popular and wrote book that looked at slow gradual changes, fossil records and that new species and extinction were slow processes.
- 8. Evolution I Charles Lyell made Hutton's work popular and wrote book that looked at slow gradual changes, fossil records and that new species and extinction were slow processes.
- 9. Evolution I Fossils form when organisms are covered with sediments. They are found in sedimentary rocks. These rocks are made when rock and soil particles are cemented by water and under pressure Because most organisms decompose, there are few fossils found of soft tissue organisms. Most fossils are made out of shells & bone
- 10. Evolution I Age of fossils are determined by: a) Radioactive isotopes or b) Carbon14 dating requires presence of carbon both use half-life to determine age of object.
- 11. Evolution I
- 12. Evolution I Carbon 14 isotope has half-life of 5, 730 years. In 5,730 years there will be half the energy left in the original C14 sample. 14 CO2 is found in all living organisms. This method only works on items less than 20,000 years old. Other isotopes are used to test surrounding rocks for dating older specimens.
- 13. Evolution II Geologic time is divided into: Eras (4), Periods (11), Epochs (7 all during the Cenozoic era)
- 14. Evolution II When organisms are found in the fossil record and are no longer living then they are said to be extinct. By studying the fossil record different organisms can be compared.
- 15. Evolution II Scientists look at homologous body structures. Example: n whale: flipper n lion: forearm n human: arm n bird: wing n fish: fin
- 16. Evolution II Some structures have no apparent use, these are called vestiges or vestigial organs. It is thought these structures were used by the organism's ancestors.
- 17. Evolution II Besides comparing homologous structures, scientists also look at 1. embryology 2. biochemistry a) genetic code b) codons some c) protein syn. pathway d) DNA RMA & amino acids e) others
- 18. Evolution II Old Theories Before Lamark and then Darwin, several theories existed. Their common factor was changes occurred on a fixed scale or time line.
- 19. Evolution II Lamark (French) Believed organisms changed in response to environment. First to turn the fixed scale into a moving scale of progress, stating new species were continually being created. At the lower end of the scale by spontaneous generation.
- 20. Evolution II Lamark His ideas appeared in his book Philosphie Zoologique (1809) . He was first to place scale from lower life forms to man. On problem is he ignored gaps in the scale. The theories arising from Lamark are: 1. of need 2. of use and disuse 3. Acquired characteristics (example: giraffes' necks). 4. acquired traits can be passed to offspring directly
- 21. Charles Darwin Darwin was born in Shrewsbury, England, 160 miles northwest of London on the 12th of February 1809, the same day that Abraham Lincoln (16th President of the USA) was born in Kentucky, USA. Lincoln died in 1865 and Darwin in 1882. On the 12th of February 1882, Darwin wrote to a friend that "my course is nearly run" and within two months, on 19 April 1882, he had a fatal heart attack and died. His remains were conveyed by a funeral cortege on April 26 and he was interred in Westminster Abbey, London. In 1876, at the age of sixty-eight, Darwin wrote in his Autobiography that the five-year voyage on His Majesty's Ship Beagle, over the years of 1831-1836 was "by far the most important event of my life and has determined my whole career" and the scientific world should be grateful for that.
- 22. Charles Darwin Charles Darwin was greatly influenced by the geologist Adam Sedgwick and naturalist John Henslow in his development of the theory of natural selection, which was to become the foundation concept supporting the theory of evolution. Darwin’s theory holds that environmental effects lead to varying degrees of reproductive success in individuals and groups of organisms. Natural selection tends to promote adaptation in organisms when necessary for survival. This revolutionary theory was published in 1859 in Darwin’s now famous treatise On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection.
- 23. Evolution II Charles Darwin Wrote Origin of the Species, which sold out in the first day and a total of six editions were sold during his life. The following ideas were expressed in his book: 1. evolution has occurred 2. mechanism of evolution is natural selection Evolution is a process. Natural selection is the mechanism by which evolution takes place (occurs).
- 24. Evolution II Six steps to Darwin's theory of natural selection: 1. All organisms produce more offspring than can actually survive. 2. Every organism faces a constant struggle to survive. 3. The individuals of a given species vary 4. The individuals that are best adapted to the environment survive. 5. The organisms that survive pass their traits on to offspring. 6. The population will become better fit for the environment.
- 25. Darwin’s voyage on the HMS Beagle Voyage of the Beagle. From de Beer (1964, p. 39).
- 26. Darwin’ Beagle Voyage "As far as I can judge of myself I worked to the utmost during the voyage from the mere pleasure of investigation, and from my strong desire to add a few facts to the great mass of facts in natural science." — Charles Darwin
- 27. Darwin’ Beagle Voyage Galapagos Islands off the coast of Ecuador
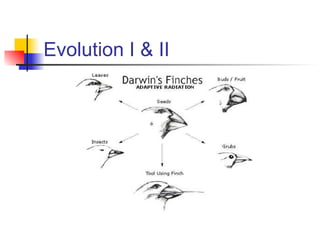
- 28. Darwin’s Finches Darwin's finches. The finches numbered 1-7 are ground finches. They seek their food on the ground or in low shrubs. Those numbered 8-13 are tree finches. They live primarily on insects. 1. Large cactus finch (Geospiza conirostris) 2. Large ground finch (G. magnirostris) 3. Medium ground finch (Geospiza fortis) 4. Cactus finch (G. scandens) 5. Sharp-beaked ground finch (G. difficilis) 6. Small ground finch (G. fuliginosa) 7. Woodpecker finch (Cactospiza pallida) 8. Vegetarian tree finch (Platyspiza crassirostris) 9. Medium tree finch (Camarhynchus pauper) 10. Large tree finch (Camarhynchus psittacula) 11. Small tree finch (C. parvulus) 12. Warbler finch (Certhidia olivacea) 13. Mangrove finch (Cactospiza heliobates)
- 29. Darwin’s Finches
- 30. The End
