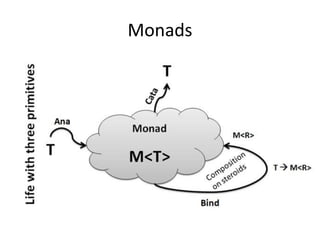
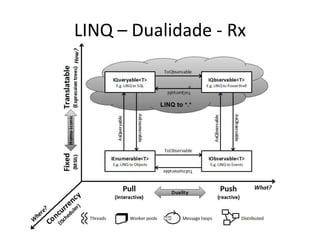
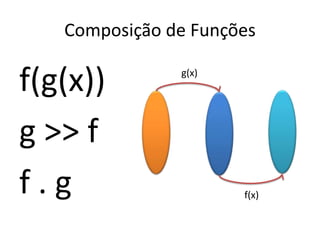
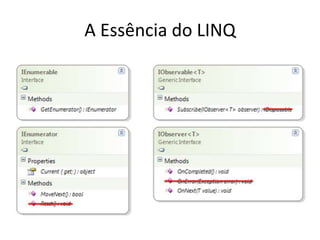
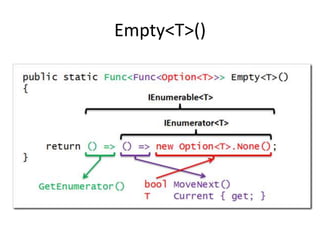
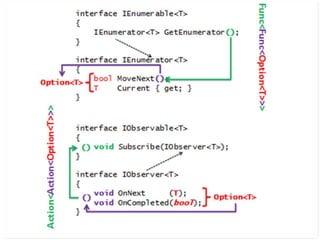
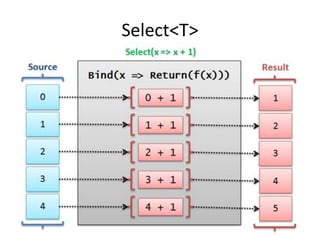
Este documento apresenta uma palestra sobre programação funcional em F#. Apresenta conceitos como composição, imutabilidade, funções de alta ordem, monads e como o LINQ pode ser entendido como uma aplicação desses conceitos funcionais. O palestrante é Rodrigo Vidal, especialista em F# e computação científica.

















![Functors
class Functor f where
fmap :: (a -> b) -> f a -> f b
instance Functor Maybe where
fmap f (Just x) = Just (f x)
fmap f (Nothing ) = Nothing
fmap (*2) [1..3]
> [2,4,6]
fmap (*2) Just 5
> Just 10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/monadicdesign-120604154855-phpapp01/85/Monadic-Design-25-320.jpg)

![Applicative Functors
class (Functor f) => Applicative f where
pure :: a -> f a
(<*>) :: f (a -> b) -> f a -> f b
let a = fmap (*) [1,2,3,4]
a :: [Integer -> Integer]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/monadicdesign-120604154855-phpapp01/85/Monadic-Design-27-320.jpg)

![Monoids
class Monoid m where
mempty :: m
mappend :: m -> m -> m
mconcat :: [m] -> m
mconcat = foldr mappend mempty](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/monadicdesign-120604154855-phpapp01/85/Monadic-Design-29-320.jpg)
![Monoids Pattern
• 1+1
• 2*2
• [1,2,3] ++ [4,5,6]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/monadicdesign-120604154855-phpapp01/85/Monadic-Design-30-320.jpg)