Macromolecule scramble intro
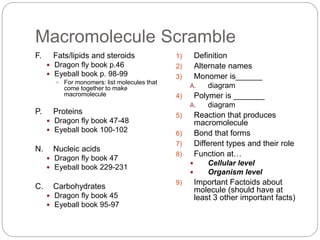
- 1. Macromolecule Scramble F. Fats/lipids and steroids Dragon fly book p.46 Eyeball book p. 98-99 For monomers: list molecules that come together to make macromolecule P. Proteins Dragon fly book 47-48 Eyeball book 100-102 N. Nucleic acids Dragon fly book 47 Eyeball book 229-231 C. Carbohydrates Dragon fly book 45 Eyeball book 95-97 1) Definition 2) Alternate names 3) Monomer is______ A. diagram 4) Polymer is _______ A. diagram 5) Reaction that produces macromolecule 6) Bond that forms 7) Different types and their role 8) Function at… Cellular level Organism level 9) Important Factoids about molecule (should have at least 3 other important facts)
- 2. Mono mer and diagra m Polyme r and diagra m Commo n Names Func tion Link that forms betwee n mono mers Role in the cell Role in organi sm Differe nt types 3 or more importan t facts Other relevant info Proteins Carbohydrate s Nucleic Acids N/A Lipids/fat s Steroids General structure
- 3. Intro to Macro molecules Macromolecules
- 4. Carbon The element of LIFE! Found in all living organisms! We are always looking for carbon based life forms Organic molecules: molecules that contain carbon C6H12O6, CO2, CH4 Some molecules are made of just CARBON and HYDROGEN…we call these HYDROCARBONS These are important in FUEL (aka GASOLINE!!) Many organic molecules, such as fats, have hydrocarbon components Hydrocarbons can undergo reactions that release a large amount of energy Inorganic molecules: molecules that do not contain carbon H2O, NH3, O2
- 5. LE 4-4 Hydrogen (valence = 1) Oxygen (valence = 2) Nitrogen (valence = 3) Carbon (valence = 4)
- 6. Structure of Carbon Structure Valence electrons: 4 How many bonds can carbon make with other atoms? 4: single, double, or triple…as long as it has 4 lines touching it This makes carbon a versatile atom…it can make long chains of carbons, branched carbon structures, even ring structures with itself
- 7. LE 4-5 Length Ethane Propane Butane 2-methylpropane (commonly called isobutane) Branching Double bonds Rings 1-Butene 2-Butene Cyclohexane Benzene
- 8. Some important words to know Molecule Group of covalently bonded atoms Macromolecule large molecules composed of thousands of covalently connected atoms Functional Groups Group of atoms within a molecule that interact in PREDICTABLE ways Polar, non-polar, acidic, basic, charged (+/-) Hydroxyl group Carbonyl group Carboxyl group Amino group Sulfhydryl group Phosphate group
- 9. LE 4-10aa STRUCTURE (may be written HO—) NAME OF COMPOUNDS Alcohols (their specific names usually end in -ol) Ethanol, the alcohol present in alcoholic beverages FUNCTIONAL PROPERTIES Is polar as a result of the electronegative oxygen atom drawing electrons toward itself. Attracts water molecules, helping dissolve organic compounds such as sugars (see Figure 5.3).
- 10. LE 4-10ac STRUCTURE NAME OF COMPOUNDS Carboxylic acids, or organic acids EXAMPLE Has acidic properties because it is a source of hydrogen ions. Acetic acid, which gives vinegar its sour taste FUNCTIONAL PROPERTIES The covalent bond between oxygen and hydrogen is so polar that hydrogen ions (H+) tend to dissociate reversibly; for example, Acetic acid Acetate ion In cells, found in the ionic form, which is called a carboxylate group.
- 11. LE 4-10ba STRUCTURE NAME OF COMPOUNDS Amine EXAMPLE Because it also has a carboxyl group, glycine is both an amine and a carboxylic acid; compounds with both groups are called amino acids. FUNCTIONAL PROPERTIES Acts as a base; can pick up a proton from the surrounding solution: (nonionized) Ionized, with a charge of 1+, under cellular conditions Glycine (ionized)
- 12. LE 4-10bc STRUCTURE NAME OF COMPOUNDS Organic phosphates EXAMPLE Glycerol phosphate FUNCTIONAL PROPERTIES Makes the molecule of which it is a part an anion (negatively charged ion). Can transfer energy between organic molecules.
- 13. What are macromolecules made of? • A polymer is a long molecule consisting of many similar building blocks called monomers • Poly=many • Mono=one • Think of a beaded bracelet…. • each bead is a MONOMER • The entire bracelet is a POLYMER • Large variety of polymers but there are less than 50 monomers…kinda like the alphabet…lots of words, only 26 letters • Three of the four classes of life’s organic molecules are polymers: Carbohydrates Proteins Nucleic acids ***Lipids/fats are not polymers but they are still macromolecules
- 14. Making and Breaking Polymers Polymerization: making polymers Dehydration Reaction Dehydrate means water loss When a water molecule (H-OH) is released to join a monomer to another monomer Hydrolysis Hydro- water Lysis- to break down Def: to break apart or disassemble a polymer by adding water (H-OH)
- 15. LE 5-2 Short polymer Unlinked monomer Dehydration removes a water molecule, forming a new bond Dehydration reaction in the synthesis of a polymer Longer polymer Hydrolysis adds a water molecule, breaking a bond Hydrolysis of a polymer
- 16. Carbohydrates Monomer: Monosaccharide Polymer: Disaccharide or Polysaccharide Link between monomers is called: Glycosidic Linkage Formed by a dehydration reaction Always have Carbon, Hydrogen, and Oxygens CxH2xOx Common name: sugar End with suffix “-ose” Function: Energy/fuel, structure, storage GLUCOSE!!!! What all cells need for energy
- 17. Carbs continued Monosaccharides Glucose fructose Disaccharides sucrose Polysaccharides Starch In plant cells; chain of glucose molecules coiled up like a phone cord Glycogen Excess sugar in animal cells is stored in this form; highly branched and more complex chain of glucose monomers Stored in muscle and liver cells When body needs energy, glycogen is broken down into glucose Cellulose Found in plant cell walls; made of glucose monomer; building material; aka FIBER; humans do NOT have the enzyme to break this polysaccharide down Passes through digestive tract and keeps it healthy but NOT a nutrient Some animals (cows) have microorganisms that live in their digestive tract that help break down cellulose Carbs are hydrophilic because of hydroxl group (-OH) Dissolve in water making sugary solutions Large carbs (starches and cellulose) do not dissolve Think about your towels and clothes, duh!
- 18. Proteins Monomer: amino acids 20 amino acids Amine (NH2) and carboxyl (COOH) groups attached to carbon Only thing different is side chain…R-group Polymer: polypeptide chains (proteins) Link between monomers is called: polypeptide bond Made by a dehydration reaction (between amine group of one aa and carboxyl group of another aa) STRUCTURE of A.A. Amino group on one end (-NH2) Carboxyl group on one end (COOH) Hydrogen R-group/side chain (changes) Function of Proteins: structural support Storage Transport cellular communications Movement defense against foreign substances Proteins account for more than 50% of the dry mass of
- 20. Protein Structure Primary structure 1’ Order of amino acids in a polypeptide chain Secondary structure 2’ Polypeptide chain folds because of interactions between amino acids HYDROGEN BONDING Tertiary Structure 3’ Gives proteins 3-D shape VERY IMPORTANT to function of protein Beta pleated sheets and alpha helices fold based on interactions between R- groups of a.a. Hydrogen bonds, polar/non-polar interactions, acid/base interactions, disulfide bonds, van der Waals forces Quaternary Structure 4’ the association of the polypeptide chains some proteins contain more than one polypeptide chain Each polypeptide chain in the protein is called a subunit Two or more subunits come together for a specific function HEMOGLOBIN On Red blood cells
- 21. Denaturation Unraveling/unfolding of protein Why would this be a problem? When protein loses its 3-D shape and thus its specific function Caused by: Unfavorable changes in pH, temperature or other environmental condition Disrupts the interactions between side chains and causes loss of shape Examples: Frying an egg Straightening your hair
- 22. Classification of Proteins According to biological function. Type: Example: Enzymes- Catalyze biological reactions ß-galactosidase Transport and Storage Hemoglobin Movement Actin And Myosin in muscles Immune Protection Immunoglobulins (antibodies) Regulatory Function within cells Transeription Factors Hormones Insulin Estrogen Structural Collagen
- 24. Fats/Lipids Made of mostly carbon and hydrogen…some oxygen Usually not soluble in water Not a polymer but is made of molecular units Glycerol + 3 Fatty Acids= FAT Linkage is called ESTER linkage Dehydration reaction Function
- 25. Types of Fats Saturated Solid at room temperature Animal fats All the carbons in the fatty acid chains contain the MAXIMUM # of hydrogen atoms around each atom SATURATED with hydrogen Only single bonds in fatty acid chain Unsaturated/polyunsaturated fats Liquid at room temperature Plant oils, fish oils One or more double bonded carbon atoms in fatty acid chain, then it is unsaturated
- 27. Steroids Chemical messengers Structure 4 fused carbon rings Ex. Cholesterol, testosterone, estradiol Function structural component of mammalian cell membranes resilience and fluidity of human membranes mobilized for the synthesis of steroid hormones protecting the human skin against external irritants and for holding water content Improvement of water balance in human skin Enhanced barrier function for stratum Inhibition of aging of skin Water retention for hair
- 28. Nucleic Acids Monomer: Nucleotide Structure of a Nucleotide Made of a phosphate group, a sugar (ribose or deoxyribose), and nitrogenous base Polymer: Chain of nucleotides (nucleic acids) Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) Ribonucleic Acid (RNA) Function DNA genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms Instructions to make RNA and proteins long-term storage of information NITROGENOUS BASES: Pyrimidines: cytosine and thymine Purines: guanine and adenine A binds to T and G binds to C in the polymer DNA RNA messenger between DNA and the protein synthesis complexes known as ribosomes essential carrier molecule for amino acids to be used in protein synthesis Three types: mRNA, tRNA, rRNA NITROGENOUS BASES: Pyrimidines: cytosine and uracil Purines: guanine and adenine A binds to U and G binds to C in the polymer RNA
- 30. Gizmo: Identifying Nutrients Title: Lab #2 Identifying Nutrients Purpose: Background: Summary of Macromolecules Vocabulary (from exploration guide) Prior Knowledge Questions 1 and 2 Gizmo Warm Up Answers to 1 and 2 (compete sentence answers) Gizmo Activity A Answer questions 1-6, COMPLETE SENTENCE ANSWERS Example: #1 Sample A does contain monosaccharides because when the Benedict test was utilized, there was a pink color change, which is an indication of monosaccharides. Gizmo Activity B (Results and Data) Copy Table 1 into Lab notebook Complete Table 1 (label) Answer Question 2 parts A, B, and C in complete sentences Answer question 3 (Conclusion of activity B) Complete sentences Copy Table 4 into lab notebook Complete Table 2 (label) Conclusion Summarize the what nutrients are and why they are important as well as the tests and procedures you used Answer questions 5 and 6
- 31. MACROMOLECULE Assessment Choose One of the Following To Complete Must Include: Each of the Macromolecules Their Structure Their Function Monomers and Polymers Diagram Be Neat AND Creative Macromolecule Comic Cards Macromolecule Song/Rap Macromolecule Children’s book Macromolecule Poem Macromolecule Advertisement/Billboard/Pamphlet
