Earth science 14.2
•Transferir como PPTX, PDF•
2 gostaram•2,308 visualizações
Denunciar
Compartilhar
Denunciar
Compartilhar
Recomendados
Recomendados
Mais conteúdo relacionado
Mais procurados
Mais procurados (20)
Lithostratigraphic units Geology By Misson Choudhury 

Lithostratigraphic units Geology By Misson Choudhury
Structural and Geological Study of a part of the Chitradurga Schist Belt

Structural and Geological Study of a part of the Chitradurga Schist Belt
Microfossils and their Applications in petroleum Industry 

Microfossils and their Applications in petroleum Industry
Destaque (6)
Geological interpretation of a low-backscatter anomaly found on the New Jerse...

Geological interpretation of a low-backscatter anomaly found on the New Jerse...
Semelhante a Earth science 14.2
Semelhante a Earth science 14.2 (20)
Origin and destruction of ocean floor ppt ; ocean floor :evolution of ocean f...

Origin and destruction of ocean floor ppt ; ocean floor :evolution of ocean f...
Mais de Tamara
Mais de Tamara (20)
Último
Último (20)
This PowerPoint helps students to consider the concept of infinity.

This PowerPoint helps students to consider the concept of infinity.
Kodo Millet PPT made by Ghanshyam bairwa college of Agriculture kumher bhara...

Kodo Millet PPT made by Ghanshyam bairwa college of Agriculture kumher bhara...
UGC NET Paper 1 Mathematical Reasoning & Aptitude.pdf

UGC NET Paper 1 Mathematical Reasoning & Aptitude.pdf
General Principles of Intellectual Property: Concepts of Intellectual Proper...

General Principles of Intellectual Property: Concepts of Intellectual Proper...
Mixin Classes in Odoo 17 How to Extend Models Using Mixin Classes

Mixin Classes in Odoo 17 How to Extend Models Using Mixin Classes
Food safety_Challenges food safety laboratories_.pdf

Food safety_Challenges food safety laboratories_.pdf
ICT Role in 21st Century Education & its Challenges.pptx

ICT Role in 21st Century Education & its Challenges.pptx
Unit-IV; Professional Sales Representative (PSR).pptx

Unit-IV; Professional Sales Representative (PSR).pptx
Seal of Good Local Governance (SGLG) 2024Final.pptx

Seal of Good Local Governance (SGLG) 2024Final.pptx
Micro-Scholarship, What it is, How can it help me.pdf

Micro-Scholarship, What it is, How can it help me.pdf
Russian Escort Service in Delhi 11k Hotel Foreigner Russian Call Girls in Delhi

Russian Escort Service in Delhi 11k Hotel Foreigner Russian Call Girls in Delhi
Earth science 14.2
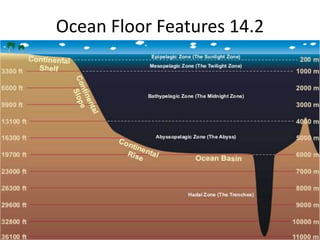
- 1. Ocean Floor Features 14.2
- 2. Continental Margin • That portion of the seafloor adjacent to the continents; it may include the continental shelf, continental slope, and continental rise.
- 3. Continental Shelf • The gently sloping surface at the base of the continental slope.
- 4. Continental Slope • The steep gradient that leads to the deep- ocean floor and marks the seaward edge of the continental shelf.
- 5. Submarine Canyon • A seaward extension of a valley that was cut on the continental shelf during a time when sea level was lower; a canyon carved into the outer continental shelf, slope, and rise by turbidity currents.
- 6. Turbidity Current • A downslope movement of dense, sediment-laden water created when sand and mud on the continental shelf and slope are dislodged and thrown into suspension.
- 7. Continental Rise • The gently sloping surface at the base of the continental slope.
- 8. Ocean Basin Floor • Area of the deep-ocean floor between the continental margin and the oceanic ridge.
- 9. Abyssal Plains • Very level area of the deep-ocean floor, usually lying at the foot of the continental rise.
- 10. Seamounts • An isolated volcanic peak that rises at least 1000 meters above the deep-ocean floor.
- 11. Mid-Ocean Ridge • A continuous elevated zone on the floor of all the major ocean basins and varying in width from 1000 to 4000 kilometers.
- 12. Seafloor Spreading • The process by which plate tectonics produces new oceanic lithosphere at ocean ridges.
- 13. Key Concept • What are the three main regions of the ocean floor? –The floor regions are: continental margins, ocean basin floor, and mid- ocean ridge.
- 14. Key Concept • How do continental margins in the Atlantic Ocean differ from those in the Pacific Ocean? –The Atlantic Ocean has thick layers of undisturbed sediment cover with very little volcanic or earthquake activity. –The Pacific Ocean crust is plunging beneath continental crust and experiences both volcanic and earthquake activity.
- 15. Key Concept • How are deep-ocean trenches formed? –Trenches are formed at sites of plate convergence where one moving plate descends beneath another and plunges back into the mantle.
- 16. Key Concept • How are abyssal plains formed? –The sediments that make up abyssal plains are carried there by turbidity currents or deposited as a result of suspended sediments settling.
- 17. Key Concept • What is formed at mid-ocean ridges? –New ocean floor is formed at mid- ocean ridges as magma rises between the diverging plates and cools.