11X1 T14 04 areas
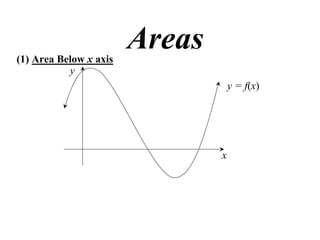
- 1. (1) Area Below x axis Areas y y = f(x) x
- 2. (1) Area Below x axis Areas y y = f(x) A1 a b x
- 3. (1) Area Below x axis Areas y y = f(x) A1 a b x f x dx 0 b a
- 4. (1) Area Below x axis Areas y y = f(x) A1 a b x f x dx 0 b a A1 f x dx b a
- 5. (1) Area Below x axis Areas y y = f(x) A1 c x a b A2 f x dx 0 b a A1 f x dx b a
- 6. (1) Area Below x axis Areas y y = f(x) A1 c x a b A2 f x dx 0 c f x dx 0 b a b A1 f x dx b a
- 7. (1) Area Below x axis Areas y y = f(x) A1 c x a b A2 f x dx 0 c f x dx 0 b a b A2 f x dx c A1 f x dx b a b
- 8. Area below x axis is given by;
- 9. Area below x axis is given by; A f x dx c b
- 10. Area below x axis is given by; A f x dx c b OR f x dx c b
- 11. Area below x axis is given by; A f x dx c b OR f x dx c b OR f x dx b c
- 12. e.g. (i) y y x3 -1 1 x
- 13. e.g. (i) y y x3 0 1 A x dx x 3 dx 3 1 0 -1 1 x
- 14. e.g. (i) y y x3 0 1 A x dx x 3 dx 3 1 0 4 x 1 4 x 0 1 40 1 41 -1 1 x
- 15. e.g. (i) y y x3 0 1 A x dx x 3 dx 3 1 0 4 x 1 4 x 0 1 40 1 41 -1 1 x 1 4 4 0 1 4 0 1 4 1 1 1 4 4 1 units 2 2
- 16. e.g. (i) y y x3 0 1 A x dx x 3 dx 3 1 0 4 x 1 4 x 0 1 40 1 41 -1 1 x 1 4 4 0 1 4 0 1 4 1 1 1 OR using symmetry of odd function 4 4 1 units 2 2
- 17. e.g. (i) y y x3 0 1 A x dx x 3 dx 3 1 0 4 x 1 4 x 0 1 40 1 41 -1 1 x 1 4 4 0 1 4 0 1 4 1 1 1 OR using symmetry of odd function 4 4 1 1 A 2 x 3 dx units 2 0 2
- 18. e.g. (i) y y x3 0 1 A x dx x 3 dx 3 1 0 4 x 1 4 x 0 1 40 1 41 -1 1 x 1 4 4 0 1 4 0 1 4 1 1 1 OR using symmetry of odd function 4 4 1 1 A 2 x 3 dx units 2 0 2 x 0 1 41 2
- 19. e.g. (i) y y x3 0 1 A x dx x 3 dx 3 1 0 4 x 1 4 x 0 1 40 1 41 -1 1 x 1 4 4 0 1 4 0 1 4 1 1 1 OR using symmetry of odd function 4 4 1 1 A 2 x 3 dx units 2 0 2 x 0 1 41 2 4 0 1 1 2 1 units 2 2
- 20. (ii) y y x x 1 x 2 -2 -1 x
- 21. (ii) y y x x 1 x 2 -2 -1 x A x 3 x 2 x dx x 3 3 x 2 2 x dx 1 0 3 2 2 1
- 22. (ii) y y x x 1 x 2 -2 -1 x A x 3 x 2 x dx x 3 3 x 2 2 x dx 1 0 3 2 2 1 1 1 x 4 x3 x 2 x 4 x3 x 2 1 1 4 2 4 0
- 23. (ii) y y x x 1 x 2 -2 -1 x A x 3 x 2 x dx x 3 3 x 2 2 x dx 1 0 3 2 2 1 1 1 x 4 x3 x 2 x 4 x3 x 2 1 1 4 2 4 0 2 1 14 13 12 1 2 4 2 3 2 2 0 4 4 1 units 2 2
- 24. (2) Area On The y axis y y = f(x) (b,d) (a,c) x
- 25. (2) Area On The y axis (1) Make x the subject y i.e. x = g(y) y = f(x) (b,d) (a,c) x
- 26. (2) Area On The y axis (1) Make x the subject y i.e. x = g(y) y = f(x) (2) Substitute the y coordinates (b,d) (a,c) x
- 27. (2) Area On The y axis (1) Make x the subject y i.e. x = g(y) y = f(x) (2) Substitute the y coordinates (b,d) d 3 A g y dy c (a,c) x
- 28. (2) Area On The y axis (1) Make x the subject y i.e. x = g(y) y = f(x) (2) Substitute the y coordinates (b,d) d 3 A g y dy c (a,c) x e.g. y y x4 1 2 x
- 29. (2) Area On The y axis (1) Make x the subject y i.e. x = g(y) y = f(x) (2) Substitute the y coordinates (b,d) d 3 A g y dy c (a,c) x e.g. y y x4 1 x y 4 1 2 x
- 30. (2) Area On The y axis (1) Make x the subject y i.e. x = g(y) y = f(x) (2) Substitute the y coordinates (b,d) d 3 A g y dy c (a,c) 16 1 x A y dy 4 1 e.g. y y x4 1 x y 4 1 2 x
- 31. (2) Area On The y axis (1) Make x the subject y i.e. x = g(y) y = f(x) (2) Substitute the y coordinates (b,d) d 3 A g y dy c (a,c) 16 1 x A y dy 4 1 5 16 e.g. y yx 4 4 1 y 4 5 1 x y 4 1 2 x
- 32. (2) Area On The y axis (1) Make x the subject y i.e. x = g(y) y = f(x) (2) Substitute the y coordinates (b,d) d 3 A g y dy c (a,c) 16 1 x A y dy 4 1 5 16 e.g. y yx 4 4 1 y 4 5 1 x y 4 4 5 5 16 4 14 5 1 2 x 124 units 2 5
- 33. (3) Area Between Two Curves y x
- 34. (3) Area Between Two Curves y y = f(x)…(1) x
- 35. (3) Area Between Two Curves y y = g(x)…(2) y = f(x)…(1) x
- 36. (3) Area Between Two Curves y y = g(x)…(2) y = f(x)…(1) a b x
- 37. (3) Area Between Two Curves y y = g(x)…(2) y = f(x)…(1) a b x Area = Area under (1) – Area under (2)
- 38. (3) Area Between Two Curves y y = g(x)…(2) y = f(x)…(1) a b x Area = Area under (1) – Area under (2) b b f x dx g x dx a a
- 39. (3) Area Between Two Curves y y = g(x)…(2) y = f(x)…(1) a b x Area = Area under (1) – Area under (2) b b f x dx g x dx a a b f x g x dx a
- 40. e.g. Find the area enclosed between the curves y x 5 and y x in the positive quadrant.
- 41. e.g. Find the area enclosed between the curves y x 5 and y x in the positive quadrant. y y x5 yx x
- 42. e.g. Find the area enclosed between the curves y x 5 and y x in the positive quadrant. y y x5 yx x x x 5
- 43. e.g. Find the area enclosed between the curves y x 5 and y x in the positive quadrant. y y x5 yx x x x 5 x5 x 0 xx 4 1 0 x 0 or x 1
- 44. e.g. Find the area enclosed between the curves y x 5 and y x in the positive quadrant. y y x5 yx A x x 5 dx 1 x 0 x x 5 x5 x 0 xx 4 1 0 x 0 or x 1
- 45. e.g. Find the area enclosed between the curves y x 5 and y x in the positive quadrant. y y x5 yx A x x 5 dx 1 x 0 x x 5 1 1 1 x5 x 0 x2 x6 2 6 0 xx 4 1 0 x 0 or x 1
- 46. e.g. Find the area enclosed between the curves y x 5 and y x in the positive quadrant. y y x5 yx A x x 5 dx 1 x 0 x x 5 1 1 1 x5 x 0 x2 x6 2 6 0 xx 4 1 0 1 1 2 1 1 6 0 x 0 or x 1 2 6 1 unit 2 3
- 47. 2002 HSC Question 4d) The graphs of y x 4 and y x 2 4 x intersect at the points 4,0 A.
- 48. 2002 HSC Question 4d) The graphs of y x 4 and y x 2 4 x intersect at the points 4,0 A. (i) Find the coordinates of A (2)
- 49. 2002 HSC Question 4d) The graphs of y x 4 and y x 2 4 x intersect at the points 4,0 A. (i) Find the coordinates of A (2) To find points of intersection, solve simultaneously
- 50. 2002 HSC Question 4d) The graphs of y x 4 and y x 2 4 x intersect at the points 4,0 A. (i) Find the coordinates of A (2) To find points of intersection, solve simultaneously x 4 x2 4x
- 51. 2002 HSC Question 4d) The graphs of y x 4 and y x 2 4 x intersect at the points 4,0 A. (i) Find the coordinates of A (2) To find points of intersection, solve simultaneously x 4 x2 4x x2 5x 4 0
- 52. 2002 HSC Question 4d) The graphs of y x 4 and y x 2 4 x intersect at the points 4,0 A. (i) Find the coordinates of A (2) To find points of intersection, solve simultaneously x 4 x2 4x x2 5x 4 0 x 4 x 1 0
- 53. 2002 HSC Question 4d) The graphs of y x 4 and y x 2 4 x intersect at the points 4,0 A. (i) Find the coordinates of A (2) To find points of intersection, solve simultaneously x 4 x2 4x x2 5x 4 0 x 4 x 1 0 x 1 or x 4
- 54. 2002 HSC Question 4d) The graphs of y x 4 and y x 2 4 x intersect at the points 4,0 A. (i) Find the coordinates of A (2) To find points of intersection, solve simultaneously x 4 x2 4x x2 5x 4 0 x 4 x 1 0 x 1 or x 4 A is (1, 3)
- 55. (ii) Find the area of the shaded region bounded by y x 2 4 x and (3) y x 4.
- 56. (ii) Find the area of the shaded region bounded by y x 2 4 x and (3) y x 4. 4 A x 4 x 2 4 x dx 1
- 57. (ii) Find the area of the shaded region bounded by y x 2 4 x and (3) y x 4. 4 A x 4 x 2 4 x dx 1 4 x 2 5 x 4 dx 1
- 58. (ii) Find the area of the shaded region bounded by y x 2 4 x and (3) y x 4. 4 A x 4 x 2 4 x dx 1 4 x 2 5 x 4 dx 1 4 1 x3 5 x 2 4 x 3 2 1
- 59. (ii) Find the area of the shaded region bounded by y x 2 4 x and (3) y x 4. 4 A x 4 x 2 4 x dx 1 4 x 2 5 x 4 dx 1 4 1 x3 5 x 2 4 x 3 2 1 1 3 5 2 1 3 5 2 4 4 4 4 1 1 4 1 3 2 3 2
- 60. (ii) Find the area of the shaded region bounded by y x 2 4 x and (3) y x 4. 4 A x 4 x 2 4 x dx 1 4 x 2 5 x 4 dx 1 4 1 x3 5 x 2 4 x 3 2 1 1 3 5 2 1 3 5 2 4 4 4 4 1 1 4 1 3 2 3 2 9 units 2 2
- 61. 2005 HSC Question 8b) (3) The shaded region in the diagram is bounded by the circle of radius 2 centred at the origin, the parabola y x 2 3 x 2 , and the x axis. By considering the difference of two areas, find the area of the shaded region.
- 62. 2005 HSC Question 8b) (3) The shaded region in the diagram is bounded by the circle of radius 2 centred at the origin, the parabola y x 2 3 x 2 , and the x axis. By considering the difference of two areas, find the area of the shaded region. Note: area must be broken up into two areas, due to the different boundaries.
- 63. 2005 HSC Question 8b) (3) The shaded region in the diagram is bounded by the circle of radius 2 centred at the origin, the parabola y x 2 3 x 2 , and the x axis. By considering the difference of two areas, find the area of the shaded region. Note: area must be broken up into two areas, due to the different boundaries.
- 64. 2005 HSC Question 8b) (3) The shaded region in the diagram is bounded by the circle of radius 2 centred at the origin, the parabola y x 2 3 x 2 , and the x axis. By considering the difference of two areas, find the area of the shaded region. Note: area must be broken up into two areas, due to the different boundaries. Area between circle and parabola
- 65. 2005 HSC Question 8b) (3) The shaded region in the diagram is bounded by the circle of radius 2 centred at the origin, the parabola y x 2 3 x 2 , and the x axis. By considering the difference of two areas, find the area of the shaded region. Note: area must be broken up into two areas, due to the different boundaries. Area between circle and parabola and area between circle and x axis
- 67. It is easier to subtract the area under the parabola from the quadrant.
- 68. It is easier to subtract the area under the parabola from the quadrant. 1 A 2 x 2 3 x 2 dx 1 2 4 0
- 69. It is easier to subtract the area under the parabola from the quadrant. 1 A 2 x 2 3 x 2 dx 1 2 4 0 1 x x 2x 1 3 3 2 3 2 0
- 70. It is easier to subtract the area under the parabola from the quadrant. 1 A 2 x 2 3 x 2 dx 1 2 4 0 1 x x 2x 1 3 3 2 3 2 0 1 3 3 2 1 1 2 1 0 3 2
- 71. It is easier to subtract the area under the parabola from the quadrant. 1 A 2 x 2 3 x 2 dx 1 2 4 0 1 x x 2x 1 3 3 2 3 2 0 1 3 3 2 1 1 2 1 0 3 2 5 units 2 6
- 72. Exercise 11E; 2bceh, 3bd, 4bd, 5bd, 7begj, 8d, 9a, 11, 18* Exercise 11F; 1bdeh, 4bd, 7d, 10, 11b, 13, 15*