DIGESTION & ABSORPTION OF BIOMOLECULES by Dr. Santhosh Kumar N.docx
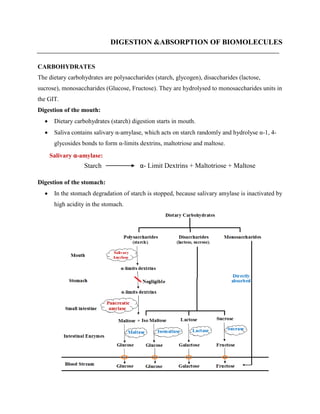
- 1. DIGESTION &ABSORPTION OF BIOMOLECULES CARBOHYDRATES The dietary carbohydrates are polysaccharides (starch, glycogen), disaccharides (lactose, sucrose), monosaccharides (Glucose, Fructose). They are hydrolysed to monosaccharides units in the GIT. Digestion of the mouth: Dietary carbohydrates (starch) digestion starts in mouth. Saliva contains salivary α-amylase, which acts on starch randomly and hydrolyse α-1, 4- glycosides bonds to form α-limits dextrins, maltotriose and maltose. Digestion of the stomach: In the stomach degradation of starch is stopped, because salivary amylase is inactivated by high acidity in the stomach. Starch α- Limit Dextrins + Maltotriose + Maltose Salivary α-amylase:
- 2. Digestion of the Small intestine: The pancreatic α-amylase secreted by pancreas & it acts on α-1, 4-glycosidic bonds on starch, but not on α-1, 6-bonds, to produce disaccharides (maltose, isomaltose) and oligosaccharides. Maltase: Maltose α-D Glucose + α-D Glucose Lactase: Lactose β-D Galactose + β-D Glucose Sucrase: Sucrose α-D Glucose + β-D Fructose Disaccharidases The final digestion of disaccharides and oligosaccharides to monosaccharides, it occurs at the mucosal lining of the upper jejunum, carried out by intestinal enzymes disaccharidases (eg; Maltase, lactase & Sucrase) to produce monosaccharides Isomaltase catalyzes hydrolysis of α-1→6 glycosidic linkage, thus splitting α-limit dextrins at the branching points & producing initially maltose then glucose. Cellulose: Cellulose cannot be digested, due to absence of β-amylase or cellulase. Undigested cellulose provides bulk or fiber in the diet and it acts as a stool softer. ABSORPTION OF MONOSACCHARIDES Digestible products of dietary carbohydrates are completely absorbed in the duodenum and upper jejunum of small intestine. Rate of absorption of important monosaccharides (Glucose & galactose are absorbed faster than fructose and mannose.) Galactose > Glucose > Fructose > Mannose Mechanisms of absorption: Carbohydrates are absorbed as monosaccharides from the intestinal lumen through the mucosal epithelial cells into blood stream of the portal venous system by different mechanisms. Absorption of glucose and galactose across the brush borders membrane of mucosal cells occurs by a carrier mediated (sodium) and energy is required (by an active transport).
- 3. Sodium dependent glucose transporter (SGLT-1) binds both glucose and Na+ at separate sites and transports them through the plasma membrane of the intestinal cells. Sodium is transported down its conc. gradients and simultaneously glucose is transported into the intestinal cells against its conc. gradients, in this mechanism energy is utilized from ATP by sodium potassium pump. Absorption of Fructose and mannose are across the brush border by facilitated diffusion mediated by a carrier system Glucose transporter-5 (GluT-5). It does not require energy & sodium transport. Absorption of pentoses by a process of simple diffusion. Intestinal cells release glucose into blood stream by the carrier mechanism called glucose transporter -type- 2 (GluT-2). GluT-2 (facilitated transport) present in intestinal epithelial cells is involved in absorption of glucose from blood stream to cells. ABNORMALITIES OF CARBOHYDRATE DIGESTION Only the monosaccharides are absorbed, any defect in the activities of disaccharides results in the passage of undigested disaccharides into the large intestine. The disaccharide draws water from the intestinal mucosa by osmosis and cause indigestion. The un-digestion carbohydrates causes’ bacterial action leads flatulence. Disaccharidases are the intestinal brush border enzyme. Any alteration in the mucosa of the small intestine causes severe diarrhea, malnutrition and intestinal disease. Lactose Intolerance: Deficiency of lactase enzyme leads to lactose intolerance. Lactase Lactose α-D-Galactose + α-D-Glucose Accumulation of undigested lactose in the gut leads to irritant diarrhea. Excessive undigested lactose leads to gas production owing to intestinal bacterial fermentation and also producing flatulence, diarrhea, distension, abdominal cramps and abdominal discomfort. Treatment for lactose intolerance to give lactose free diet. Sucrase deficiency: It is inherited deficiency of sucrase enzyme.
- 4. Sucrase Sucrose α-D-Glucose + β-D-Fructose A symptom of sucrase deficiency occurs in early childhood. Deficiency of the enzyme sucrase, sucrose is not converted into glucose & fructose. Accumulation of sucrose leads to diarrhea & flatulence (accumulation of gas in the intestine). Disacchariduria: Increased excretion of disaccharides in urine with the deficiency of enzyme disaccharidases. It mainly seen in patients with intestinal damage ( like celiac disease) II. PROTEINS Digestion and absorption takes place in GI tract at different levels with proteolytic enzymes aided by gastro intestinal hormones Digestion in stomach Hydrochloric acid secreted by parietal cells of stomach denatures proteins and makes it susceptible to hydrolysis by protease enzymes. Pepsin: It is secreted as inactive zymogen –pepsinogens by chief cells of stomach Pepsinogens is converted to pepsin by HCl HCl Pepsinogens Pepsin Later, pepsin itself causes activation of pepsinogens to pepsinogens to pepsin (auto catalysis). Pepsin Pepsinogens Pepsin It is an endopeptidase with an optimum pH of 1 of 2. Its end products are proteases and peptones. It hydrolysis peptide bonds of phenyl alanine, tyrosine, tryptophan, glutamate Digestion in duodenum Proteolytic enzymes of pancreatic juice carry on further digestion
- 5. Pancreatic enzymes secreted trypsinogen, chymotrypsinogen, procarboxypeptidase, proelastes and collagenase. These are zymogens released from pancrease mediated by the secretion of cholecystokinin and secretin ( two polypeptide hormones of digestive tract) Trypsin It is secreted as inactive trypsinogen. The activation is brought about by an enzyme enterokinase of intestinal juice. It is an endopeptidase, hydrolyses peptide bonds formed by basic amino acids arginine, histidine and lysine It acts on proteins, proteoses, peptones converting them to polypeptides. Optimum pH is 8 to 9. Enterokinase Trypsinogen Trypsin Chymotrypsin It is secreted as inactive chymotrypsinogen. It is an endopeptidase specific for peptide bonds of aromatic amino acids (Phenyl alanine, tyrosine and tryptophan). Optimum pH is 7 to 8 Trypsin Chymotrypsinogen Chymotrypsin Proelastase: It is an endopeptidase. Hydrolyses peptide bonds next to small amino acid residues such as glycine, alanine and serine Trypsin Proelastase Elastase Carboxypeptidase: It is an exopeptidase. It hydrolyses peptide bonds adjacent to carboxyl terminal, liberating amino acids Trypsin Procarboxypeptidase Carboxypeptidase In small intestine: Amino peptidase Present in intestinal juice, it is an exopeptidase. Proteins ↓ Proteoses ↓ Peptones ↓ Amino acids Digestion of proteins
- 6. It hydrolyses peptide bonds adjacent to amino terminal, liberating amino acids. Dipeptidase: Present in intestinal juice It hydrolyses dipeptides to liberate amino acids Dipeptide Amino acid + Amino acid End products of protein digestion is amino acids ABSORPTION These are six different carrier proteins for different groups of amino acids. L-amino acids are preferentially absorbed compared to D- amino acids. Amino acids are absorbed in small intestine by active transport, which is sodium dependent system. Amino acids are carried to liver and further metabolized Gamma glutamyl cycle (Meisters cycle) It takes place in kidney tubules and brain. Amino acids enter into the cell with help of glutathione. Tripeptide glutathione (GSH) reacts with the neutral amino acids to form gamma glutamyl amino acid .This is catalyzed by gamma glutamyl transferase The glutamyl amino acid is then cleaved to give the free amino acid inside the membrane. The net result is the transfer of an amino acid across the membrane. The transport of one molecule of amino acid and regeneration of GSH requires 3 molecules of ATP The transport of one amino acid with regeneration of glutathione required three molecules of ATP Meisters cycle
- 7. III. LIPIDS Dietary lipids consist of triglycerides, phospholipids & cholesterol esters and cholesterol. Most of the fat in the human diet is in the form of triacylglycerol (TAG). In the digestive tract, TAG is hydrolyzed by the enzyme lipase, to release free fatty acids and mono acyl glycerides. Digestion in mouth Digestion of dietary lipids starts in the mouth. Lingual lipase is secreted by sublingual glands. They act on triglycerides containing short chain fatty acids. Digestion in stomach Very small amounts of lipase are present in gastric juice. Digestion of fat is negligible Digestion in small intestine • It occurs in two process a) Emulsification of lipids by bile salts b) Enzymatic degradation of lipids Degradation of Triacylglycerols (fats) Pancreatic lipase is the major enzyme that digests dietary fats. Pancreatic lipase catalyzes hydrolysis of ester bonds present at 1st & 3rd position of TG to gives 2-mono glycerides. Further 2-mono glycerides undergo isomerizationto 1-MAG, Then 1-MAG is hydrolysed by pancreatic lipase. Products of lipase are 2-monoglycerides, 1–monoglycerides, Glycerol & FFAs. Glycerol directly enters the portal blood. Degradation of cholesterol esters: Cholesteryl esterases hydrolyses of ester bonds present at 3rd Carbon of cholesteryl esters to gives cholesterol.
- 8. Degradation of Phospholipids Pancreatic juice is rich in Phospholipase A2 isresponsible for the hydrolysis of phospholipids, which cleaves the fatty acid at the 2nd position of phospholipids. The products of phospholipase are FFAs & Lysophospholipids. The major digestible products (2-mono acylglycerol, FFA, cholesterol & lyso- phospholipids) now ready for absorption in the intestinal lumen by passive process. ABSORPTION OF LIPIDS Products combine with bile salts to form micelles. Micelles are absorbed into the intestinal mucosal cells. Micelles serve as the major vehicles for the transport of lipids from the intestinal lumen to intestinal mucosa. In intestinal mucosal cells, TGs are resynthesized from absorbed FFA & mono acyl glycerol. The resynthesized TGs cannot pass in to portal blood, but it enters the lymphatic vessels as a chylomicrons. The lymphatic duct then discharges the chylomicrons into bloodstream through thoracic duct & left subclavian vein, reached to heart, then to peripheral tissues & finally to liver. Chylomicrons are hydrolyzed in adipose tissues by lipoprotein lipase to yield FFA & glycerol. In adipose tissues, the FFAs are re esterified with glycerol-3-P to synthesize TGs, which are stored as fuel reserve and provides the energy to skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle & liver.