Nucleotides- 13
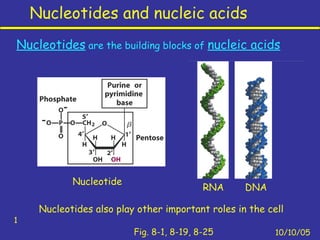
- 1. Nucleotides and nucleic acids 10/10/05 1 Fig. 8-1, 8-19, 8-25 Nucleotides are the building blocks of nucleic acids Nucleotides also play other important roles in the cell Nucleotide DNARNA
- 2. Roles of nucleotides 10/10/05 2 • Building blocks of nucleic acids (RNA, DNA) •Analogous to amino acid role in proteins • Energy currency in cellular metabolism (ATP: adenosine triphosphate) • Allosteric effectors • Structural components of many enzyme cofactors (NAD: nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide)
- 3. Roles of nucleic acids 10/10/05 3 • DNA contains genes, the information needed to synthesize functional proteins and RNAs • DNA contains segments that play a role in regulation of gene expression (promoters) • Ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs) are components of ribosomes, playing a role in protein synthesis • Messenger RNAs (mRNAs) carry genetic information from a gene to the ribosome • Transfer RNAs (tRNAs) translate information in mRNA into an amino acid sequence • RNAs have other functions, and can in some cases perform catalysis
- 4. Structure of nucleotides 10/10/05 4 Fig. 8-1 A phosphate group Nucleotides have three characteristic components: A nitrogenous base (pyrimidines or purine) A pentose sugar
- 5. Basic Structure of Nucleic Acids Monophosphate Diphosphate Triphosphate Adenine Guanine Thymine Cytosine Uracil Nucleoside (Adenosine) Nucleotide (Adenosine monophosphate, AMP) Purine Pyrimidine 核苷 核苷酸 磷酸 五環糖 Ribose, Deoxyribose 鹼基 1’ 2’3’ 4’ 5’ JuangRH(2004)BCbasics
- 6. Structure of nucleosides 10/10/05 5 Remove the phosphate group, and you have a nucleoside. H
- 7. ATP is a nucleotide - energy currency 10/10/05 6 ∆G = -50 kJ/mol triphosphate Base (adenine) Ribose sugar
- 8. NAD is an important enzyme cofactor 10/10/05 7 Fig. 13-15 NADH is a hydride transfer agent, or a reducing agent. Derived from Niacin nicotinamide
- 9. Nucleotides play roles in regulation 10/10/05 8 Fig. 6-30
- 10. Structure of nucleotides 10/10/05 9 Below is the general structure of a nucleotide. The pentose sugar, the base, and the phosphate moieties all show variations among nucleotides. Know this!
- 12. Ribose 10/10/0511 Fig. 8-3 • Ribose (β-D-furanose) is a pentose sugar (5- membered ring). • Note numbering of the carbons. In a nucleotide, "prime" is used (to differentiate from base numbering). 5 1 23 4
- 13. Ribose 10/10/0512 Fig. 8-3 • An important derivative of ribose is 2'-deoxyribose, or just deoxyribose, in which the 2' OH is replaced with H. • Deoxyribose is in DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) • Ribose is in RNA (ribonucleic acid). • The sugar prefers different puckers in DNA (C-2' endo) and RNA C-3' endo).
- 14. The purine or pyrimidine base 10/10/05 13
- 15. Pyrimidine and purine 10/10/05 14 Fig. 8-1 Know these! Nucleotide bases in nucleic acids are pyrimidines or purines.
- 16. Pyrimidine and purine 10/10/05 15 Nucleotide bases in nucleic acids are pyrimidines or purines.
- 17. Major bases in nucleic acids 10/10/05 16 Fig. 8-2 • Among the pyrimidines, C occurs in both RNA and DNA, but • T occurs in DNA, and • U occurs in RNA Know these! • The bases are abbreviated by their first letters (A, G, C, T, U). • The purines (A, G) occur in both RNA and DNA
- 18. Some minor bases 10/10/05 17 Fig. 8-5 • 5-Methylcytidine occurs in DNA of animals and higher plants • N6 -methyladenosine occurs in bacterial DNA Fig. 8-5
- 20. Variation in phosphate group 10/10/05x Fig. 8-6, 8-42 • Adenosine 3', 5'-cyclic monophosphate (cyclic AMP, or cAMP) is an important regulatory nucleotide. • In hydrolysis of RNA by some enzymes, ribonucleoside 2',3'-cyclic monophosphates are isolable intermediates; ribonucleoside 3'- monophosphates are end products • Another variation - multiple phosphates (like ATP). cAMP 19 10/10/05
- 21. Nucleotides in nucleic acids 10/10/05 20 • Bases attach to the C-1' of ribose or deoxyribose • The pyrimidines attach to the pentose via the N-1 position of the pyrimidine ring • The purines attach through the N-9 position • Some minor bases may have different attachments.
- 22. Deoxyribonucleotides 10/10/0521 Fig. 8-4 2'-deoxyribose sugar Deoxyribonucleotides are abbreviated (for example) A, or dA (deoxyA), or dAMP (deoxyadenosine monophosphate) Phosphorylate the 5' position and you have a nucleotide(here, deoxyadenylate or deoxyguanylate) with a base (here, a purine, adenine or guanine) attached to the C-1' position is a deoxyribonucleoside (here deoxyadenosine and deoxyguanosine).
- 24. Ribonucleotides 10/10/05 23 Fig. 8-4 • The ribose sugar with a base (here, a pyrimidine, uracil or cytosine) attached to the ribose C-1' position is a ribonucleoside (here, uridine or cytidine). • Phosphorylate the 5' position and you have a ribonucleotide (here, uridylate or cytidylate) • Ribonucleotides are abbreviated (for example) U, or UMP (uridine monophosphate)
- 25. The major ribonucleotides 10/10/05 24 Fig. 8-4
- 28. Nucleic acids 10/10/05 27 Fig. 8-7 Nucleotide monomers can be linked together via a phosphodiester linkage formed between the 3' -OH of a nucleotide and the phosphate of the next nucleotide. Two ends of the resulting poly- or oligonucleotide are defined: The 5' end lacks a nucleotide at the 5' position, and the 3' end lacks a nucleotide at the 3' end position.
- 29. Sugar-phosphate backbone 10/10/05 28 Berg Fig. 1.1 • The polynucleotide or nucleic acid backbone thus consists of alternating phosphate and pentose residues. • The bases are analogous to side chains of amino acids; they vary without changing the covalent backbone structure. • Sequence is written from the 5' to 3' end: 5'-ATGCTAGC-3' • Note that the backbone is polyanionic. Phosphate groups pKa ~ 0.
- 30. The bases can take syn or anti positions 10/10/05 29 Fig. 8-18b
- 31. Sugar phosphate backbone conformation 10/10/05 30 Fig. 8-18a • Polynucleotides have unrestricted rotation about most backbone bones (within limits of sterics) • with the exception of the sugar ring bond • This behavior contrasts with the peptide backbone. • Also in contrast with proteins, specific, predictable interactions between bases are often formed: A with T, and G with C. • These interactions can be interstrand, or intrastrand.
- 32. Compare polynucleotides and polypeptides 10/10/05 31 • As in proteins, the sequence of side chains (bases in nucleic acids) plays an important role in function. • Nucleic acid structure depends on the sequence of bases and on the type of ribose sugar (ribose, or 2'-deoxyribose). • Hydrogen bonding interactions are especially important in nucleic acids.
- 33. Interstrand H-bonding between DNA bases 10/10/05 32 Fig. 8-11 Watson-Crick base pairing
- 34. DNA structure determination 10/10/0533 • Franklin collected x-ray diffraction data (early 1950s) that indicated 2 periodicities for DNA: 3.4 Å and 34 Å. • Watson and Crick proposed a 3- D model accounting for the data.
- 35. DNA structure 10/10/05 34 Fig. 8-15 • DNA consists of two helical chains wound around the same axis in a right-handed fashion aligned in an antiparallel fashion. • There are 10.5 base pairs, or 36 Å, per turn of the helix. • Alternating deoxyribose and phosphate groups on the backbone form the outside of the helix. • The planar purine and pyrimidine bases of both strands are stacked inside the helix.
- 36. DNA structure 10/10/05 35 Fig. 8-15 • The furanose ring usually is puckered in a C-2' endo conformation in DNA. • The offset of the relationship of the base pairs to the strands gives a major and a minor groove. • In B-form DNA (most common) the depths of the major and minor grooves are similar to each other.
- 37. Base stacking in DNA 10/10/05 36 Berg Fig. 1.4; 5.13 • C-G (red) and A-T (blue) base pairs are isosteric (same shape and size), allowing stacking along a helical axis for any sequence. •Base pairs stack inside the helix.
- 38. DNA strands 10/10/05 37 Fig. 8-16 • The antiparallel strands of DNA are not identical, but are complementary. • This means that they are positioned to align complementary base pairs: C with G, and A with T. • So you can predict the sequence of one strand given the sequence of its complement. • Useful for information storage and transfer! • Note sequence conventionally is given from the 5' to 3' end
- 39. B,A and Z DNA 10/10/0538 Fig. 8-19 • B form - The most common conformation for DNA. • A form - common for RNA because of different sugar pucker. Deeper minor groove, shallow major groove • A form is favored in conditions of low water. • Z form - narrow, deep minor groove. Major groove hardly existent. Can form for some DNA sequences; requires alternating syn and anti base configurations. 36 base pairs Backbone - blue; Bases- gray
- 40. Nucleic acids 10/10/05 39 Fig. 8-19
- 41. RNA has a rich and varied structure 10/10/05 40 Fig. 8-26 Watson- Crick base pairs (helical segments; Usually A-form). Helix is secondary structure. Note A-U pairs in RNA. DNA can form structures like this as well.
- 42. RNA displays interesting tertiary structure 10/10/05 41 Fig. 8-28Fig. 8-25 Single- stranded RNA right- handed helix T. thermophila intron, A ribozyme (RNA enzyme) (1GRZ) Hammerhead ribozyme (1MME) Yeast tRNAPhe (1TRA)
- 43. The mother of all biomolecules 10/10/05 42 1ffk Large subunit of the ribosome(proteins at least)
