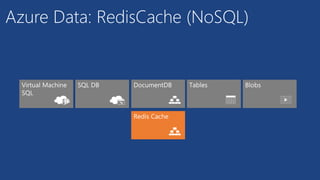
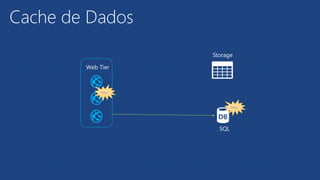
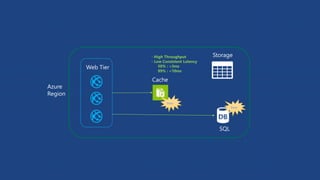
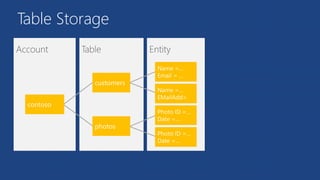
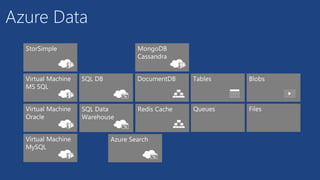
O documento apresenta os principais serviços de dados do Azure, incluindo máquinas virtuais, SQL Database, DocumentDB, Redis Cache e armazenamento. Ele discute as diferenças entre SQL e NoSQL, com exemplos de DocumentDB e tabelas do Azure. Por fim, aborda serviços avançados como StorSimple, Azure Search e SQL Data Warehouse.