Freebodydigram
•Transferir como PPT, PDF•
11 gostaram•3,948 visualizações
mechanics
Denunciar
Compartilhar
Denunciar
Compartilhar
Recomendados
Recomendados
This document gives the class notes of Unit 5 shear force and bending moment in beams. Subject: Mechanics of materials.
Syllabus contest is as per VTU, Belagavi, India.
Notes Compiled By: Hareesha N Gowda, Assistant Professor, DSCE, Bengaluru-78.Unit 5 shear force and bending moment in beams

Unit 5 shear force and bending moment in beamsHareesha N Gowda, Dayananda Sagar College of Engg, Bangalore
Mais conteúdo relacionado
Mais procurados
This document gives the class notes of Unit 5 shear force and bending moment in beams. Subject: Mechanics of materials.
Syllabus contest is as per VTU, Belagavi, India.
Notes Compiled By: Hareesha N Gowda, Assistant Professor, DSCE, Bengaluru-78.Unit 5 shear force and bending moment in beams

Unit 5 shear force and bending moment in beamsHareesha N Gowda, Dayananda Sagar College of Engg, Bangalore
Mais procurados (20)
Chapter 6-influence lines for statically determinate structures

Chapter 6-influence lines for statically determinate structures
wind load and its types also calculations of wind load and example ..... 

wind load and its types also calculations of wind load and example .....
Destaque
Destaque (20)
Causes of settlement, foundation loading and computation

Causes of settlement, foundation loading and computation
Introduction of system of coplanar forces (engineering mechanics)

Introduction of system of coplanar forces (engineering mechanics)
Semelhante a Freebodydigram
Semelhante a Freebodydigram (20)
Engineering Mechanics Chapter 5 Equilibrium of a Rigid Body

Engineering Mechanics Chapter 5 Equilibrium of a Rigid Body
2-Analysis of Statically Determinate Structures.pdf

2-Analysis of Statically Determinate Structures.pdf
Forces acting on the beam with shear force & bending moment

Forces acting on the beam with shear force & bending moment
Basic mechanical engineering (BMET-101/102) unit 5 part-1 simple stress and ...

Basic mechanical engineering (BMET-101/102) unit 5 part-1 simple stress and ...
Último
Model Call Girl Services in Delhi reach out to us at 🔝 9953056974 🔝✔️✔️
Our agency presents a selection of young, charming call girls available for bookings at Oyo Hotels. Experience high-class escort services at pocket-friendly rates, with our female escorts exuding both beauty and a delightful personality, ready to meet your desires. Whether it's Housewives, College girls, Russian girls, Muslim girls, or any other preference, we offer a diverse range of options to cater to your tastes.
We provide both in-call and out-call services for your convenience. Our in-call location in Delhi ensures cleanliness, hygiene, and 100% safety, while our out-call services offer doorstep delivery for added ease.
We value your time and money, hence we kindly request pic collectors, time-passers, and bargain hunters to refrain from contacting us.
Our services feature various packages at competitive rates:
One shot: ₹2000/in-call, ₹5000/out-call
Two shots with one girl: ₹3500/in-call, ₹6000/out-call
Body to body massage with sex: ₹3000/in-call
Full night for one person: ₹7000/in-call, ₹10000/out-call
Full night for more than 1 person: Contact us at 🔝 9953056974 🔝. for details
Operating 24/7, we serve various locations in Delhi, including Green Park, Lajpat Nagar, Saket, and Hauz Khas near metro stations.
For premium call girl services in Delhi 🔝 9953056974 🔝. Thank you for considering us!Call Now ≽ 9953056974 ≼🔝 Call Girls In New Ashok Nagar ≼🔝 Delhi door step de...

Call Now ≽ 9953056974 ≼🔝 Call Girls In New Ashok Nagar ≼🔝 Delhi door step de...9953056974 Low Rate Call Girls In Saket, Delhi NCR
Process of Integration the Laser Scan Data into FEA Model and Level 3 Fitness-for-Service Assessment of Critical Assets in Refinery & Process IndustriesFEA Based Level 3 Assessment of Deformed Tanks with Fluid Induced Loads

FEA Based Level 3 Assessment of Deformed Tanks with Fluid Induced LoadsArindam Chakraborty, Ph.D., P.E. (CA, TX)
Call Girl Meerut Indira Call Now: 8617697112 Meerut Escorts Booking Contact Details WhatsApp Chat: +91-8617697112 Meerut Escort Service includes providing maximum physical satisfaction to their clients as well as engaging conversation that keeps your time enjoyable and entertaining. Plus they look fabulously elegant; making an impressionable. Independent Escorts Meerut understands the value of confidentiality and discretion - they will go the extra mile to meet your needs. Simply contact them via text messaging or through their online profiles; they'd be more than delighted to accommodate any request or arrange a romantic date or fun-filled night together. We provide –(INDIRA) Call Girl Meerut Call Now 8617697112 Meerut Escorts 24x7

(INDIRA) Call Girl Meerut Call Now 8617697112 Meerut Escorts 24x7Call Girls in Nagpur High Profile Call Girls
Booking open Available Pune Call Girls Koregaon Park 6297143586 Call Hot Indian Girls Waiting For You To Fuck
Booking Contact Details
WhatsApp Chat: +91-6297143586
pune Escort Service includes providing maximum physical satisfaction to their clients as well as engaging conversation that keeps your time enjoyable and entertaining. Plus they look fabulously elegant; making an impressionable.
Independent Escorts pune understands the value of confidentiality and discretion - they will go the extra mile to meet your needs. Simply contact them via text messaging or through their online profiles; they'd be more than delighted to accommodate any request or arrange a romantic date or fun-filled night together.
We provide -
01-may-2024(v.n)
Booking open Available Pune Call Girls Koregaon Park 6297143586 Call Hot Ind...

Booking open Available Pune Call Girls Koregaon Park 6297143586 Call Hot Ind...Call Girls in Nagpur High Profile
Último (20)
FULL ENJOY Call Girls In Mahipalpur Delhi Contact Us 8377877756

FULL ENJOY Call Girls In Mahipalpur Delhi Contact Us 8377877756
Call Now ≽ 9953056974 ≼🔝 Call Girls In New Ashok Nagar ≼🔝 Delhi door step de...

Call Now ≽ 9953056974 ≼🔝 Call Girls In New Ashok Nagar ≼🔝 Delhi door step de...
FEA Based Level 3 Assessment of Deformed Tanks with Fluid Induced Loads

FEA Based Level 3 Assessment of Deformed Tanks with Fluid Induced Loads
Call Girls Walvekar Nagar Call Me 7737669865 Budget Friendly No Advance Booking

Call Girls Walvekar Nagar Call Me 7737669865 Budget Friendly No Advance Booking
(INDIRA) Call Girl Meerut Call Now 8617697112 Meerut Escorts 24x7

(INDIRA) Call Girl Meerut Call Now 8617697112 Meerut Escorts 24x7
CCS335 _ Neural Networks and Deep Learning Laboratory_Lab Complete Record

CCS335 _ Neural Networks and Deep Learning Laboratory_Lab Complete Record
Call Girls In Bangalore ☎ 7737669865 🥵 Book Your One night Stand

Call Girls In Bangalore ☎ 7737669865 🥵 Book Your One night Stand
Block diagram reduction techniques in control systems.ppt

Block diagram reduction techniques in control systems.ppt
Booking open Available Pune Call Girls Koregaon Park 6297143586 Call Hot Ind...

Booking open Available Pune Call Girls Koregaon Park 6297143586 Call Hot Ind...
Cara Menggugurkan Sperma Yang Masuk Rahim Biyar Tidak Hamil

Cara Menggugurkan Sperma Yang Masuk Rahim Biyar Tidak Hamil
Freebodydigram
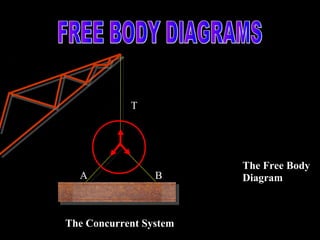
- 1. T A B The Concurrent System The Free Body Diagram
- 2. Concept of Free Body Diagrams Particle System Rigid Body Systems Concept of Equilibrant Graphical Determination of Equilibrant Applied and Reaction Forces in Beams Types of Beam Supports Free Body diagram of Rigid Bodies
- 3. Free Body Diagrams • Essential step in solving Equilibrium problems •Complex Structural systems reduced into concise FORCE systems WHAT IS A FREE BODY DIAGRAM? A FBD is a simplified representation of a PARTICLE or RIGID BODY that is isolated from its surroundings and on which all applied forces and reactions are shown. All forces acting on a particle original body must be considered, and equally important any force not directly applied on the body must be excluded.
- 5. Draw the Free Body Diagrams
- 6. REAL LIFE CONCURRENT SYSTEMS Equilibrium of a Particle
- 9. 1. Two cables support the traffic light weighing 250 pounds. Determine the tension in the cables AB and BC. • Solution: • Resolving T1 along x and y directions: • Resolving T2 along x and y directions: • . °20 °30A B °20 °30 200lb A C B T1 T2 T1 T2 T1Y T2Y T1X T2X T3=200lb 12 21 21 21 085.1 866.0*9396.0* 30cos20cos 0 TT TT TT TTFR XXxx = = °=° =+== ∑ 2005.0342.0 20030sin20sin 0200 21 21 21 =+ =°+° =−+== ∑ TT TT TTFR yyyy 1
- 10. • Substituting equation 1 in the above equation, we get .342T1+.5425T2=200 .8845T1=200 T1=226lb • From equation 1 we get T2=1.085*226 T2= 245.56lb Answers: Tension in cable AB = 226lb Tension in cable BC = 245.56lb
- 12. 400# F1 F2 300N 450N F1 X Y X X X Y Y Y 30=θ 60=θ F 3 kN 7 kN 4.5 kN 7.5 kN 2.25 kN F 60=θ 30=θ P P PP 1 2 3 4 θ θ θ 20=θ 4 3 12 5 3
- 13. CONCEPT OF THE EQUIBILIRIANT Resultant 1F 2F R E Equilibrant
- 14. ASimple Supported Beam A Cantilever Beam RIGID BODY SYSTEMS
- 15. A Propped Cantilever with Three Concentrated Load A Simply Supported Beam with Three concentrated Loads
- 16. APPLIED AND REACTION FORCES IN BEAMS In the Chapter on Force Systems, we discussed the concept of APPLIED FORCES, REACTION FORCES and INTERNAL FORCES Here we well discuss the relevance and importance of APPLIED FORCES and REACTION FORCES in the case of Beams. Before we proceed further please study the animated visuals on the next slide
- 17. APPLIED FORCES AND REACTION FORCES ON RIGID BODY SYSTEMS A Foundation resting on Soil, with APPLIED FORCES and REACTION FORCES A Simple Supported Beams with APPLIED FORCES and REACTION FORCES A Cantilever Beam with APPLIED FORCES and REACTION FORCES
- 18. A Beam is an example of Rigid Body. Generally loads are applied on the beams. And the beams develop reactions. We named the loads hat are applied on the beams like Dead Load, Live Load, Wind Load. Earthquake Loads as APPLIED FORCES, and the consequent reactions that are simultaneously developed as REACTION FORCES. These REACTION FORCES generally develop at the supports. We use the same color code as described earlier for clarity. The reactions develop as a direct consequence of Newton’s Third Law,. Which states that for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. In the three examples presented, if we separate the rigid body for its supports we can see equal and opposite forces acting at the supports..
- 19. From the above we can describe the concept of the FREE BODY DIAGRAM of a Rigid Body as folows. It is representing the rigid body with all the Forces- the APPLIED FORCES and REACTION FORCES acting on it It is axiomatic that the Rigid Body must be in equilibrium under the action of the APPLIED FORCES and the REACTION FORCES. Hence the FREE BODY DIAGRAMS can also be called as EQUILIBRIUM DIAGRAMS, even though the former name is more popular. Finding the REACTION of beams for various types of APPLIED LOADS is a basic requirement in STATICS
- 20. The above diagrams, which show the complete system of applied and reactive forces acting on a body, are called free body diagrams. The whole system of applied and reactive forces acting on a body must be in a state of equilibrium. Free-body diagrams are, consequently ,often called equilibrium diagrams. Drawing equilibrium diagrams and finding reactions for loaded structural members is a common first step in a complete structural analysis
- 21. Roller, Hinge and Fixed Supports Hinge supports Roller Supports Fixed Supports
- 22. ROLLER SUPPORT Applied Force Reactive Forces The Reactive Force must always be perpendicular to the surface for a ROLLER
- 23. Roller Support Roller Support allows horizontal movement It allows the beam to bend
- 24. Rocker Support A Rocker Support is similar to the Roller Support
- 25. A variation of Roller Support
- 26. PIN or HINGE SUPPORT Applied Force Reactive Force The Reactive Force can be in any direction
- 27. Pin or Hinge Support Pin support does no allow any movement It allows the beam to bend
- 28. FIXED SUPPORT No movement No Rotation
- 29. Half the strength of the Bridge is lost by not allowing the Bridge to expand due to the Temperature Rise Why Roller Support is Important? 500 ft. 2.34” T= 100 degT= 40 deg
- 30. Why Hinge Support is Important ?
- 31. Why Fixed Support is Important? A Cantilever has to be fixed to support a load Hinge
- 32. REAL LIFE HINGES A Steel Hinge A Concrete Hinge A Neoprene Pad Hinge The shear deformation of the Neoprene pad mimics the horizontal movement of a Roller The close confinement of the steel rods will not allow moment transfer, but only Vertical & Horizontal Forces Top part Bottom part Pin The rotation of the top part about the pin allows a Hinge action
- 33. Question 1. What is the difference between a Rigid Body and a Particle Question 2: Explain the Difference between a Roller Support, Hinge Support and Fixed Support
- 34. FREE BODY DIAGRAMS OF RIGID SYSTEMS
- 37. Free Body Diagrams 1. Try to draw the free body diagram for a axle of a bicycle wheel as shown below: 2. Draw the free body diagram for a propped cantilever shown below: 3. Does a Neoprene pad bearing function like a Hinge or a Roller. 4. Attempt to draw the Free body diagram for the circled part of the building P Axle
- 38. 5. Draw the Free Body Diagram for the following Dam: Water
