Earth Science 19 2
- 1. Pressure Centers and winds 19.2
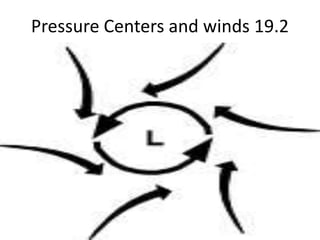
- 2. Cyclone A low pressure center characterized by a counterclockwise flow of air in the Northern Hemisphere.
- 3. Anticyclone A high-pressure center characterized by a clockwise flow of air in the Northern Hemisphere.
- 4. Trade winds Two belts of wind that blow almost constantly from easterly directions and are located on the north and south sides of the subtropical highs.
- 5. Westerlies The dominant west to east motion of the atmosphere that characterizes the regions on the poleward side of the subtropical highs.
- 6. Polar Easterlies In the global pattern of prevailing winds, winds that blow from the polar high toward the subpolar low; These winds, however, should not be thought of as persistent winds, such as the trade winds.
- 7. Polar Front The stormy frontal zone separating cold air masses of polar origin from warm air masses of tropical origin.
- 8. Monsoon Seasonal reversal of wind direction associated with large continents, especially Asia; In the winter, the wind blows from land to sea. In summer, the wind blows sea to land.
- 9. Key Concept Describe how winds blow around pressure centers in the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. In cyclones, the pressure decreases from the outer isobars toward the center. In anticyclones, just the opposite is the case—the values of the isobars increase from the outside toward the center.
- 10. Key Concept What are the air pressure patterns within cyclones and anticyclones? When the pressure gradient and the Coriolis effect are applied to pressure centers in the Northern Hemisphere, winds blow counterclockwise around a low. Around a high, they blow clockwise.
- 11. Key Concept How does friction control net flow of air around a cyclone and an anticyclone? In either hemispheres, friction causes a net flow of air inward around a cyclone and a net flow of air outward around an anticyclone.
- 12. Key Concept How does the atmosphere attempt to balance the unequal heating of Earth’s surface? The atmosphere balances these differences by acting as a giant heat-transfer system. This system moves warm air toward high latitudes and cool air toward the equator.