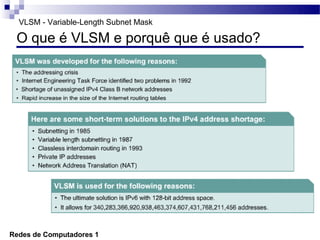
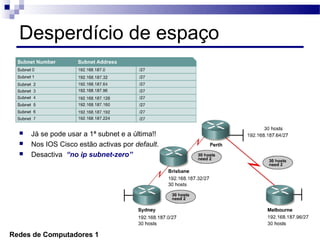
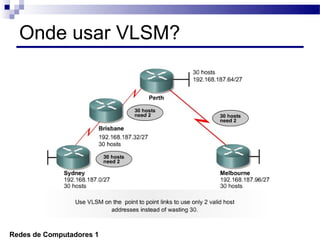
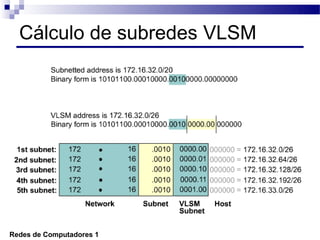
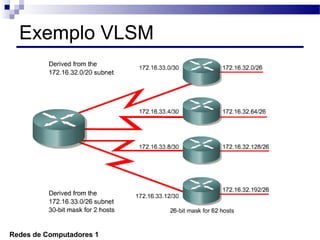
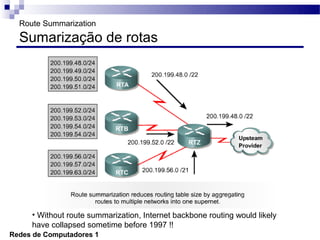
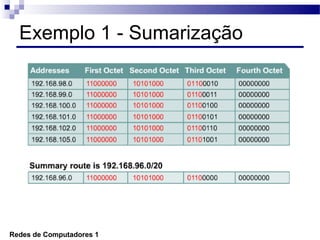
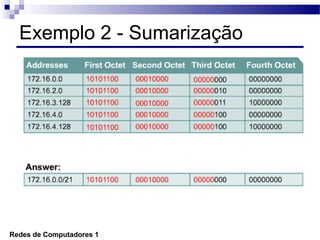
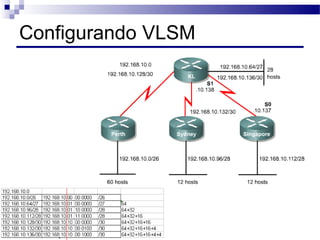
O documento discute conceitos de protocolos de encaminhamento nas redes de computadores, incluindo a agregação de rotas e a sumarização usando VLSM (Variable-Length Subnet Mask). VLSM é utilizado para otimizar o uso de espaço de endereçamento ao permitir a utilização de subredes de tamanhos diferentes. A agregação de rotas é crucial para reduzir o tamanho da tabela de encaminhamento e garantir a eficiência do roteamento.