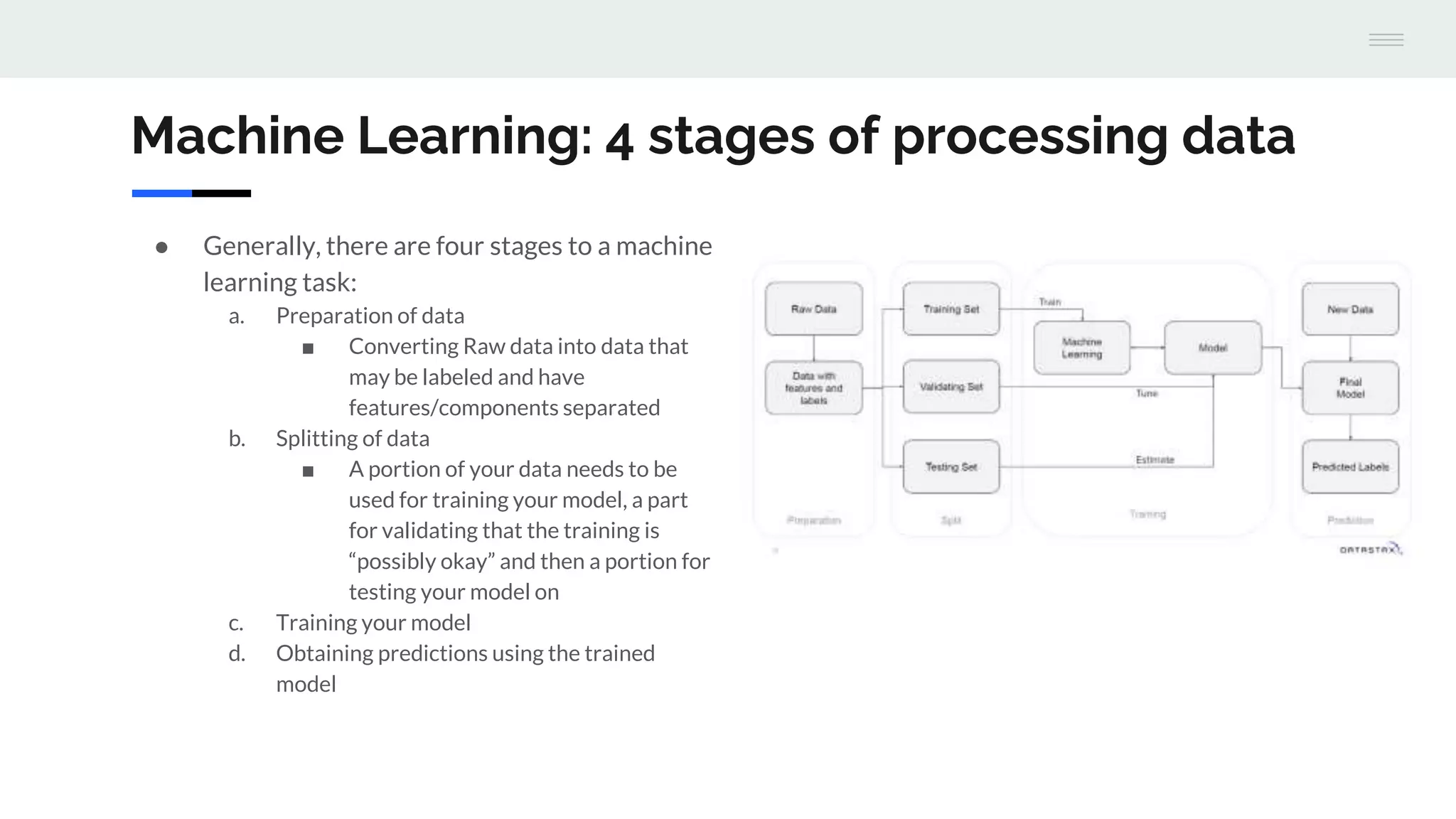
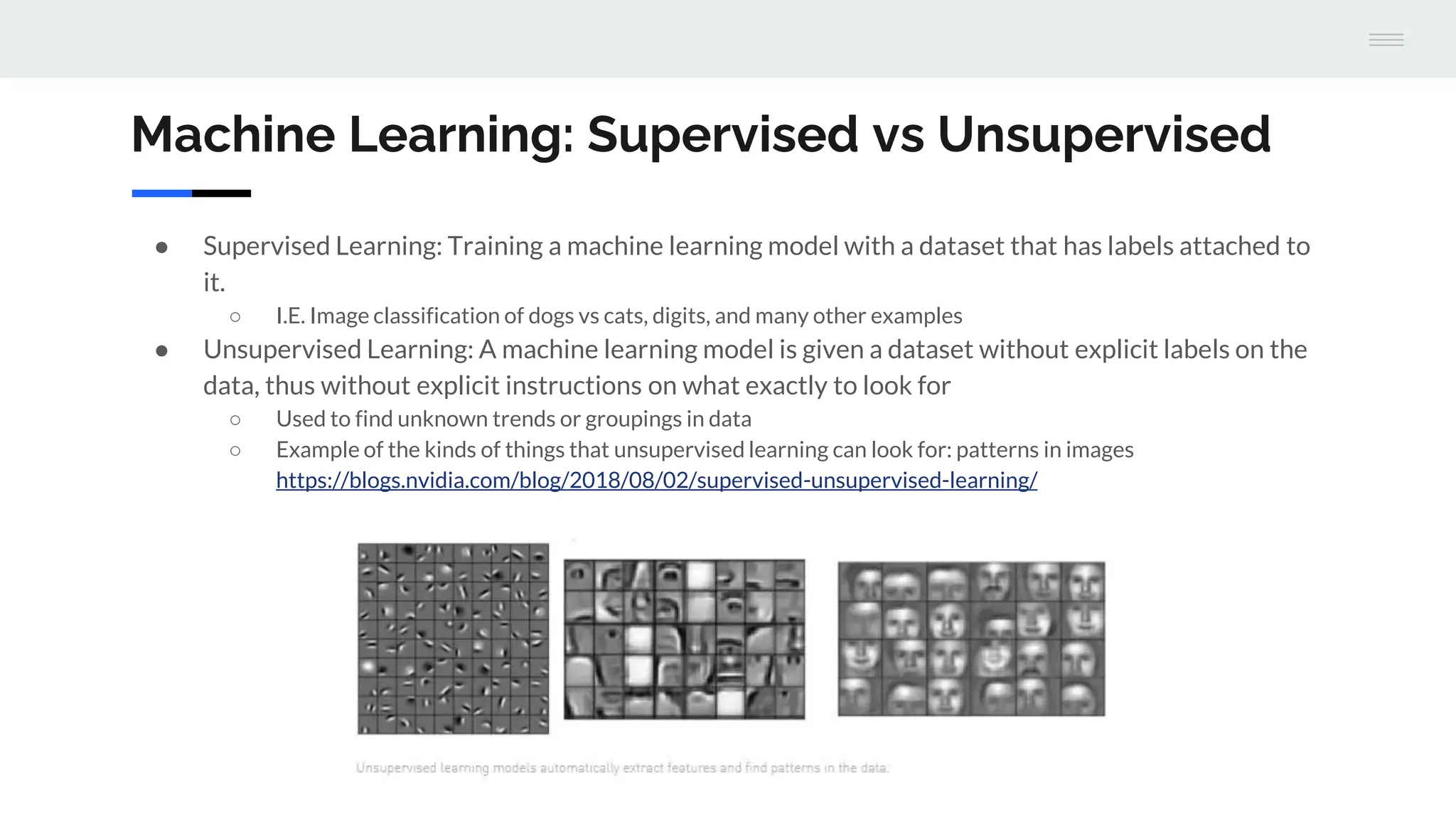
The document provides an overview of machine learning, focusing on its definition, applications, and stages of data processing, while also discussing the differences between supervised and unsupervised learning. It highlights the use of Apache Spark and Cassandra for machine learning tasks, emphasizing their scalability and capabilities in handling large datasets. Additionally, various resources for learning and implementing machine learning are included, alongside a demo project with Jupyter notebooks.