The structure of dna and genome ogranization
- 1. The Structure of DNA and Genome Organization BY-Sanju sah St. Xavier’s college, maitighar, Kathmandu Department of microbiology
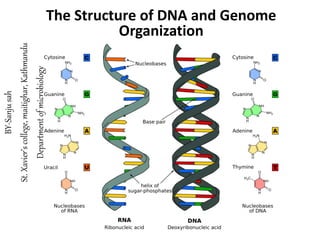
- 2. DNA is usually composed of two polynucleotide chains twisted around each other in the form of a double helix. The backbone of each strand of the helix is composed of alternating sugar and phosphate residues; the bases project inward but are accessible through the major and minor grooves. The two strands are linked by hydrogen bonds between the bases. Structure of nucleic acids
- 3. The only arrangement of these bases that is consistent with maintaining the helix in its correct conformation is when adenine is paired with thymine and guanine with cytosine. One strand therefore consists of an image of the other; the two strands are said to be complementary. Note that the purines are larger than the pyrimidines, and that this arrangement involves one purine opposite a pyrimidine at each position, so the distance separating the strands remains constant Structure of nucleic acids…
- 4. • Adenine: 6-amino purine • Guanine: 2-amino-6-oxy purine • Uracil: 2,4-dioxypyrimidine • Thymine: 2,4-dioxy-5-methyl pyrimidine • Cytosine: 2-oxy-4-amino Pyrimidine Uracil
- 5. • The nucleotide consists of a phosphate joined to a sugar, known as 2’-deoxyribose, to which a base is attached. • The sugar is called 2’-deoxyribose because there is no hydroxyl at position 2’. • water molecule is removed between the hydroxyl on the 1’ carbon of the sugar and the base to form a glycosidic bond. • The sugar and base alone are called a nucleoside. Nucleotides: the fundamental building block of DNA
- 6. • linking the phosphate to 2’-deoxyribose by removing a water molecule from between the phosphate and the hydroxyl on the 5’ carbon to make a 5’phosphomonoester. Nucleotides: the fundamental building block of DNA • Adding a phosphate (or more than one phosphate) to a nucleoside creates a nucleotide.
- 7. • Nucleotides are joined to each other in polynucleotide chains through the 3’-hydroxyl of 2’-deoxyribose of one nucleotide and the phosphate attached to the 5’-hydroxyl of another nucleotide. • This is a phosphodiester linkage in which the phosphoryl group between the two nucleotides has one sugar esterified to it through a 3’-hydroxyl and a second sugar esterified to it through a 5’-hydroxyl. Nucleotides: the fundamental building block of DNA
- 8. Figure: Formation of nucleotide by removal of water
- 9. Figure: Detailed structure of polynucleotide
- 10. Figure: The helical structure of DNA. (a) Schematic model of the double • helix. (b) Space-filling model of the double helix
- 11. Nucleotides Are the Monomeric Units of Nucleic Acids Structure and components of Nucleic Acid Molecule • A unit consisting of a base bonded to a sugar is referred to as a nucleoside . • The four nucleoside units in RNA are called adenosine, guanosine, cytidine, and uridine, whereas those in DNA are called deoxyadenosine, deoxyguanosine, deoxycytidine, and thymidine.
- 12. • In each case, N-9 of a purine or N-1 of a pyrimidine is attached to C-1 of the sugar. • The base lies above the plane of sugar when the structure is written in the standard orientation; that is, the configuration of the N-glycosidic linkage is β . Nucleotides Are the Monomeric Units of Nucleic Acids…
- 13. Nucleotides Are the Monomeric Units of Nucleic Acids… • A nucleotide is a nucleoside joined to one or more phosphate groups by an ester linkage. • The most common site of esterification in naturally occurring nucleotides is the hydroxyl group attached to C-5’ of the sugar. • A compound formed by the attachment of a phosphate group to the C-5’ of a nucleoside sugar is called a nucleoside 5’ - phosphate or a 5’ -nucleotide. • For example, ATP is adenosine 5 -triphosphate. Another nucleotide is deoxyguanosine 3 –monophosphate.
- 14. • The four nucleotide units in DNA are called deoxyadenylate, deoxyguanylate, deoxycytidylate, and deoxythymidylate, and thymidylate. • Note that thymidylate contains deoxyribose; by convention, the prefix deoxy is not added because thymine-containing nucleotides are only rarely found in RNA. Nucleotides Are the Monomeric Units of Nucleic Acids…
- 15. Nucleotides Are the Monomeric Units of Nucleic Acids… • The abbreviated notations pApCpG or pACG denote a trinucleotide of DNA consisting of the building blocks deoxyadenylate monophosphate, deoxycytidylate monophosphate, and deoxyguanylate monophosphate linked by a phosphodiester bridge, where "p" denotes a phosphate group. Structure of a DNA Chain. The chain has a 5’ end, which is usually attached to a phosphate, and a 3’ end, which is usually a free hydroxyl group.
- 16. Nucleotides Are the Monomeric Units of Nucleic Acids… • The 5’ end will often have a phosphate attached to the 5’ -OH group. Note that, like a polypeptide, a DNA chain has polarity. • One end of the chain has a free 5’ -OH group (or a 5’ -OH group attached to a phosphate), whereas the other end has a 3’ -OH group, neither of which is linked to another nucleotide. • By convention, the base sequence is written in the 5’ -to-3’ direction. • Thus, the symbol ACG indicates that the unlinked 5’ -OH group is on deoxyadenylate, whereas the unlinked 3’ -OH group is on deoxyguanylate. Because of this polarity, ACG and GCA correspond to different compounds.
- 17. Nucleotides Are the Monomeric Units of Nucleic Acids… • A striking characteristic of naturally occurring DNA molecules is their length. • A DNA molecule must comprise many nucleotides to carry the genetic information necessary for even the simplest organisms. • For example, the DNA of a virus such as polyoma, which can cause cancer in certain organisms, is as long as 5100 nucleotides in length. • Each position can be one of four bases, corresponding to two bits of information (22 = 4). Thus, a chain of 5100 nucleotides corresponds to 2 × 5100 = 10,200bits, or 1275 bytes (1 byte = 8 bits). • The E. coli genome is a single DNA molecule consisting of two chains of 4.6 million nucleotides, corresponding to 9.2 million bits, or 1.15 megabytes, of information. Electron Micrograph of Part of the E. coli genome. [Dr. Gopal Murti/Science Photo Library/Photo Researchers.]
- 18. Nucleotides Are the Monomeric Units of Nucleic Acids… • DNA molecules from higher organisms can be much larger. • The human genome comprises approximately 3 billion nucleotides, divided among 24 distinct DNA molecules (22 autosomes, x and y sex chromosomes) of different sizes. • One of the largest known DNA molecules is found in the Indian muntjak, an Asiatic deer; its genome is nearly as large as the human genome but is distributed on only 3 chromosomes (Figure 5.9). • The largest of these chromosomes has chains of more than 1 billion nucleotides. If such a DNA molecule could be fully extended, it would stretch more than 1 foot in length. Some plants contain even larger DNA molecules. The Indian Muntjak and Its Chromosomes. Cells from a female Indian muntjak (right) contain three pairs of very large chromosomes (stained orange).
- 19. Nucleic Acid Chains with Complementary Sequences - a Double-Helical Structure • The covalent structure of nucleic acids accounts for their ability to carry information in the form of a sequence of bases along a nucleic acid chain. • nucleic acid structure facilitate the process of replication - generation of two copies of a nucleic acid from one. • These features depend on the ability of the bases to form specific base pairs in such a way that a helical structure consisting of two strands is formed. • The double helical structure of DNA facilitates the replication of the genetic material. • The Double Helix Is Stabilized by Hydrogen Bonds and Hydrophobic Interactions
- 20. Nucleic Acid Chains with Complementary Sequences - a Double-Helical Structure • Maurice Wilkins and Rosalind Franklin obtained x-ray diffraction photographs of fibers of DNA. • The characteristics of these diffraction patterns indicated that DNA was formed of two chains that wound in a regular helical structure. • From these and other data, James Watson and Francis Crick inferred a structural model for DNA that accounted for the diffraction pattern and was also the source of some remarkable insights into the functional properties of nucleic acids (Figure 5.11).
- 21. Nucleic Acid Chains with Complementary Sequences - a Double-Helical Structure X-Ray Diffraction Photograph of a Hydrated DNA Fiber. The central cross is diagnostic of a helical structure. The strong arcs on the meridian arise from the stack of nucleotide bases, which are 3.4 Å apart. [Courtesy of Dr. Maurice Wilkins. Watson-Crick Model of Double-Helical DNA. One polynucleotide chain is shown in blue and the other in red. The purine and pyrimidine bases are shown in lighter colors than the sugar-phosphate backbone. (A) Axial view. The structure repeats along the helical axis (vertical) at intervals of 34 Å, which corresponds to 10 nucleotides on each chain. (B) Radial view, looking down the helix axis.
- 22. The features of the Watson-Crick model of DNA deduced from the diffraction patterns are: 1. Two helical polynucleotide chains are coiled around a common axis. The chains run in opposite directions. 2. The sugar-phosphate backbones are on the outside and, therefore, the purine and pyrimidine bases lie on the inside of the helix. 3. The bases are nearly perpendicular to the helix axis, and adjacent bases are separated by 3.4 Å. The helical structure repeats every 34 Å, so there are 10 bases (= 34 Å per repeat/3.4 Å per base) per turn of helix. There is a rotation of 36 degrees per base (360 degrees per full turn/10 bases per turn). 4. The diameter of the helix is 20 Å.
- 23. Structures of the Base Pairs Proposed by Watson and Crick.
- 24. Chargaff's rules • In the 1950s, a biochemist named Erwin Chargaff discovered that the amounts of the nitrogenous bases (A, T, C, and G) were not found in equal quantities. • However, the amount of A always equalled the amount of T, and the amount of C always equalled the amount of G. • These findings turned out to be crucial to uncovering the model of the DNA double helix. • Erwin Chargaff reported that the ratios of adenine to thymine and of guanine to cytosine were nearly the same in all species studied. • all the adenine:thymine and guanine:cytosine ratios are close to 1, whereas the adenine-to-guanine ratio varies considerably. • The meaning of these equivalences was not evident until the Watson-Crick model was proposed, when it became clear that they represent an essential facet of DNA structure.
- 25. Structures of the Base Pairs Proposed by Watson and Crick.
- 27. • The Double Helix Facilitates the Accurate Transmission of Hereditary Information • The Double Helix Can Be Reversibly Melted- The melting temperature (T m) is defined as the temperature at which half the helical structure is lost. Strands may also be separated by adding acid or alkali to ionize the nucleotide bases and disrupt base pairing. • Some DNA Molecules Are Circular and Supercoiled • Single-Stranded Nucleic Acids Can Adopt Elaborate Structures • Other features/characters of Double helix
- 28. Electron Micrographs of Circular DNA from Mitochondria. (A) Relaxed form. (B) Supercoiled form. [Courtesy of Dr. David Clayton.] Stem-Loop Structures. Stem-loop structures may be formed from single- stranded DNA and RNA molecules.
- 29. Axial View of DNA. Base pairs are stacked nearly one on top of another in the double helix
- 30. B-form A-form and Z-DNA
- 33. Major and Minor Grooves in B-Form DNA. The major groove is depicted in orange, and the minor groove is depicted in yellow. The carbon atoms of the backbone are shown in white. B-Form DNA.
- 34. • The information from the base composition of DNA, the knowledge of dinucleotide structure, and the insight that the X-ray crystallography suggested a helical periodicity were combined by Watson and Crick in 1953 in their proposed model for a double helical structure for DNA. • They proposed two strands of DNA - each in a right-hand helix - wound around the same axis. • The two strands are held together by H-bonding between the bases (in anti conformation)
- 35. The base-pairing scheme immediately suggests a way to replicate and copy the genetic information. • Figure: Antiparallel (a), plectonemically coiled (b, c, d) DNA strands. The arrows in a are pointed 3’ to 5’, but they illustrate the antiparallel nature of the duplex. • The two strands of the duplex are antiparallel and plectonemically coiled. • The nucleotides arrayed in a 5' to 3' orientation on one strand align with complementary nucleotides in the the 3' to 5' orientation of the opposite strand.
- 37. Various types of conformations that the DNA can adopt depend on different factors such as; • Hydration level • Salt concentration • DNA sequence • Quantity and direction of super-coiling • Presence of chemically modified bases • Different types of metal ions and its concentrations • Presence of polyamines in solution
- 38. Dimensions of B-form (the most common) of DNA • 0.34 nm between bp, 3.4 nm per turn, about 10 bp per turn • 1.9 nm (about 2.0 nm or 20 Angstroms) in diameter Major and minor groove • The major groove is wider than the minor groove in DNA (Figure 2.5.2d ), and many sequence specific proteins interact in the major groove. The N7 and C6 groups of purines and the C4 and C5 groups of pyrimidines face into the major groove, thus they can make specific contacts with amino acids in DNA- binding proteins. Thus specific amino acids serve as H-bond donors and acceptors to form H-bonds with specific nucleotides in the DNA. H-bond donors and acceptors are also in the minor groove, and indeed some proteins bind specifically in the minor groove. Base pairs stack, with some rotation between them.
- 41. • The results of x-ray diffraction studies of dehydrated DNA fibers revealed a different form called A-DNA, which appears when the relative humidity is reduced to less than about 75%. • A-DNA, like B-DNA, is a right-handed double helix made up of antiparallel strands held together by Watson-Crick base- pairing. • The A helix is wider and shorter than the B helix, and its base pairs are tilted rather than perpendicular to the helix axis A-DNA
- 42. Space-filling models of ten base pairs of B- form and A-form DNA depict their right- handed helical structures. The B-form helix is longer and narrower than the A- form helix.
- 45. • Alexander Rich and his associates discovered a third type of DNA helix when they solved the structure of dCGCGCG. • They found that this hexanucleotide forms a duplex of antiparallel strands held together by Watson-Crick base- pairing, as expected. • this double helix is left-handed, in contrast with the right- handed screw sense of the A and B helices. • Furthermore, the phosphates in the backbone zigzagged; hence, they called this new form Z-DNA Z-DNA
- 46. Z-DNA: DNA oligomers such as dCGCGCG adopt an alternative conformation under some conditions. This conformation is called Z-DNA because the phosphate groups zigzag along the backbone. Z-DNA
- 49. Propeller Twist The bases of a DNA base pair are often not precisely coplanar. They are twisted with respect to each other, like the blades of a propeller.
- 50. Because the two glycosidic bonds are not diametrically opposite each other, each base pair has a larger side that defines the major groove and a smaller side that defines the minor groove. The grooves are lined by potential hydrogen-bond donors (blue) and acceptors (red).
