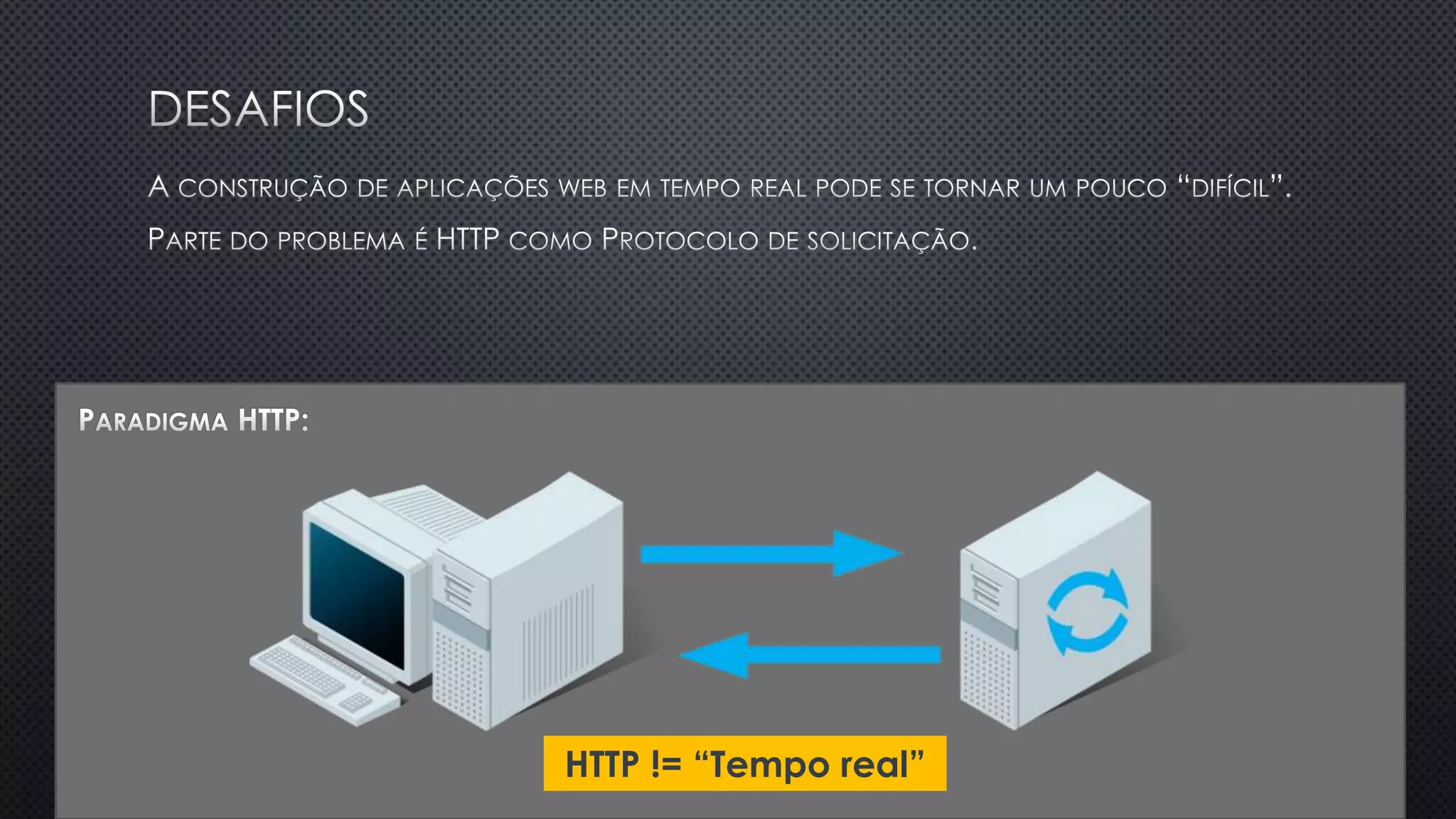
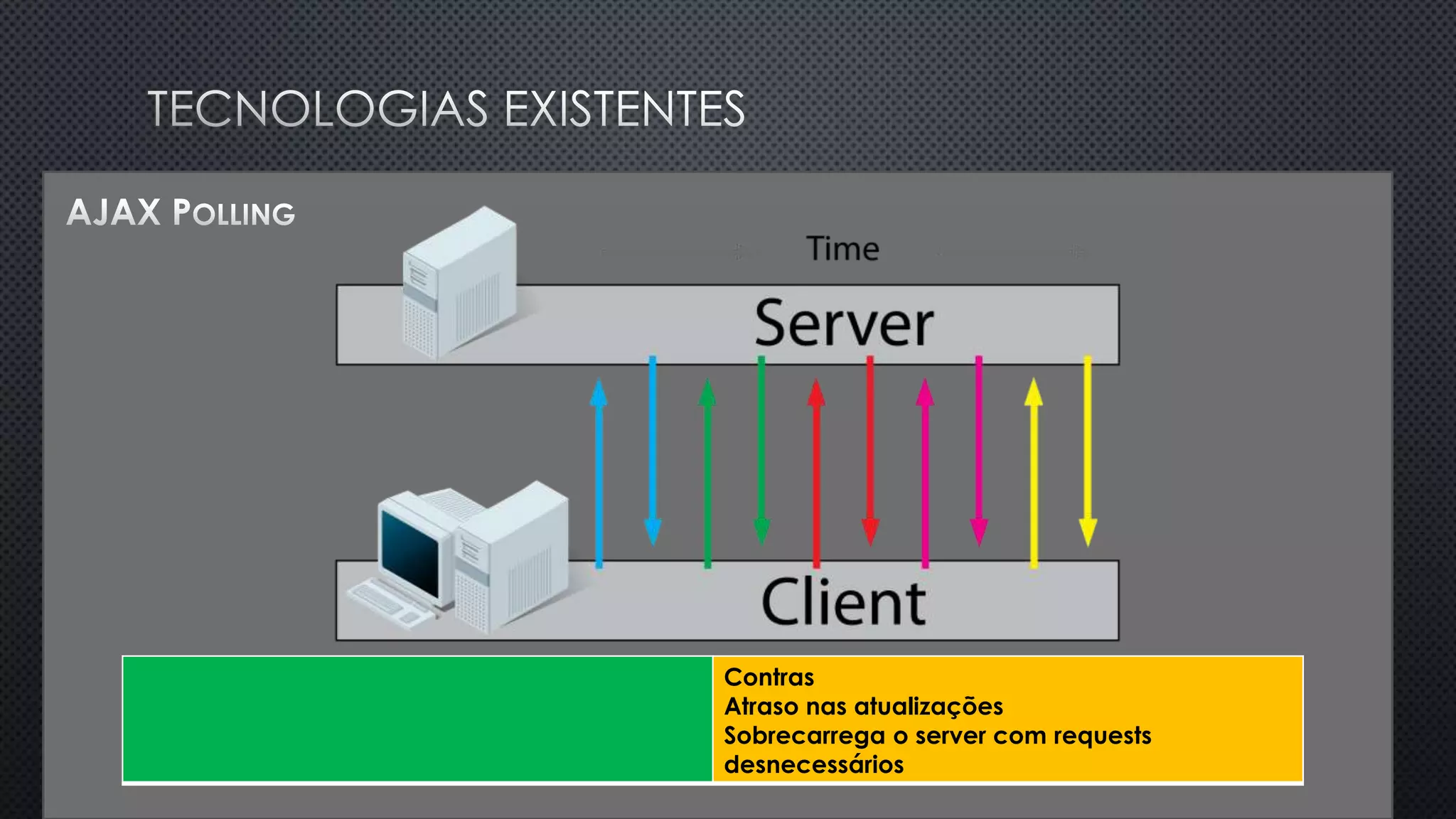
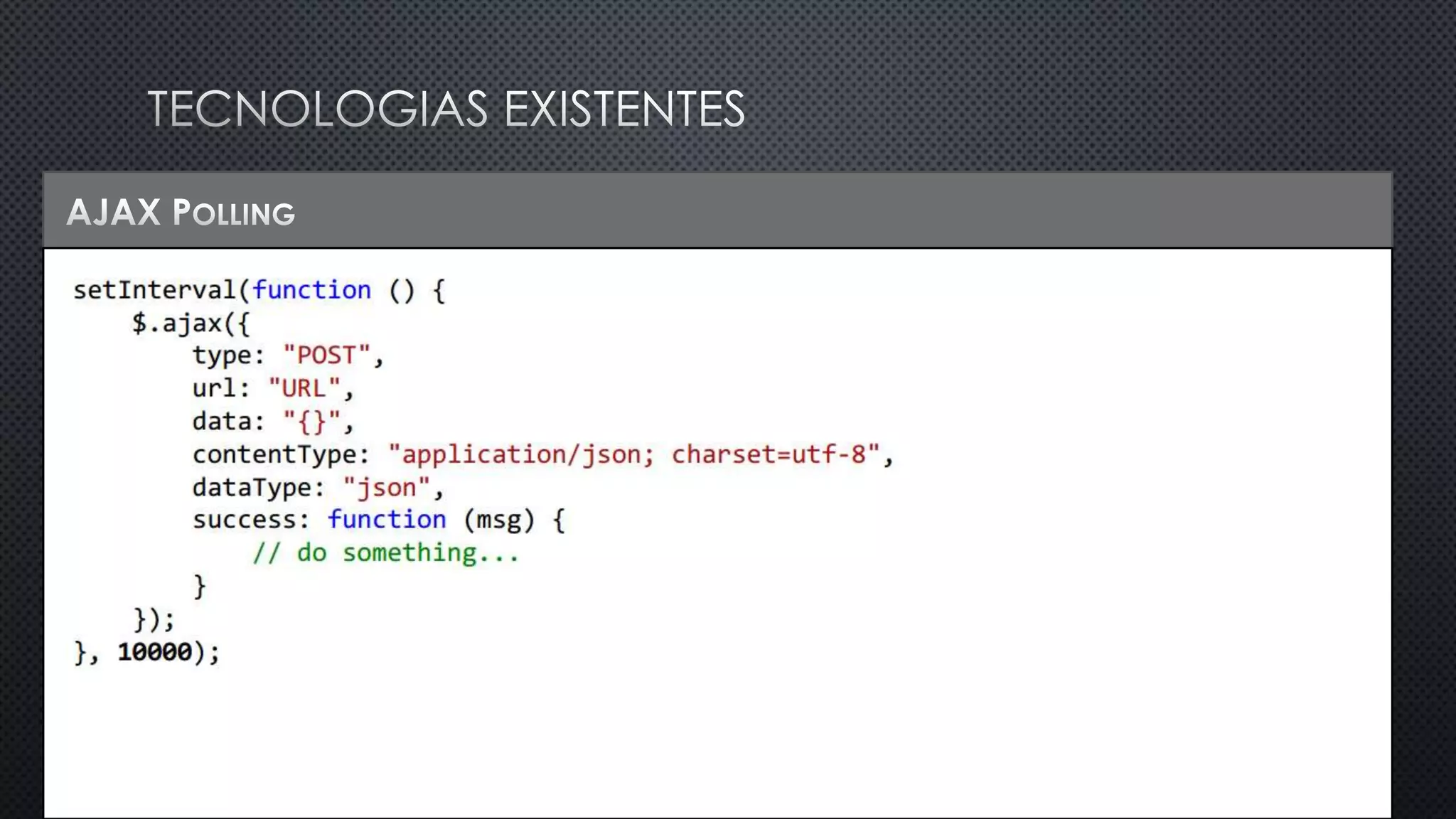
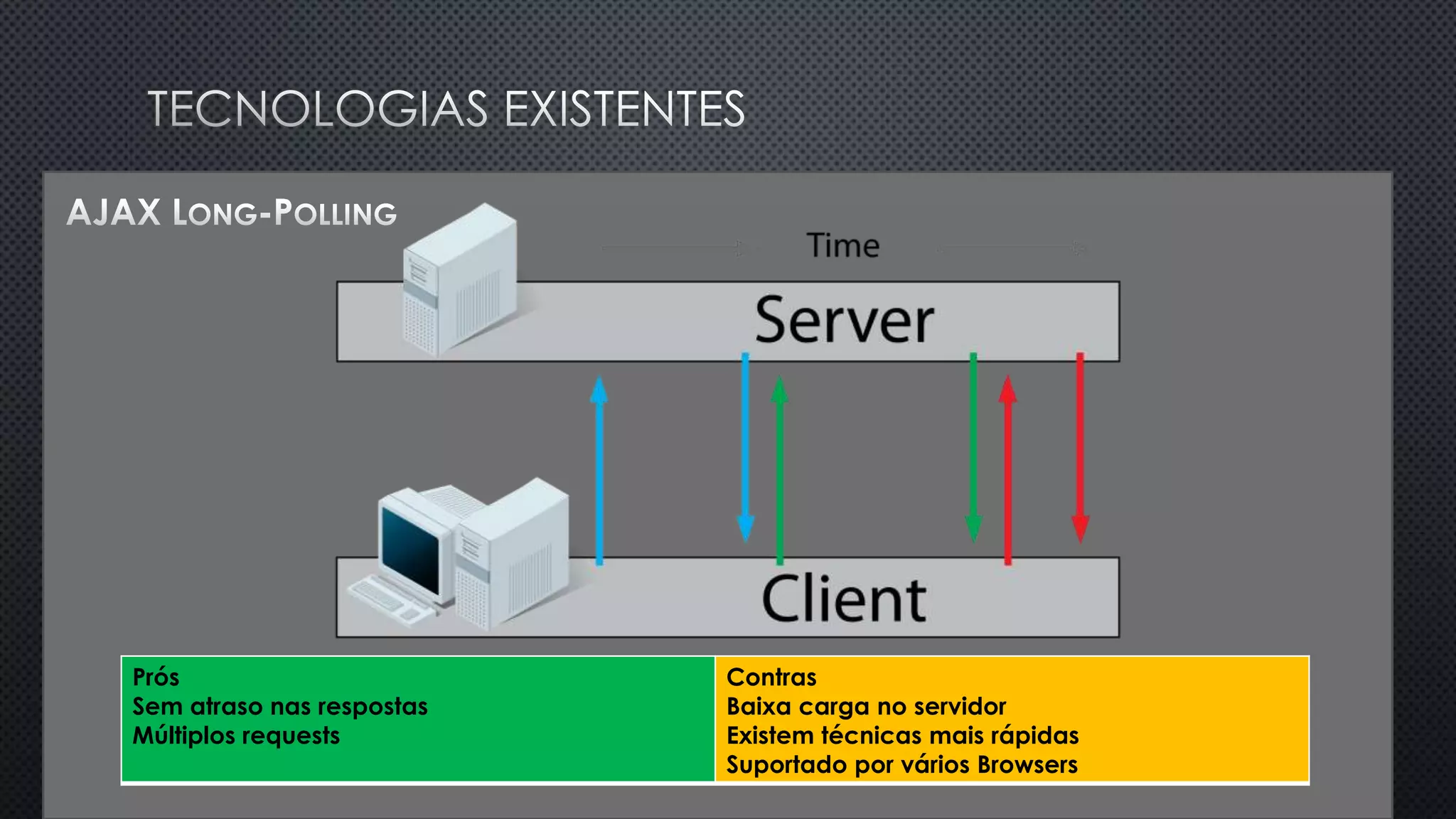
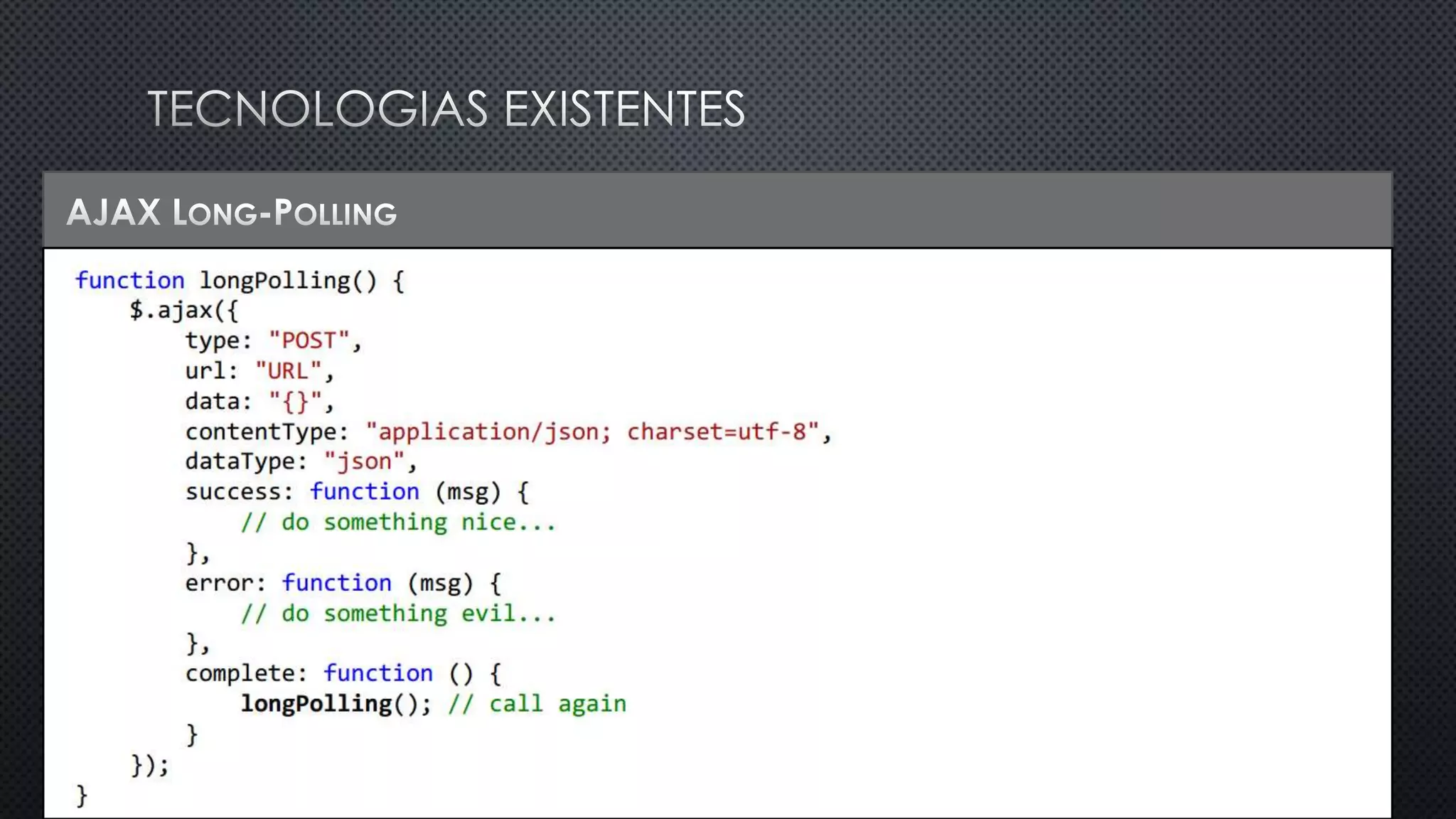
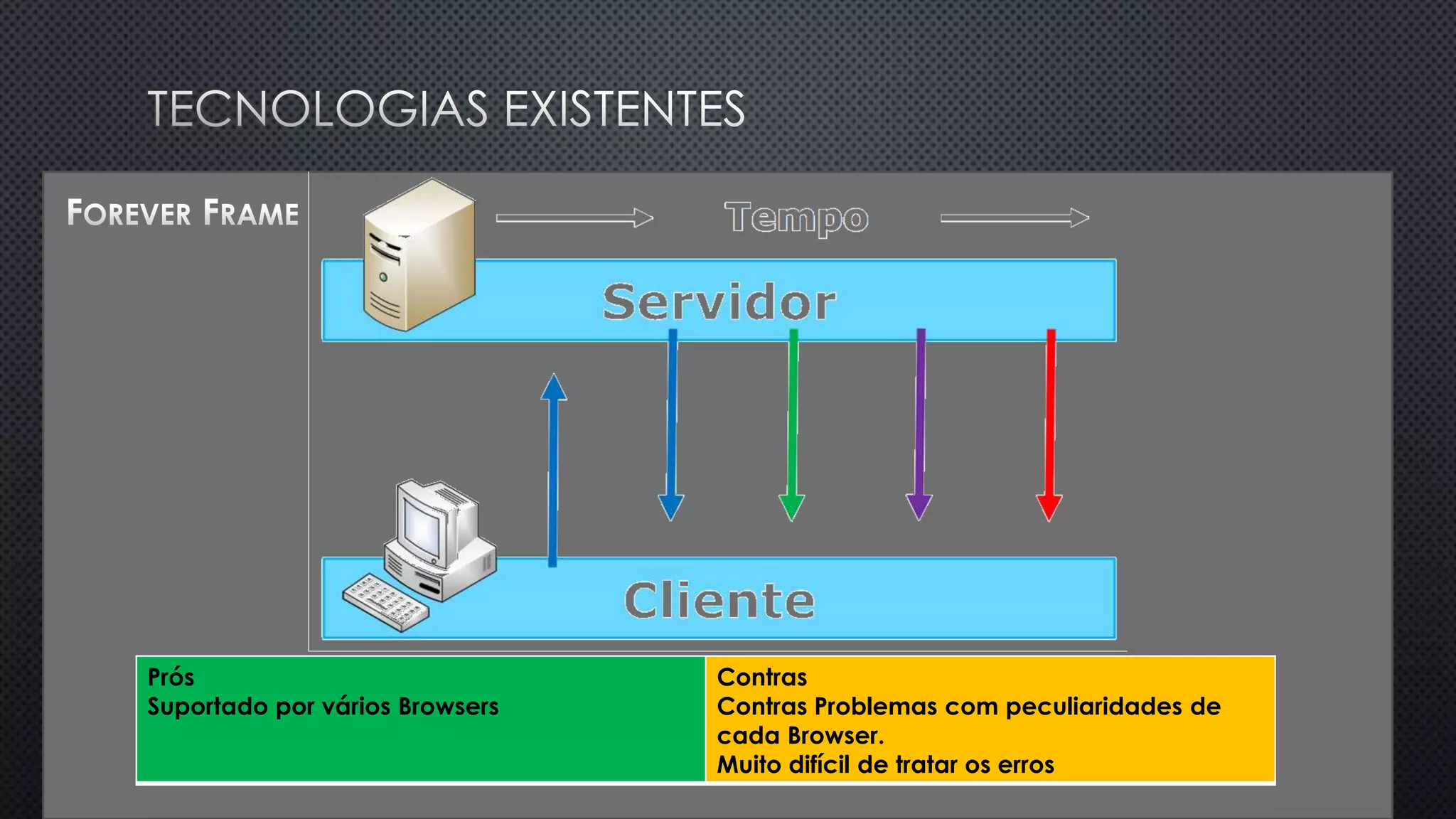
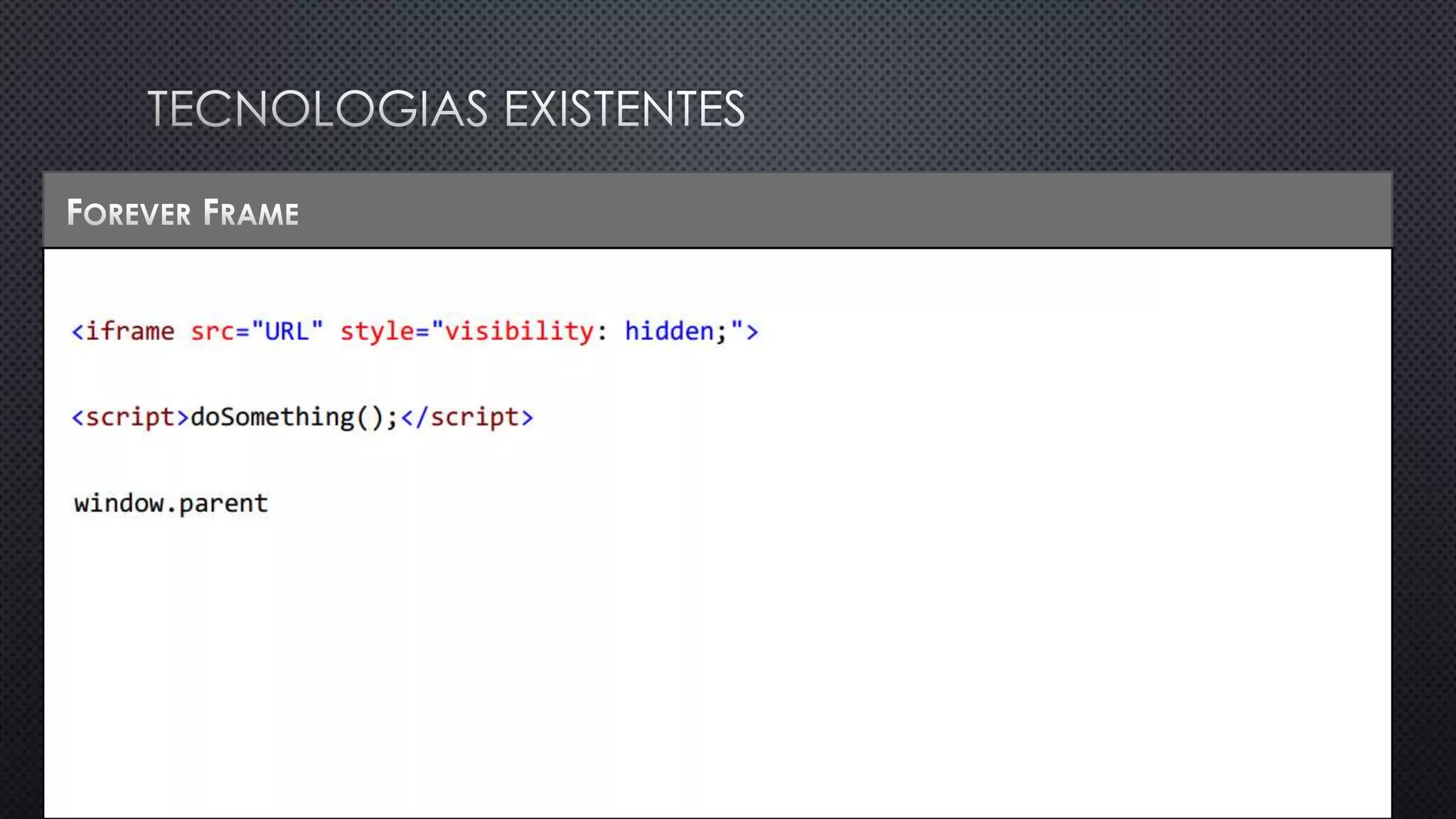
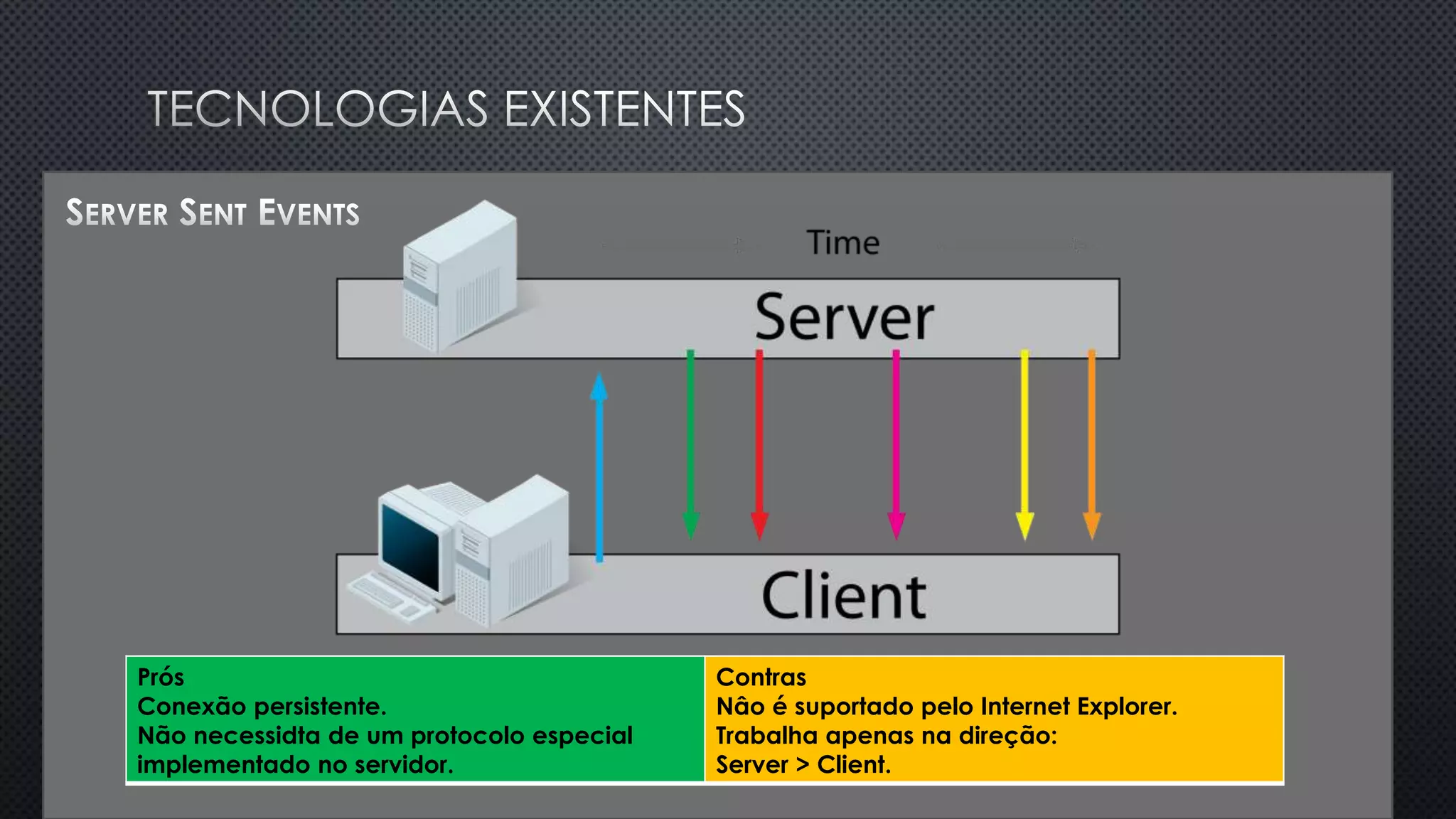
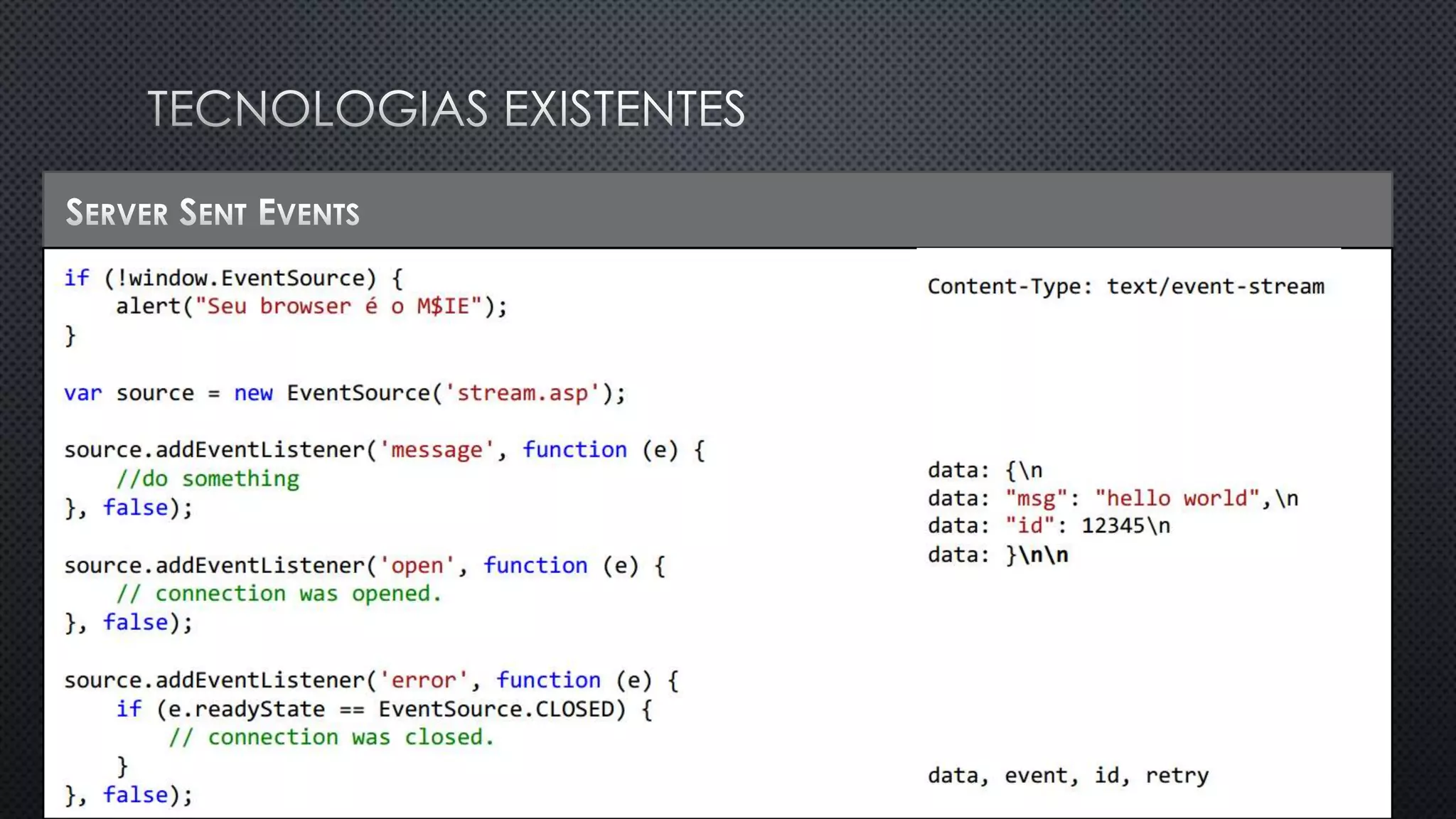
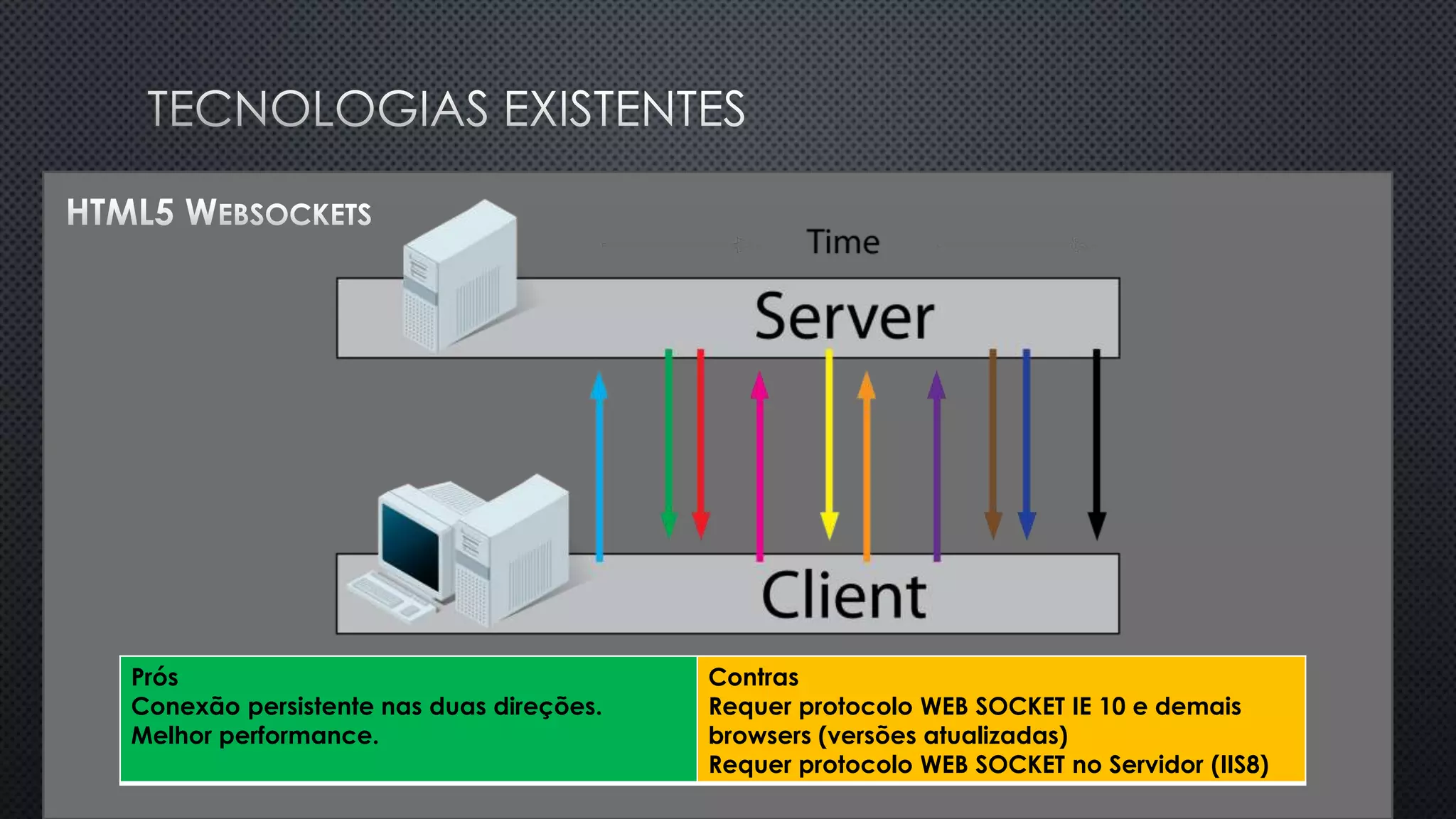
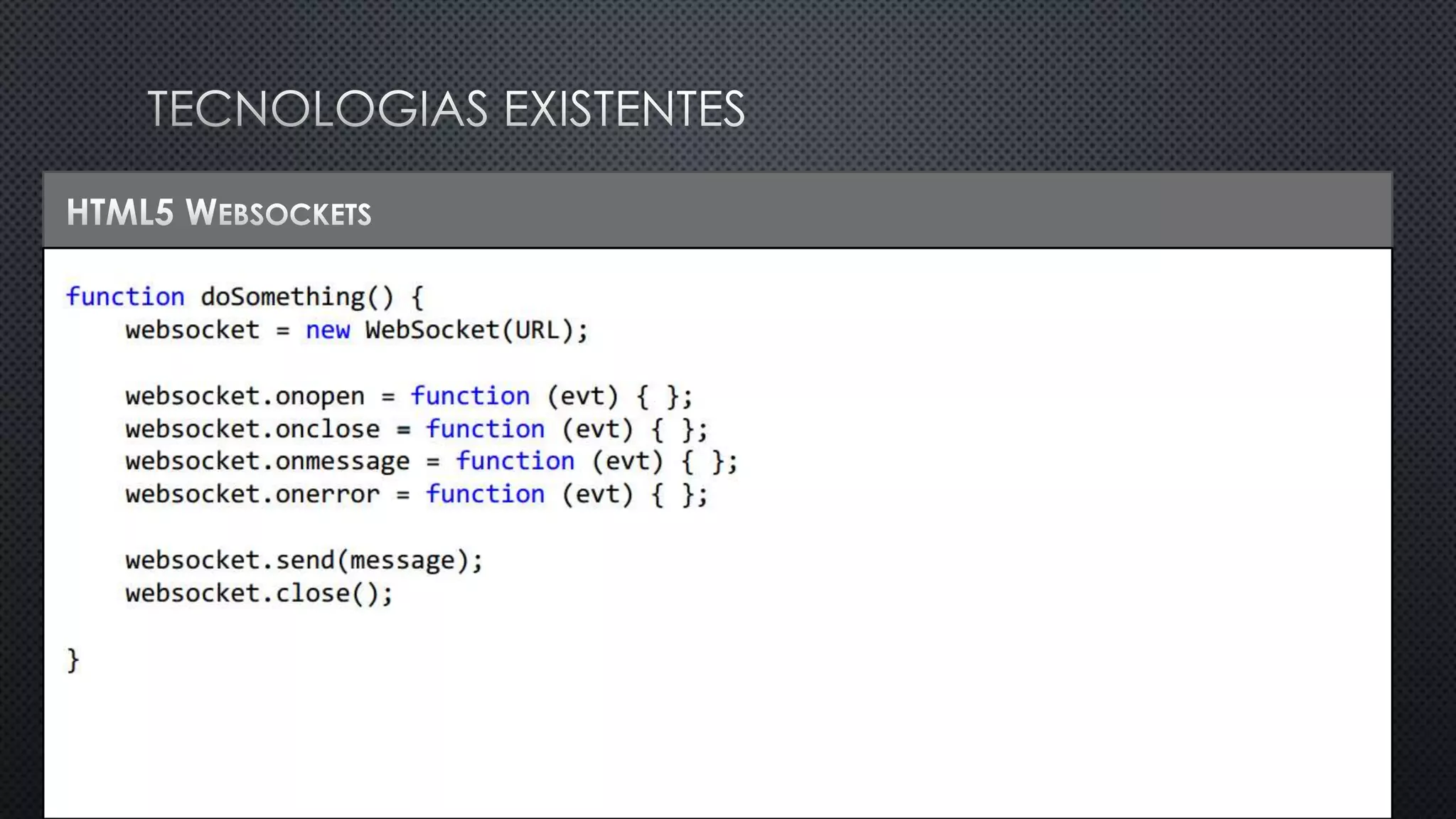
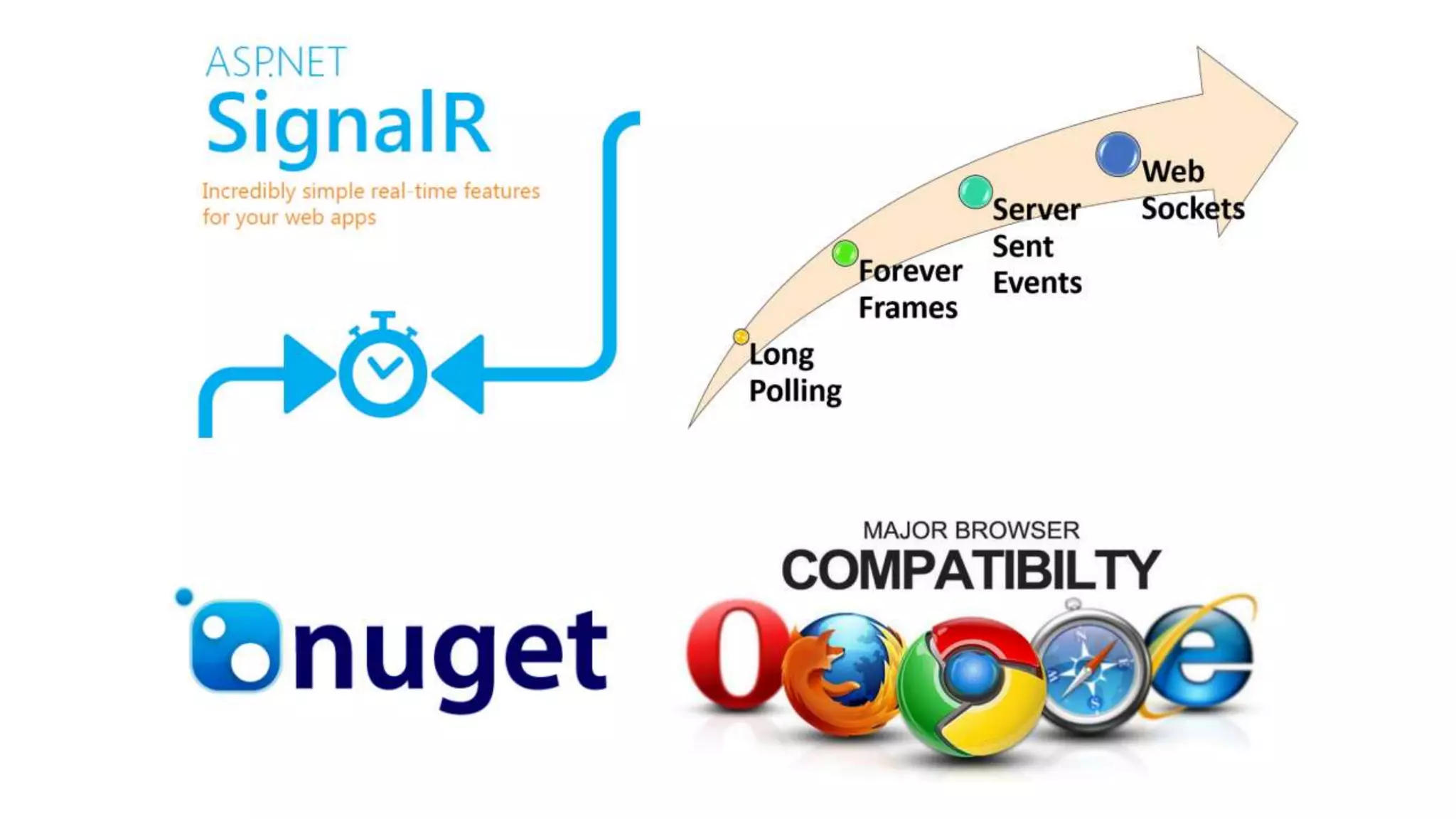
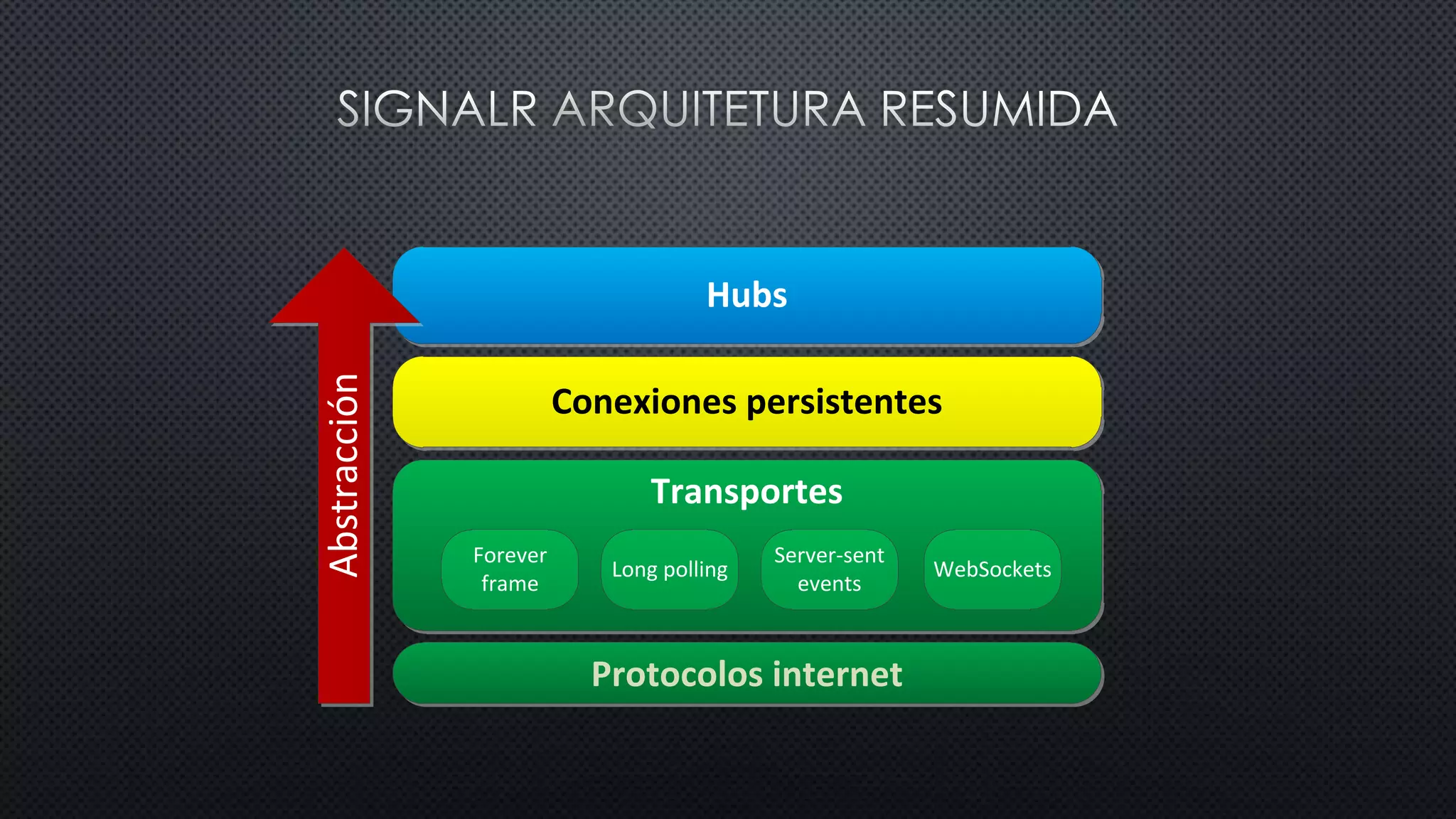
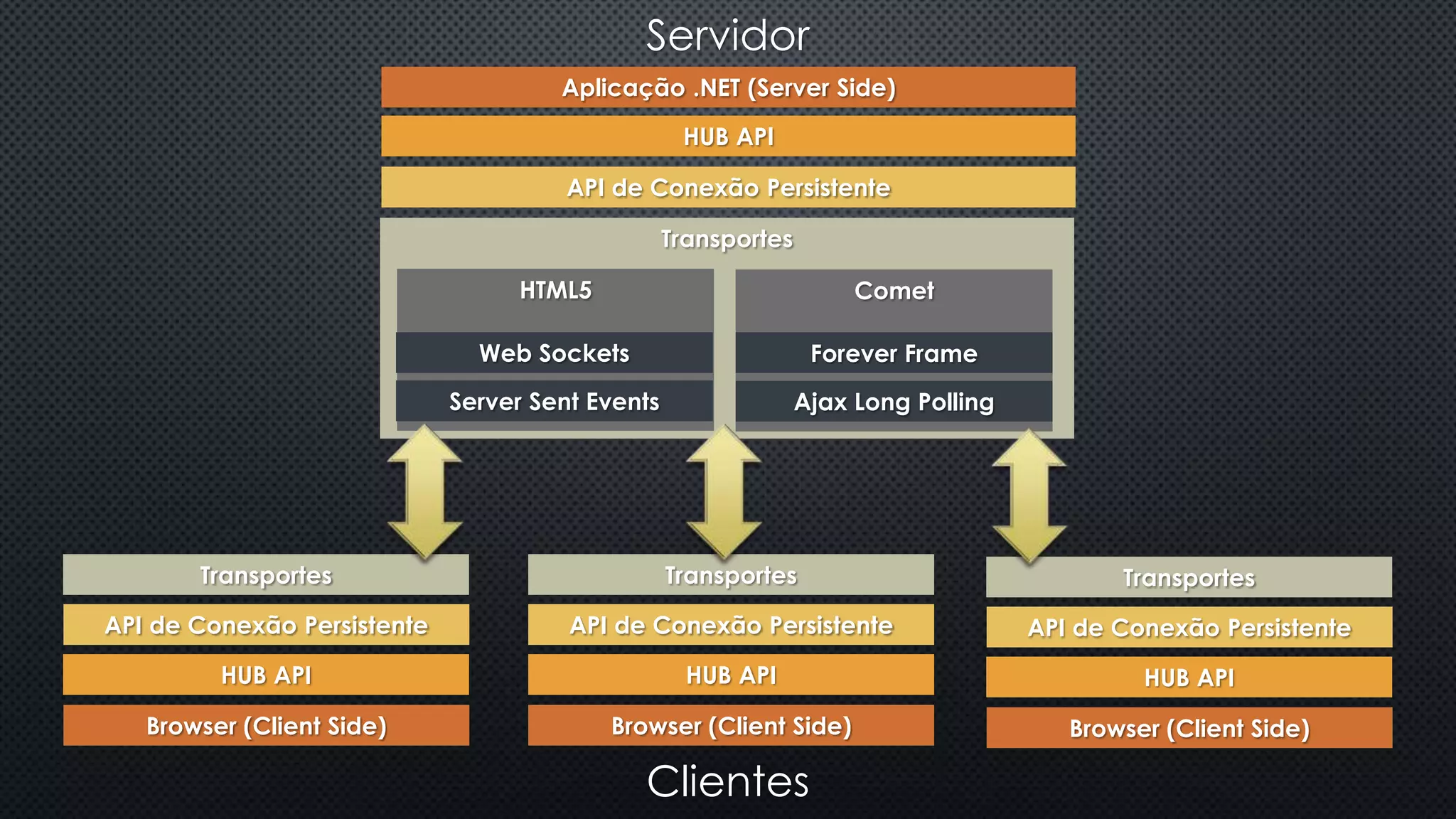
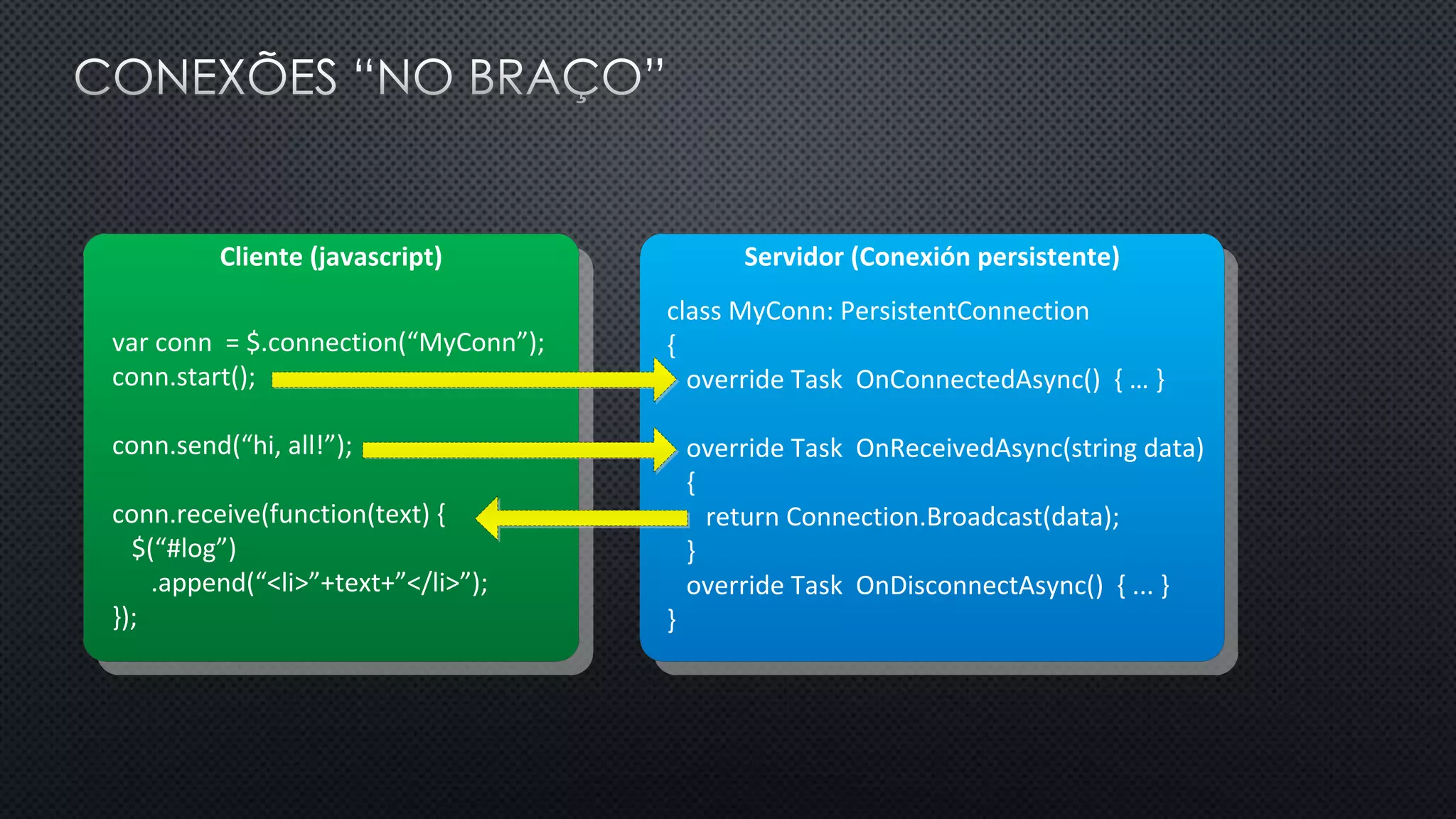
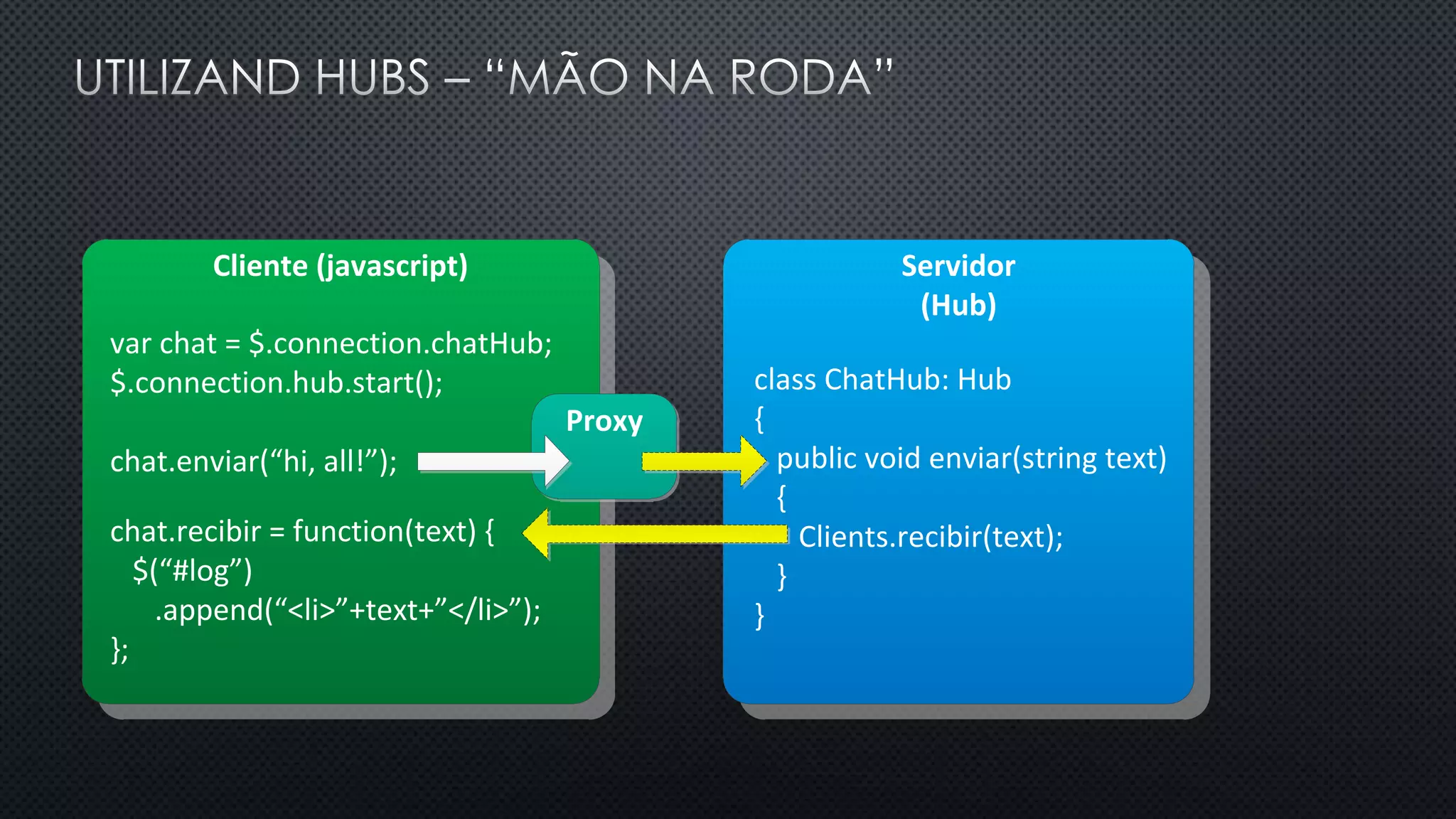
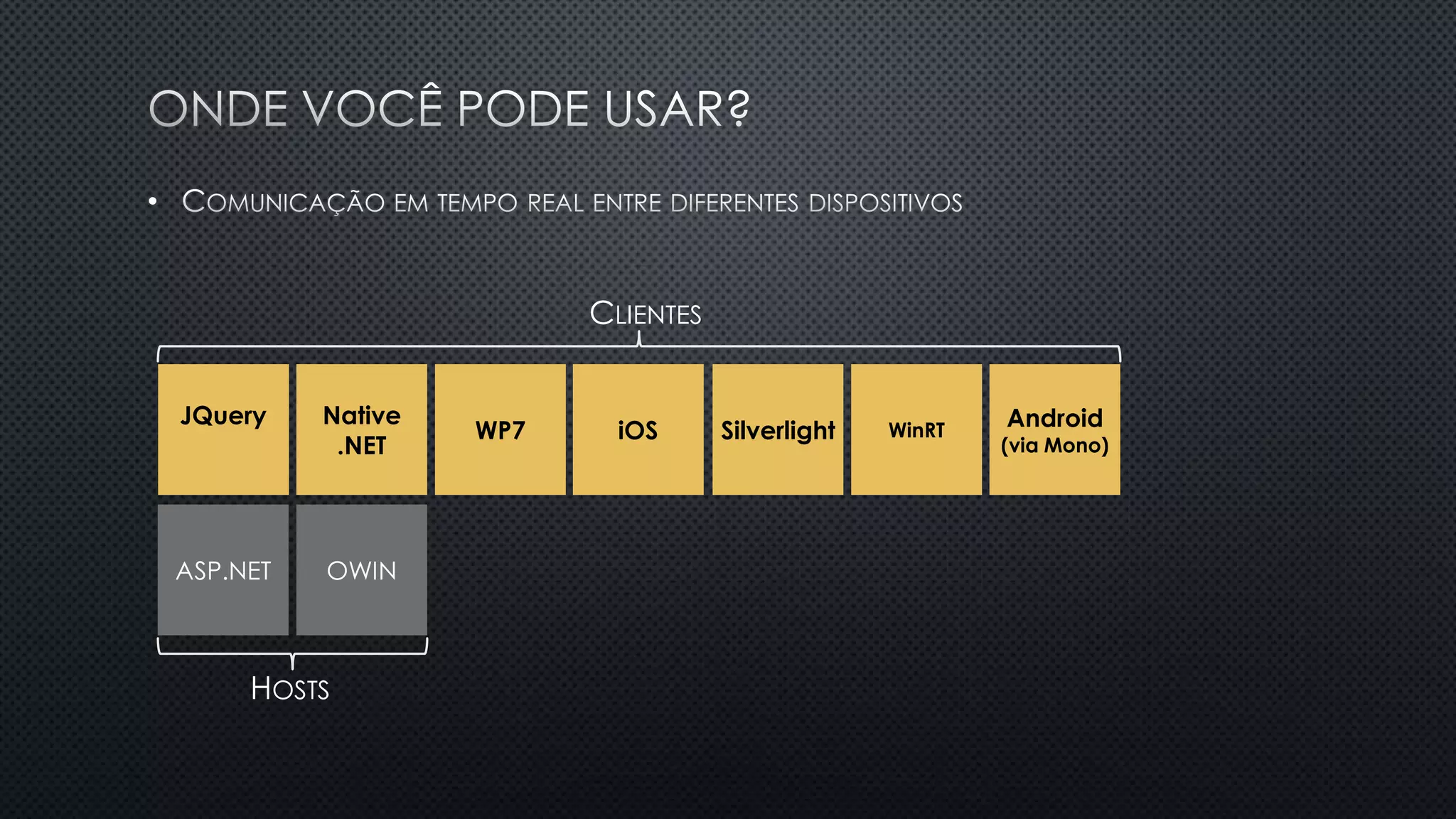
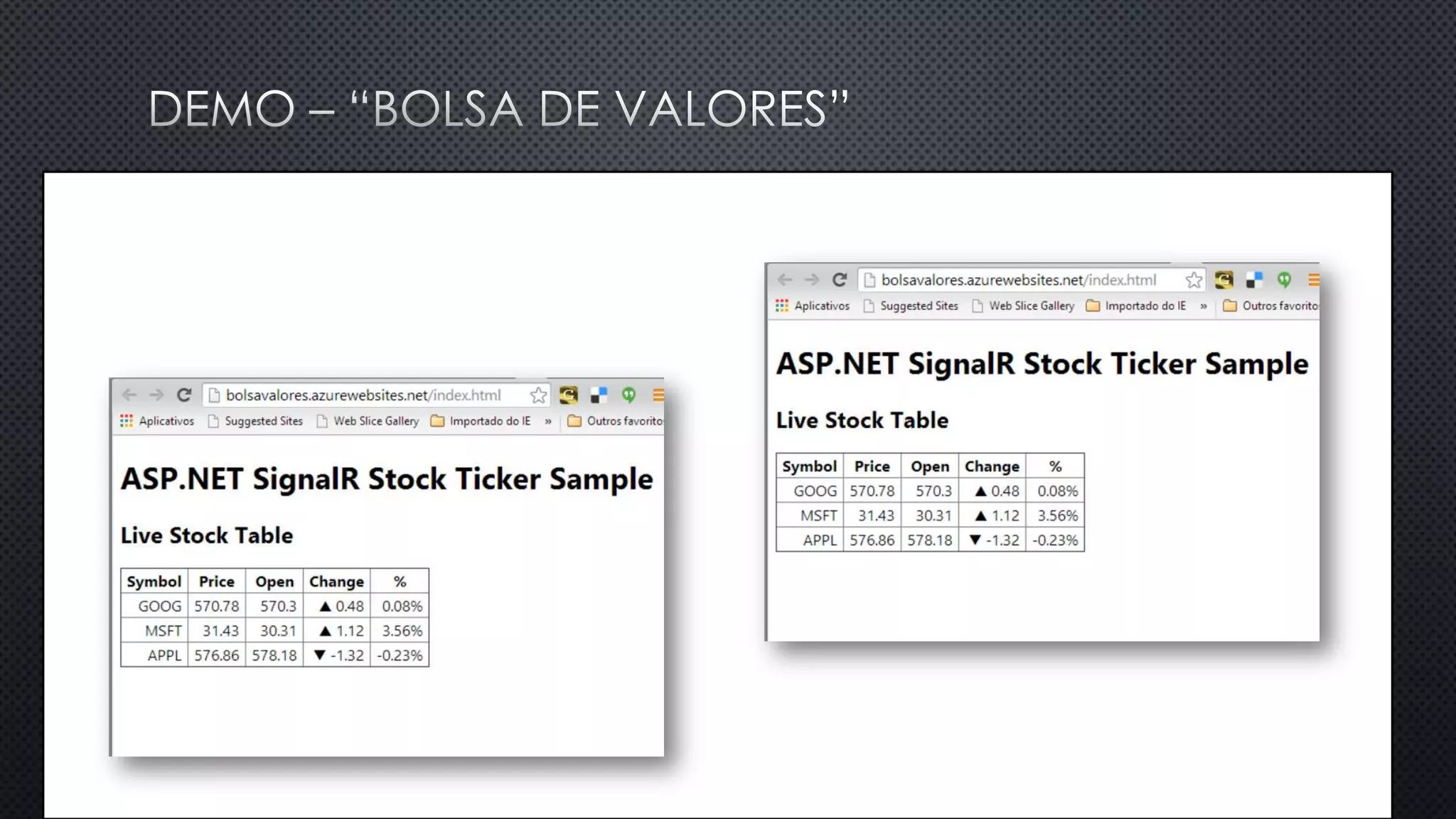
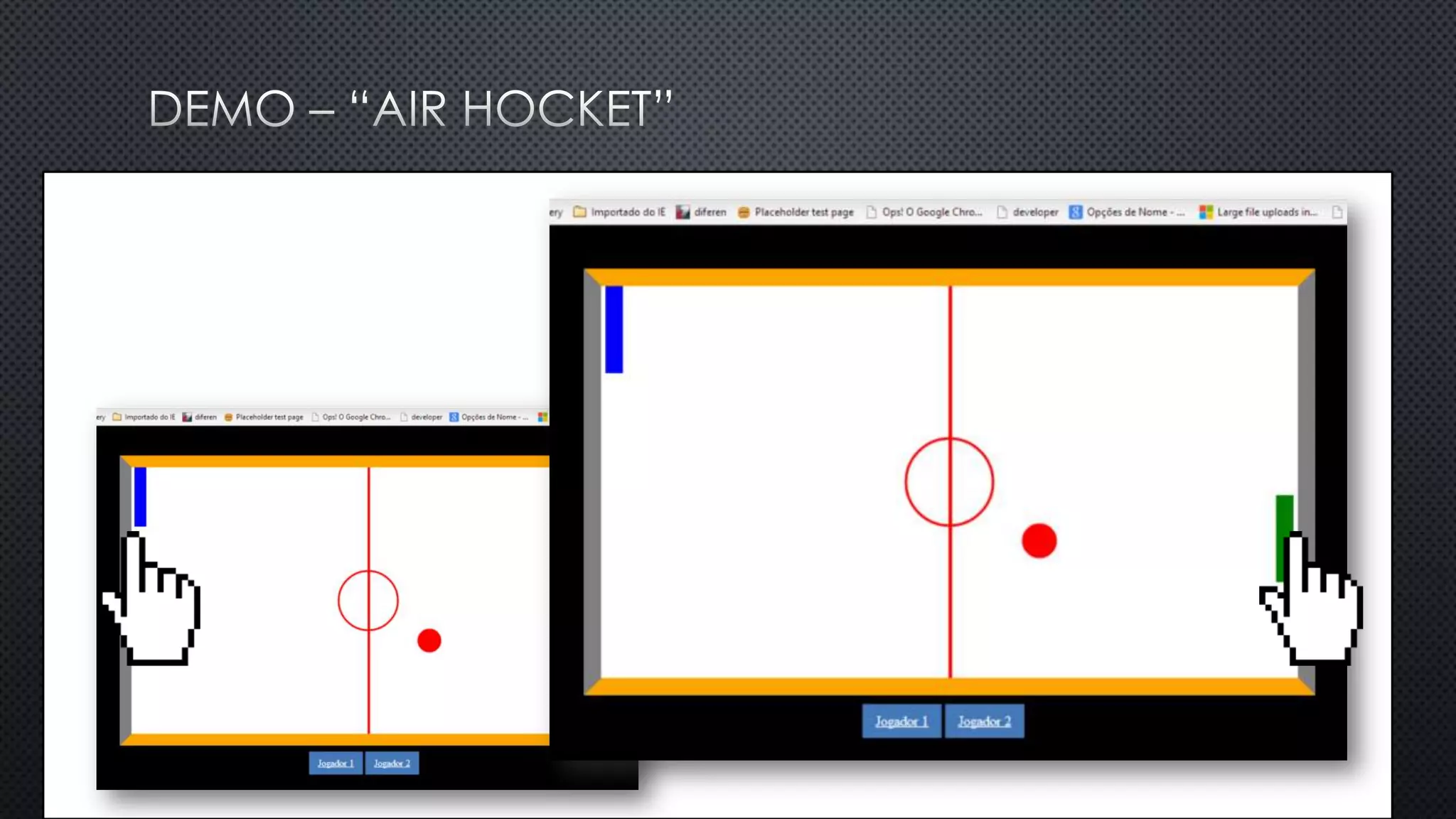
O documento discute as vantagens e desvantagens de várias técnicas de conexão persistente entre servidores e clientes, incluindo SignalR, que permite comunicação em tempo real na web. SignalR usa vários protocolos como WebSockets e polling de longa duração para fornecer conexões persistentes independentemente do navegador. O documento também fornece links para recursos adicionais sobre SignalR.