IB Chemistry on Allotrope, Alloy, Graphene and crystalline structure
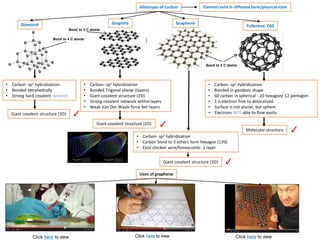
- 1. Allotropes of Carbon Element exist in different form/physical state Diamond Fullerene, C60 •Carbon-sp2hybridization •Bonded in geodesic shape •60 carbon in spherical -20 hexagon/ 12 pentagon •1 πelectron free to delocalized. •Surface is not planar, but sphere •Electrons NOTable to flow easily. Graphene •Carbon-sp2hybridization •Carbon bond to 3 others form hexagon (120) •Exist chicken wire/honeycomb-1 layer Click hereto view Click hereto view Click hereto view •Carbon-sp3hybridization •Bonded tetrahedrally •Strong hard covalent network •Carbon-sp2hybridization •Bonded Trigonalplanar (layers) •Giant covalent structure (2D) •Strong covalent network within layers •Weak Van Der Waals force bet layers Giant covalent structure (3D) Giant covalent structure (2D) Molecular structure ✓ ✓ ✓ Giant covalent structure (2D) ✓ Uses of graphene Graphite Bond to 4 C atoms Bond to 3 C atoms Bond to 3 C atoms …
- 2. Allotropes of Carbon Element exist in different form/physical state Diamond Fullerene, C60 Graphene Graphite Electrical conductivity Special property Electrical conductivity Electrical conductivity Electrical conductivity Special property Good -Within layer, C sp2hybridized -ONEfree delocalized πelectron Very Good -Within layer, C sp2hybridized -ONEfree delocalizedπelectron moving across the layer easily Poor -C sp3hybridized -No free moving electron Semiconductor ✓ ✗ -Surface sphere, notplanar -Electrons CANNOTflow easily. -Lower electron mobility -Soft, layer slide across each other -Hardest substance -Jewellery Special property graphite lubricant electrode Lightest/strongest material replacing silicon in photovoltaic cell Drug delivery Transistor/Electronic Transparent conducting electrode Clickhereuses graphene Drug in graphene
- 3. Allotropes of Carbon Element exist in different form/physical state Fullerene, C60 Graphene Click hereto view touch screen Electron in hexagonal rings do not delocalized over whole molecule. 6:6 bond shorter than 6:5 6:5 bond bet hexagon and pentagon Macroscopic properties •High tensile strength •Highelectrical /heat conductivity •High ductility andchemical inactivity 60 carbon in spherical ((20 hexagon/12 pentagon) Potential medicinal use •Trap/bind drug inside/outside cage •Target cancer cells Drug inside Drug bind outside •sp2hybridization •Exist as 2D/chicken wire/honeycomb •Stronger than diamond, x200 stronger steel •Conductive than copper •Flexible/Transparent/lighter than rubber •Solar cell and batteries Graphenetouch screen and photovoltaic cell Click herefor application of graphene Single sheet conductor Rool into conductive nanotubes Electrical contact photovoltaic cell Lightest and strongest replacing silicon in photovoltaic cell 6:6 bond length bet two hexagon Double bond Single bond
- 4. Uses of Carbon Allotropes •Conduct current/heat very well •Conduct current at speed of light •Electron delocalized above/below plane •High electron mobility Click herediscovery graphene Click hereCNT Click hereto view sp2hybridization graphene rool into rool into Carbon Nanotube (CNT) CNT-fullerene family of carbon allotropes. Hollow cylindrical molecule Rolling single or multiple layers of graphenesheet. Single-wall SWNT/ multi-wall MWCNT High tensile, stable, unreactive Single wall Nanotube (SWNT) Multi wall Nanotubes (MWNT) Click hereTEDtalk graphene 1 layer thick Uses of CNT Strong tubes as space elevator Filter off salt (desalination) Drug delivery to body Attachment drug therapeutics
- 5. Metallic Bonding Metals Metallic bonding Electrostatic forces attraction -bet lattice of positive ions with delocalized electron Metallic elements-Cu, Na, K, Cu Lattice of positive ions with sea of free electrons Metallic Bonding Metallic Property Electrical conductivity Malleability/Ductile High melting point Delocalized free moving electron carry charge/heat heat flow High Temp Low Temp Thermal conductivity electron flow ✓ Form sheet by hammering Ductile -stretch into wires Bend and shaped Atom able to roll/slide to new position without breaking metallic bond Strong Electrostatic force attraction -between lattice of positive ions with delocalized electron
- 6. Melting Point •Temp when solid turn to liquid (temp remain constant) •Energy absorb to overcome forces attraction bet molecule Factors affecting melting point for metals •Melting point across Period 2/3 •Melting point down Gp1 Gp 1 Period 2/3 Metallic Bonding Melting Point metals period 2 period 3 Li Be B C N O F Ne Na Mg AI Si P S CI Melting point across Period 2 and 3 Electrostatic forces attraction -bet lattice of positive ions with delocalized electron Melting point across Period 2 and 3 Size of atom decrease ↓ Number delocalized electron increase ↑ Electrostatic forces attraction INCREASES ↑ Melting point INCREASE ↑ ✓ Electrostatic force attraction Metallic Bonding Metalic Bonding INCREASE ↑
- 7. Melting Point Factors affecting melting point for metals Gp 1 Period 2/3 Metallic Bonding Melting Point metals Melting point down Group 1 Electrostatic forces attraction -bet lattice of positive ions with delocalized electron Melting point down Gp1 Size of atom increase ↑ Valence electron further away from positive nucleus Electrostatic forces attraction DECREASES ↓ Melting point DECREASE ↓ ✓ Electrostatic force attraction Metallic Bonding Size of atom increases Metallic Bonding DECREASE ↓ •Temp when solid turn to liquid (temp remain constant) •Energy absorb to overcome forces attraction bet molecule •Melting point across Period 2/3 •Melting point down Gp1
- 8. Melting Point Gp 1 Period 2/3 Metallic Bonding Melting Point metals Electrostatic forces attraction -bet lattice of positive ions with delocalized electron ✓ Electrostatic force attraction Metallic Bonding Number delocalized electrons Factors affecting Metallic Bonding Charge on cation Radius cation Higher ↑ charge cation Higher ↑metallic bonding (melting point) Bigger ↑ radius cation Lower ↓ metallic bonding (melting point) Higher ↑ number delocalized electrons Why m/p Na (Gp1) less than Mg (Gp2) ? Why melting point different? ONE delocalized electron per atom TWO delocalized electron per atom Radius cation Bigger ↑ Radius cation Smaller ↓ MELTING POINT MELTING POINT Higher ↑metallic bonding (melting point) Charge cation smaller ↓ Charge cation Bigger ↑ •Temp when solid turn to liquid (temp remain constant) •Energy absorb to overcome forces attraction bet molecule •Melting point across Period 2/3 •Melting point down Gp1 +1 +2
- 9. Heating mixture metals together Alloy cool/solidifies, mechanical property diff from its individual constituents Metals/non-metals often enhance its properties. Induce strength/hardness by occupying empty spaces bet lattice structure Metals •Same type of elements/atom arrangement •Malleable –shaped by hammering •Ductile –deform/ turn to wire Aluminium -Soft/malleable structure-crystalline lattice same type atoms Click herefor list of alloys Metals VsAlloy Alloy •Mixture metals / non metal •Property alloy far superior than its element/metal •Stronger, harder and enhanced qualities than metals structure-crystalline lattice different atomic sizes Duralumin (Aluminium+ Copper) Strong aircraft Metals Alloy Vs Vs Iron -Soft/malleable Steel -Strong/Hard What makes alloy strong? Metal occupy spaces in between Heat mixture metals Malleable (hammer) Ductile (Stretch) Mixture of metals in lattice Strong + hard ✓ ✓ ✗ ✗ Click hereuses alloy -nitinolrobot
- 10. Metals Structure-crystalline lattice same type atoms Metals VsAlloy Property alloy far superior than its element/metal Structure-crystalline lattice different atomic sizes Vs Malleable (hammer) Ductile (Stretch) Mixture of metals in lattice Alloy Component Property/Uses Steel Iron+ Carbon Structural material Stainless steel Iron+ Carbon +Nickel +Chromium Corrosion resistance Brass Copper+ Zinc Decorative Bronze Copper+ Tin Coins and medals Duralumin Aluminium+ Copper + Manganese Aircraft Nichrome Nickel+ Chromium Heating element Pewter Tin+ Copper + Antimony Decorative Nitinol Nickel+ Titanium Shape memory, actuator Bold –Base main metal used Same type atom arrangement Ductile – Deform/turn to wire Malleable – Shaped by hammer Alloy Mixture metals/non metal Stronger, harder-enhance qualities than metals + ✓ Metal + Metal = Alloy Click heredifferent alloys Types of Alloy Steel Stainless steel Brass Bronze Duralumin Nichrome Pewter Click hereuses alloy -nitinol robot ✓
- 11. Crystalline Structure Giant metallic Giant Ionic Giant Covalent Network Simple Molecular Non Polar Polarmolecule H2Bonding Particles Atoms(Metals) Na, K, Li, Ca, Mg Ion (+ve/-ve ions) Na+CI-, K+CI- Atoms from Gp4 (Carbon/Silicon) Molecules with Molecule with Molecule with H atom -Similar EN value -Different EN value -bonded to N, O, F -Bond polarity cancel –Dipole moment (electronegative atom) -Symmetrical -Asymmetrical Bonding Lattice of positive ions with sea of electrons Electrostatic forces attraction bet +ion with electron Lattice of positive and negative ions Electrostatic forces attraction bet +ion with -ion Giant covalent throughout 3D structure. Within molecule Within molecule Within molecule -strong covalent -strong covalent -strong covalent Between molecule Between molecule Between molecule -weak intermolecular -weak intermolecular -weak intermolecular -VDF -VDF -VDF -Dipole-dipole -Dipole -dipole -H2bonding Physical Property State Solid (Non volatile) Solid (Non volatile) Solid (Non volatile) Liq/Gas Liq/Gas Liq/Gas (Volatile) (Volatile) (Volatile) Melting Point HIGH HIGH VERY HIGH Very Low Very Low Very Low Conduct Good Conductor -free moving electron Good conductor -free moving ions in molten/aqstate Poor conductor -Diamond, SiO2 Semiconductor -Graphite, C60 Good conductor -Graphene Poor conductor Poor conductor Poor conductor Solubility Insoluble Soluble in polar solvent Insoluble Soluble in polar Soluble in non polar Soluble in polar solvent solvent solvent Sea electrons +ve / -ve ions Strong Covalent Metallic Bonding Ionic Bonding ✓ CI CI CI CI CI CI .... Between molecule Within molecule .... Between molecule Within molecule H2 Bonding Carbon atoms Silicon atoms
