The Cell
- 1. THE CELL Represented by- Radiate
- 2. Introduction The cell is the functional and structural unit of living body. Cell Tissue Organ Organ system Living body
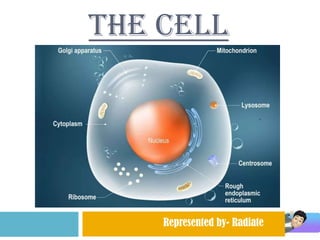
- 3. 3D model of a typical animal cell
- 4. Introduction Many cells are group together to form tissue. Many tissue group together to form organ. Many organ group together to form organ system. Many organ system group together and co-ordinate to form of living body. Cell of different tissue perform different function. A cell is of microscopic jelly like structure which is known as ‘Protoplasm’ (nucleus, mitochondria etc.). Protoplasm are held together by a cell membrane are plasma membrane. Cell possess the quality of all living matter, include in those of cell preservation and reproduction.
- 5. Labeled diagram of a typical animal cell
- 6. Plasma membrane or Cell membrane Plasma (cell) membrane is the outer surface of the cell. It is covering of the cell which is 0.1 in thickness. It can be seen only under electron microscope. It is formed of 40% lipids and 60% protein. It is selectively formidable for certain substance. It has osmotic properties (low concentrations to high concentrations). The cell membrane is a double layer of phospholipids molecules. Proteins in the cell membrane provide structural support, form channels for passage of materials, act as receptor sites, function as carrier molecules, and provide identification markers.
- 8. 1. Nucleus It is the largest structure of the cell which almost present of centre of cell. It is more or less spherical in shape, it is bounded by nuclear membrane which protect the nucleus. The nucleus contains:- (a) Nucleolus (b) Chromatin
- 9. (a) Nucleolus It is highly coiled filamentous structure present in the nucleus. It has no membrane surrounding it. It contains numerous granules. Nucleus is responsible for ribosomal RNA synthesis. It contains one or more nucleoli, which is essential for growth, metabolism, reproduction and transmission. It store ribosomal RNA and control the synthesis of ribose and protein.
- 11. (b) Chromatin These are fibrous thread like structure which are presented in nucleus. They are composed of DNA and protein. The protein carried genetic information at the time of cell division, chromatin change into chromosome. The number of chromosomes is constant for particular species of organism. In man there are 23 pair of chromosome present. It control nuclear metabolism and cell membrane and it stored heredity information.
- 13. 2. Mitochondria Mitochondria is a Greek word, it means; Mito- Thread Chondria- Granules Mitochondria are granules or filamentous of cytoplasm. These are regarded as biochemical machine, which convert the potential energy of food stuff into kinetic energy. So, they are known as power house of the cell. They occur in cytoplasm as variable number. For e.g. few hundred to few thousand.
- 14. 2. Mitochondria Mitochondria is composed of two layer of membrane they are; 1. An outer layer which are smooth. 2. An inner layer folded into sheets of tubules called as ‘cristae’. Both these layer enclosed a central cavity is known as ‘matrix’. Mitochondria is made of phospholipids, protein and some ribonucleic acid, they also contain some important enzyme system. The energy molecule adenosine tri phosphate (ATP) is produce in mitochondria.
- 16. Chemical composition Mitochondria consist of protein 73% and lipids 25- 30% of the total lipids, 90% phospholipids and rest 10% are cholesterol, Vitamin-E and other inorganic material are present. A small of DNA & RNA is also present in mitochondria. These are known as mitochondrial DNA and mitochondrial RNA. 50 mitochondria are able to synthesize their own protein and enzyme.
- 17. Function of mitochondria 1. Oxidation of food stuff: Mitochondria are generally known as power house of the cell because these brings about oxidation of food stuff. They act as power house of cell release energy by the oxidation of food at the site of cellular respiration. 2. Metabolism of fat: The mitochondria said to possess reverse stock of fat which is needed during germination of seed. 3. Energy conservation: During the process of cell division, the ATP play on important role to convert the potential energy into kinetic energy.
- 18. 3. Endoplasmic reticulum It is the most extensive cell organelle present in the cytoplasm. Endoplasmic reticulum is a two types they are; 1. Granular endoplasmic reticulum: It is also known as rough surfaced endoplasmic reticulum. This type of reticulum contains ribosome which are responsible for protein synthesis. 2. Agranular endoplasmic reticulum: It is also known as smooth surface endoplasmic reticulum. They do not contain ribosome. This type of endoplasmic reticulum is responsible for fatty acids and steroid synthesis. They also stored and release calcium.
- 20. 4. Golgi apparatus It is cup shaped structure which are present in cytoplasm. It is situated between the nucleus and apex of cell. Golgi body are double membrane cell organelles, they are three types; 1. Vesicles 2. Vacuoles 3. Cistern
- 22. 5. Lysosome Lysosome are small spherical or oval shape which are surrounded by a single membrane. They are spherical vesicles that contain hydrolytic enzymes that can break down many kinds of biomolecules. The damage intracellular organelles are also broken down and digested by lyposome, therefore the lyposome are also called as suicide bag of cell.
- 24. 6. Centrosomes It is a small, rod shaped body found near the nucleus. It play a important role during cell division. Centrosomes are made of from arrangement of two barrel-shaped clusters of microtubules, called centrioles, and a complex of proteins that help additional microtubules to form.
- 26. 7. Microsomes They are extremely small membrane, bound bodies present in cytoplasm. Microsome originate from endoplasmic reticulum. Microsome contains ribosome and granular matrix, so they are also responsible for protein synthesize. Granular matrix contains enzymes that is; A. Oxidases- Generate H2O2 B. Catalases- Convert H2O2 into H2O
- 27. Function of cell A. Ingestion and assimilation: The cell ingests chemical substance like amino acids from intracellular fluid. These substance are used to build up complicated substance like proteins. B. Growth and repair: The ingested and assimilate materials are use to synthesize new protoplasm. This leads to increase in size and growth of cell. Worn out parts of the cell are also replaced by this process.
- 28. Function of cell C. Metabolism: i. Anabolism:- In this process, the ingested and assimilate food material is used for growth and repair. ii. Catabolism:- In this process, the food material is broken down to release energy for various function of cell. D. Respiration: It involves transport of oxygen from lungs through blood to the tissues and removal of waste product like CO2.
- 29. Function of cell E. Excretion: The cell eliminates waste products. These waste products are carried by blood for elimination through lungs and kidneys. F. Irritability and contractility: The cell is active by mean of these two function. The cell responds to any stimulus (like; physical, chemical, thermal, electrical and mechanical) by contracting or the impulse is conducted as that occurs in nerve cell.
- 30. Function of cell G. Selective gate-keeper: Cell membrane act as a selective gate-keeper by functioning as a semi permeable membrane.
