Tugas 2 inggris case study
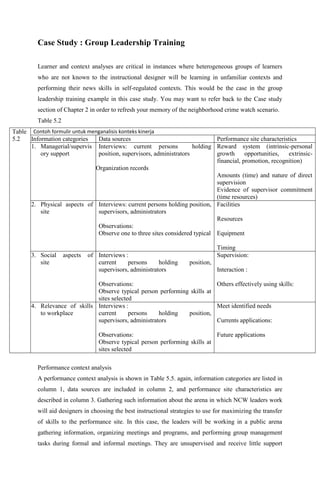
- 1. Case Study : Group Leadership Training Learner and context analyses are critical in instances where heterogeneous groups of learners who are not known to the instructional designer will be learning in unfamiliar contexts and performing their news skills in self-regulated contexts. This would be the case in the group leadership training example in this case study. You may want to refer back to the Case study section of Chapter 2 in order to refresh your memory of the neighborhood crime watch scenario. Table 5.2 Table Contoh formulir untuk menganalisis konteks kinerja 5.2 Information categories Data sources Performance site characteristics 1. Managerial/supervis Interviews: current persons holding Reward system (intrinsic-personal ory support position, supervisors, administrators growth opportunities, extrinsic- financial, promotion, recognition) Organization records Amounts (time) and nature of direct supervision Evidence of supervisor commitment (time resources) 2. Physical aspects of Interviews: current persons holding position, Facilities site supervisors, administrators Resources Observations: Observe one to three sites considered typical Equipment Timing 3. Social aspects of Interviews : Supervision: site current persons holding position, supervisors, administrators Interaction : Observations: Others effectively using skills: Observe typical person performing skills at sites selected 4. Relevance of skills Interviews : Meet identified needs to workplace current persons holding position, supervisors, administrators Currents applications: Observations: Future applications Observe typical person performing skills at sites selected Performance context analysis A performance context analysis is shown in Table 5.5. again, information categories are listed in column 1, data sources are included in column 2, and performance site characteristics are described in column 3. Gathering such information about the arena in which NCW leaders work will aid designers in choosing the best instructional strategies to use for maximizing the transfer of skills to the performance site. In this case, the leaders will be working in a public arena gathering information, organizing meetings and programs, and performing group management tasks during formal and informal meetings. They are unsupervised and receive little support
- 2. excepts for the country NCW coordinator and the assigned local police support person. Providing these supports individuals with information and strategies for supporting the NCW leaders in their communities could prove very beneficial for enhancing each leader‟s effectiveness in the community. Table 5.3 Table Example Form For Analyzing Performance Context 5.3 Information Categories Data Sources Learning Site Characteristics 1. Number/ nature of Interviews: Number sites Managers Facilities Site visits: Equipment Observations Resource Constraint: 2. Site compatibly Interviews: Instructional strategies: with instructional Managers, instructors Delivery approaches needs Site visits: Time Observations Personnel Other 3. Site compatibly Interviews: Location (distance) with learner needs Managers, instructors, Conveniences: Learners Space: Site visits: Equipment : Observations Other: 4. Feasibility for Interviews: Supervisory characteristics: simulating work Managers, instructors, Physical characteristics: place Learners Social characteristics Site visits: other Observations LEARNING CONTEXT ANALYSIS Table 5.6 contains a learning context analysis for the group leadership instructional goal. A list of the information categories appears in the first column, the data sources in the second column, and learning context characteristics in the third column. From this information, we can infer that the design team has a very good instructional situation. The importance of the neighborhood crime problem and the political/social priority currently attached to it has created the financial and professional resources, facilities, equipment, and personnel to provide quality instructional products and training sessions. The only apparent limitations placed on the designers are those related to balancing learning efficiency and cost effectiveness. For additional learning support and a school curriculum example of analyzing learners and contexts, be sure to go to the Course Management site materials for chapter 5.
- 3. Table 5.4 Table Description Of Learner Characteristics For Newly Appointed 5.4 Neighborhood Crime Watch (NCW) leaders Information Categories Data Sources Learner Characteristics 1. Entry Interviews and Performance setting: behaviors Observations Learners have no prior experience as Three current and Neighborhood Crime Watch chairpersons, and three newly elected most have no prior experience in serving as the NCW chairs, the leader in problem solving discussions county NCW supervisor, three Learners have served as members in work or police liaison officers community related committee meetings; however most have had no formal training in Test data: problem solving through interactive discussions Posttest performance from group membership training 2. Prior Interviews and Learners have general knowledge of the group knowledge of Observations leadership area from participating as members topic area Three current and in group discussions and from observing three newly elected different leaders they have had through the NCW chairs, the years. As adults who have interacted more or county NCW less successfully with colleagues, they possess, supervisor, three at least at an awareness level, many of the skills police liaison officers required to be effective discussion leaders. Test data: Posttest performance from group membership training 3. Attitudes Interviews and Learners believe the group problem solving toward content Observations skills they will learn are beneficial and will help Three current and them become good, contributing members of three newly elected team efforts. They also believe that acquiring NCW chairs, the the upcoming group leadership skills will help county NCW them ensure that their committee meetings will supervisor, three be effective and productive police liaison officers Test data: Posttest performance from group membership training 4. Attitudes Interviews and Learners have experience learning through live toward Observations lectures, web based instruction, and live group potential Three current and problem solving simulations as a result of the delivery three newly elected prior instruction. system NCW chairs, the They liked the convenience of the web based county NCW instruction, and they believe that simulations supervisor, three were helpful police liaison officers Test data: Posttest performance from group membership training
- 4. 5. Motivation for Interviews and Learners are positive about their selection of instruction Observations leaders, and are anxious to develop/ refine their (ARCS) Three current and leadership skills. They believe the leadership three newly elected skills are relevant to their jobs as Neighborhood NCW chairs, the Crime Watch chair persons, and they are county NCW confident they can become effective group supervisor, three discussion leaders. police liaison officers These factors, along with the interactive nature of the instruction, should help ensure that Test data: learners are attentive during instruction. Posttest performance from group membership training 6. Educational Interviews and Education levels : learners vary in their formal and ability Observations education with some completing high school, level Three current and some college, and some graduate degrees three newly elected NCW chairs, the Ability levels: besides academic progress, county NCW learners‟ interpersonal skills are a concern. supervisor, three Based on experience in the prior “group police liaison officers member” training, it seems that learners are heterogeneous with some high in interpersonal Records: skills, some moderate and some low Biographical data from NCW Chairperson Application Form Test data: Posttest performance from group membership training 7. General Attitude data : Learners are experienced with a variety of learning Questionnaire from learning formats: however, they prefer not to be preferences group membership publicly “put on the spot” until they are training completely clear about trainer and group expectations and the skills they are to Interviews and demonstrate in a group setting. In workshop observations: setting, they prefer a short cycle of (1) All 16 learners in presentation (what do you expect of me?), (2) group membership private rehearsal (how can I best accomplish training session this?) and then (3) interactive “on the spot” simulations (can I manage group interactions/progress with real people and problems?). they like simulations and like to be involved 8. Attitudes Interviews: Respondents have positive feelings about the toward training NCW Supervisor, organization developing the materials, bout web organization police liaison officers, base instruction delivered via the Internet, and current NCW leader about the county learning center they used during prior training. All think the training is a good idea for helping them become acquainted with other NCW leaders from across the county and that these relationship. They also believe the training is helping them become acquainted with other NCW leaders from across the country and that these relationships will help them build an interpersonal network of support.
- 5. Interview : Heterogeneity : Learners are extremely NCW supervision, heterogeneous in that they come from various police liaison officer neighborhood throughout a country ;come from NCW Records : a wide variety of work settings and areas of Needs assessments, expertise ;have varying years of work 9. General group history with NCW experience ;and represent a mix of age, gender, characteristics leaders, biographical and cultural backgrounds. a. Heterogeneity forms for leaders Size: There will be a total of twenty learners b. Size c. Overall Observations : per training site to maximize learning efficiency impressions Three current NCW for live group interactive work. leaders conducting Overall impressions: Instruction will need to be neighborhood efficient, effective, and convenient or meeting. „volunteer‟ participants may choose not to read materials, complete computer-based activities independently, or attend all group sessions. Table Description of Performance Context for Neighborhood Crime Watch (NCW) Leaders 5.5 Information Categories Data Sources Learner Characteristics 1. Managerial Interview : Supervision of NCW chairperson is minimal. /supervision Three current Supervision mainly takes the form of providing support Neighborhood Crime current information. For example, they receive Watch (NCW) organizational bulletins, materials, and chairpersons ;3 police information from NCW web site. They receive support /liaison immediate notification of current crimes persons ;and the committed in their neighborhood, details of country NCW those crimes, and statistical summaries of local program administrator and area crimes on NCW web site from Records : assigned police liaison person. Police liaison Studied NCW charter person also serves as on-call resource person and literature ;studied for chairpersons seeking information, and records for NCW attends NCW meeting as resource person for leaders (function, total group questions. duties, etc) 2. Physical Interview : Facilities: There are no facilities provided by aspects of site Three current NCW Association or police for scheduled Neighborhood Crime NCW meetings. Meetings typically occur Watch (NCW) within the neighborhood in a committee chairpersons ;3 police member‟s home or in a neighborhood support /liaison association facility persons ;and the Resources: No money is provided for NCW country NCW member meetings. Any resources required program administrator (meeting announcement, materials distributed Records : to attendees, refreshments, act) for operating Studied NCW charter the meetings are sponsored by participating and literature ;studied NCW members. records for NCW Equipment :No particular equipment is required leaders (function, for the NCW meetings duties, etc) Observations : Attended 3 NCW meetings in different regions of the country 3. Social aspects Interview : Supervisions : the chairperson has no of site Three current supervision during the conduct of the meeting Neighborhood Crime Watch (NCW) Interaction : the chairperson is actively
- 6. chairpersons ;3 police interacting with community members who support /liaison attend the NCW meetings. This interaction is a persons ;and the leader to manage the work of the group. The country NCW chairperson has a police officer at meetings to program administrator serve as a content expert on crime and the law, Records : and can invite other experts to meetings as the Studied NCW charter topic to be discussed warrants and literature ;studied records for NCW Others effectively using skills: there are no leaders (function, others effectively using discussion leadership duties, etc) skills in the meetings because the chairperson is Observations : the single designated NCW leader for the Attended 3 NCW community. Others in the group may have meetings in different discussion leadership skills developed in the regions of the country workplace or in other community settings. 4. Relevance of Interview : Meet identified needs: the leadership training skills to Three current should meet NCW‟s identified needs of workplace Neighborhood Crime improving the effectiveness of NCW Watch (NCW) chairpersons in the problem solving/solutions chairpersons ;3 police meetings. New chairpersons will be able to use support /liaison the skills for their first neighborhood meeting persons ;and the session, and the skills will serve them well in country NCW the future meetings. program administrator Records : Studied NCW charter and literature ;studied records for NCW leaders (function, duties, etc) Observations : Attended 3 NCW meetings in different regions of the country Records: Reviewed needs assessment study describing characteristics of effective/ineffective NCW leader Table Description of Learning Context for Neighborhood Crime Watch (NCW) Chairpersons 5.6 Information Categories Data Sources Learner Characteristics 1. Number/nature Interview : Number : one site per county in each of fifty of sites counties across state managers Facilities : the web based instruction will occur over the Internet and be delivered Site visits directly into the new NCW leaders‟ homes Observations: The group instruction is to occur in each county‟s government training facility. Typical facilities across the state contain one lecture hall for eighty to one hundred persons, three to five classrooms for twenty to twenty five persons, one conference room for sixteen to
- 7. twenty persons, one learning center open 8:00 a.m until 8:00 p.m with one to two managers available for materials distribution , equipment assistance, and learner guidance, one administrative office. Depending on scheduling conflicts, all facilities are available for the NCW chairperson training. Equipment: typical centers contain chalkboards, overhead projection screens and projectors, LCD projector for computer display projection onto screens; newsprint pads and stands, five to six multimedia computer workstations. Resources: a state grant is provided to create centrally the web base instruction that will be distributed statewide. In addition, the grant will fund for each county a group instructor, instructional materials, mailings and secretarial assistance (scheduling/ communication) Constraints: 1. The learning center is busy. Scheduling instruction may be difficult; however, there is less use evenings and weekends when planned training will occur for community volunteers. 2. The regular instructors available in each site are not content experts in group discussion leadership. Instructor training will need to be developed and implemented. One expert trainer may need to be available for troubleshooting across the sites. 2. Site Interview : Instructional strategies: a variety of compatibility instructional strategies can be employed with instructional managers including self-study print materials, needs computers based instruction, classroom Instructors presentations and discussion, and simulated, small-group discussion sessions in conference Site visits rooms. Observations: Delivery approaches: support is available for production and use of all typical print and non print materials. Support is also available for newer technologies such as WWW and other computer based, multimedia formats. The training center is also wired and equipped for local area and wide area telecommunications and teleconferencing. Time: instructional time in the center is limited to fifteen hours for project due to
- 8. constraints placed by volunteer NCW chairpersons. This time is typically divided into ten weekly, ninety-minute periods. Independent study time is possible off site between these scheduled sessions. Personnel: Each site has an administrator, several trainers, technicians, and secretaries. There are no trainers present who have provided small group leadership instruction for NCW volunteers, although they have provided leadership training for city and county government employees. 3. Site Interview : Location (distance): the learning centers are compatibility located centrally within each county area, with learner managers making transportation for group sessions needs convenient. Instructors, learners Conveniences: restaurants are located in the Site visits areas, and there is a coffee shop within most of the centers. Observations: Space: the classrooms can be used for group simulations and the conference rooms for smaller group “meeting” rehearsals. Equipment: if needed, the five to eight computer workstations can be scheduled to avoid time conflicts with NCW leaders. 4. Feasibility for Interview : Supervisory characteristics: this cannot be simulating work- simulated since leaders will have no place managers supervision and little support in their neighborhoods (county NCW coordinator and Instructors, learners local police officers) Site visits Physical characteristics: within the neighborhood, learners will work as the Observations: leaders of Neighborhood Crime Watch interactive group discussions. These discussions with learners as leaders can readily be simulated in the centers. SUMMARY To begin this stage of instructional design, you should have completed or be working on the goal analysis and the subordinate skills analysis including the identification of entry behaviors. You should also have general ideas about the target population for which instruction will be developed. These ideas usually include general descriptions such as kindergarten children, seventh graders, college freshmen, ambulance drivers, or automobile operators convicted of reckless driving following a serious accident.
- 9. The first task is to identifying the general characteristics that members of the target population bring to the instruction. These characteristics include descriptions such as reading levels, attention span, previous experience, motivation levels in previous instructional situations. Another important characteristic is the extent and context of related knowledge and skills that members of the target population already possess. One outcome from these target group analysis activities is a description of the learners‟ characteristics that will facilitate later design considerations such as appropriate contexts, motivational information and activities, materials formatting, and the amount of material to be presented at one time. The second task is to describe the performance context, or environment, where learners will assume their natural roles as students, employees, citizens, or clients and actually use the information and skills prescribed in the instructional goal. Categories of information about the performance site that are important to describe include whether the learner will receive managerial or supervisory support in the performance context, the physical and social aspects of the information and skills to be learned to the performance site. The final task in this section is to describe the learning context. Critical issues in the learning context are discovered through a review of resources that could support instruction and constraint that could inhibit instruction or limit instructional options. Both resources and constraints are usually analyzed in categories such as finances, personnel, time, facilities, equipment, and local culture. In addition, you should describe the compatibility of the learning site with your instructional needs and the learners‟ needs. Finally, you should describe the feasibility of simulating the performance site within the learning site. The closer you can simulate the performance site, the more likely learners will be able to transfer and implement newly acquired skills.
