2.3 Notes
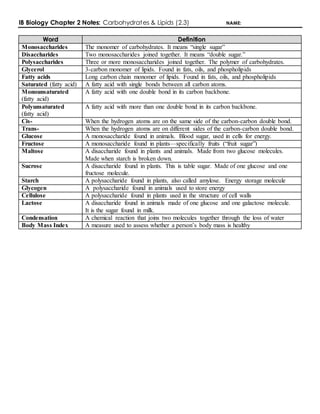
- 1. IB Biology Chapter 2 Notes: Carbohydrates & Lipids (2.3) NAME: Word Definition Monosaccharides The monomer of carbohydrates. It means “single sugar” Disaccharides Two monosaccharides joined together. It means “double sugar.” Polysaccharides Three or more monosaccharides joined together. The polymer of carbohydrates. Glycerol 3-carbon monomer of lipids. Found in fats, oils, and phospholipids Fatty acids Long carbon chain monomer of lipids. Found in fats, oils, and phospholipids Saturated (fatty acid) A fatty acid with single bonds between all carbon atoms. Monounsaturated (fatty acid) A fatty acid with one double bond in its carbon backbone. Polyunsaturated (fatty acid) A fatty acid with more than one double bond in its carbon backbone. Cis- When the hydrogen atoms are on the same side of the carbon-carbon double bond. Trans- When the hydrogen atoms are on different sides of the carbon-carbon double bond. Glucose A monosaccharide found in animals. Blood sugar, used in cells for energy. Fructose A monosaccharide found in plants—specifically fruits (“fruit sugar”) Maltose A disaccharide found in plants and animals. Made from two glucose molecules. Made when starch is broken down. Sucrose A disaccharide found in plants. This is table sugar. Made of one glucose and one fructose molecule. Starch A polysaccharide found in plants, also called amylose. Energy storage molecule Glycogen A polysaccharide found in animals used to store energy Cellulose A polysaccharide found in plants used in the structure of cell walls Lactose A disaccharide found in animals made of one glucose and one galactose molecule. It is the sugar found in milk. Condensation A chemical reaction that joins two molecules together through the loss of water Body Mass Index A measure used to assess whether a person’s body mass is healthy
- 2. 2.3.1 Monosaccharide monomers are linked togetherby condensation reactions to form disaccharides and polysaccharide polymers. 2.3.9 Use of molecular visualization software to compare cellulose, starch, and glycogen. 2.3.5 Structure and function of cellulose and starch in plants and glycogen in humans. 2.3.4 Triglycerides are formed by condensation from three fatty acids and one glycerol. 2.3.7 Lipids are more suitable for long-term energy storage in humans than carbohydrates. 2.3.10 Determination of body mass index by calculation or use of a nomogram. Monosaccharide: Disaccharide: Polysaccharide: Describe what occurs in a condensation reaction: In the JMol software images of monosaccharides,what color are the following atoms? Hydrogen = Carbon = Oxygen = Cellulose: Starch: Glycogen: Outline reasons why lipids are betterlong-term energy storage: State the formula for calculating BMI: BMI Status Under 18.5 18.5-24.9 25.0-29.9 30 and above
- 3. 2.3.2 Fatty acids can be saturated,monounsaturated, or polyunsaturated. 2.3.3 Unsaturated fatty acids can be Cis or Trans isomers. 2.3.6 Scientific evidence for health risks of trans-fats and saturated fats. 2.3.8 Evaluation of evidence and the methods used to obtain evidence for health claims made about lipids. Saturated: Monounsaturated: Polyunsaturated: Cis- Trans- Label the ‘Cis’ and ‘Trans’ configurations,below:
