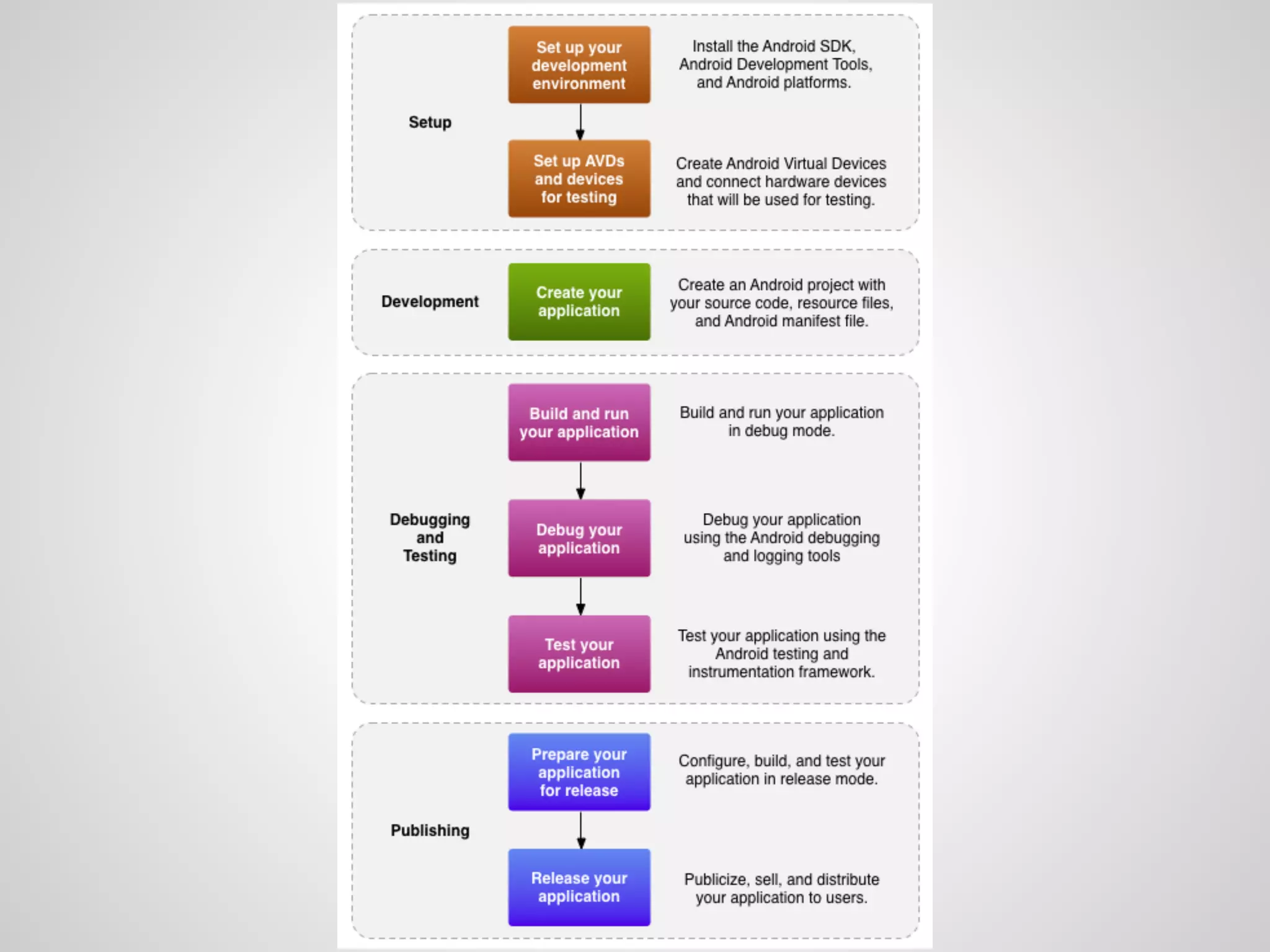
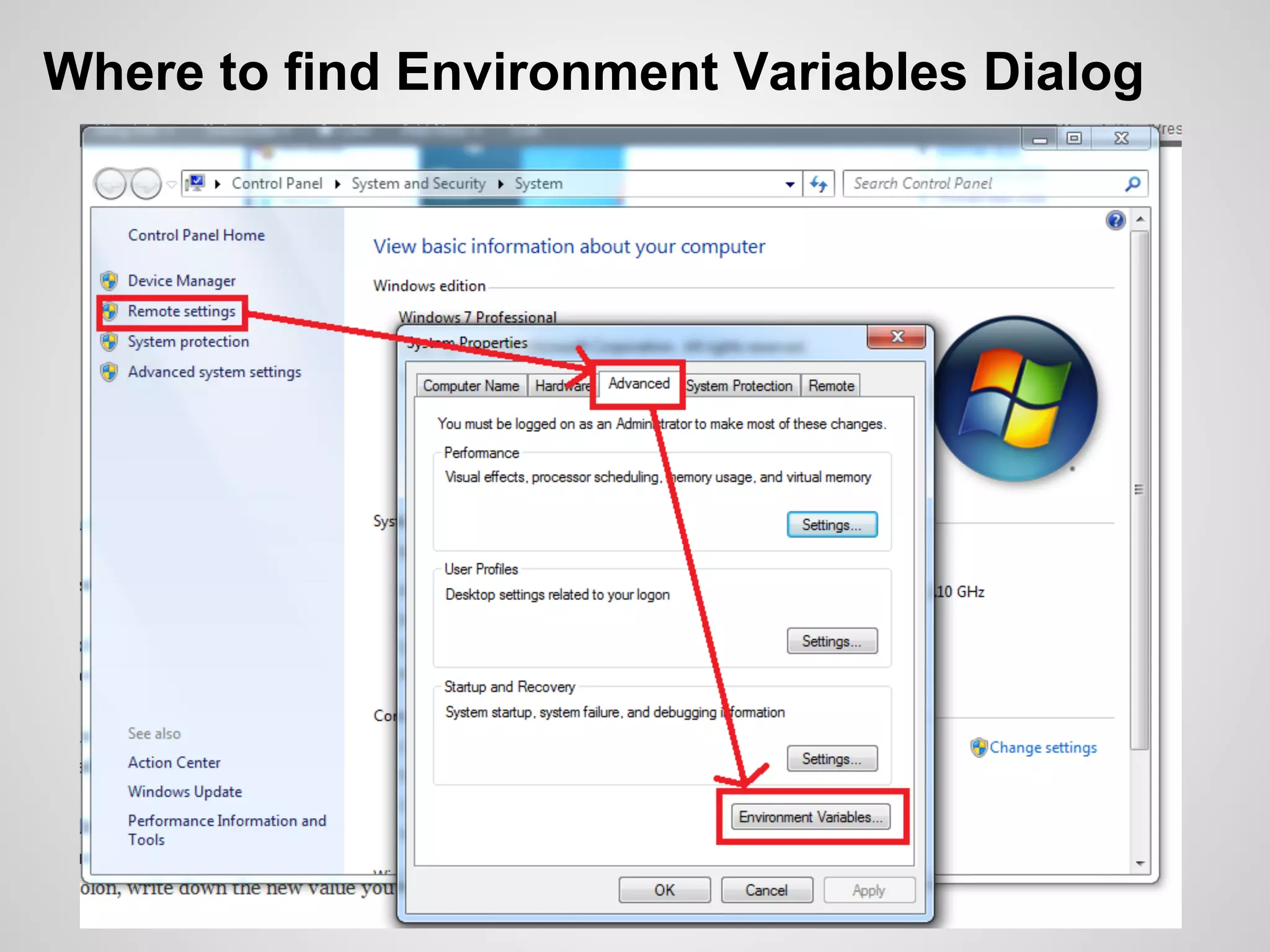
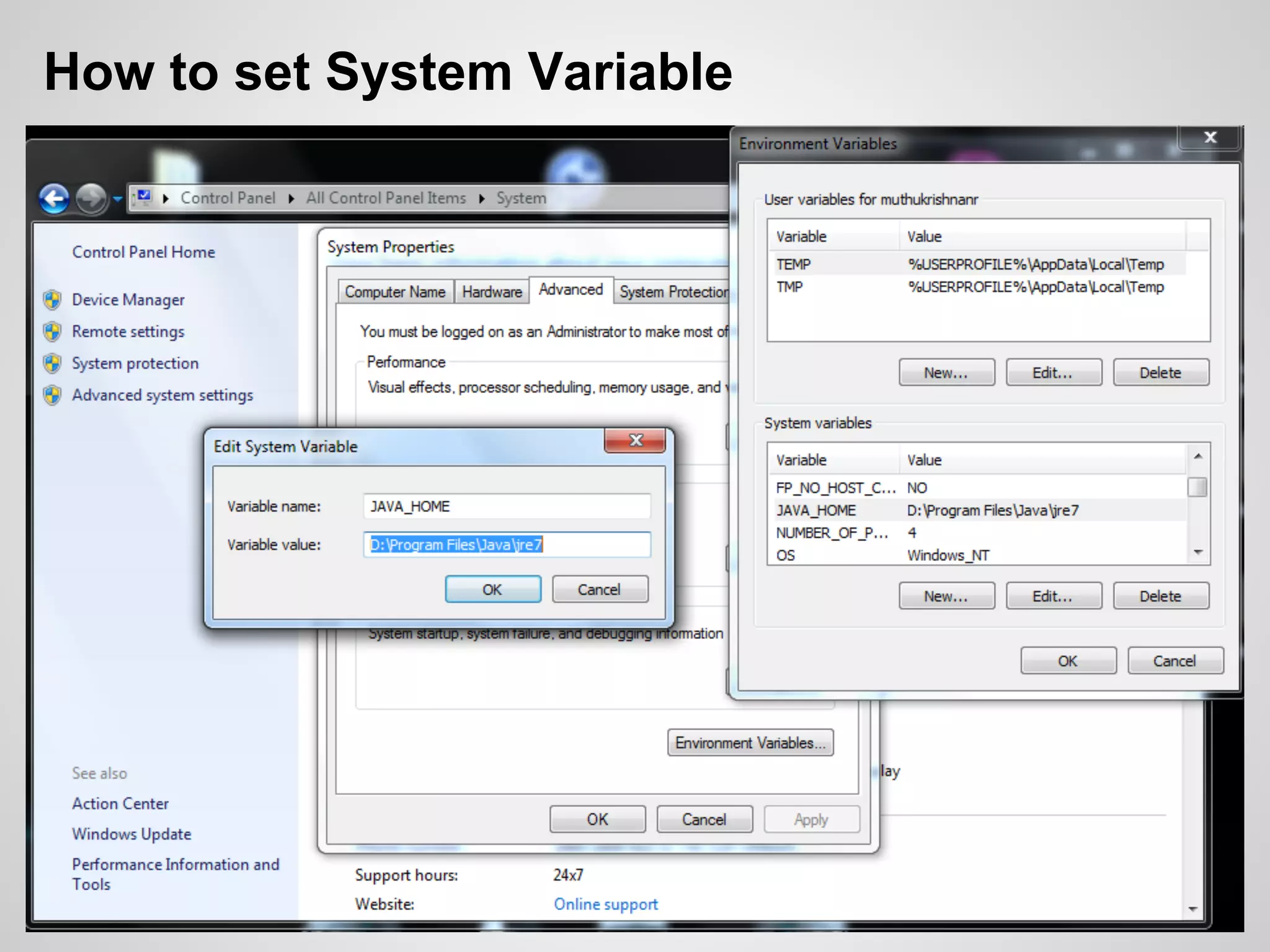
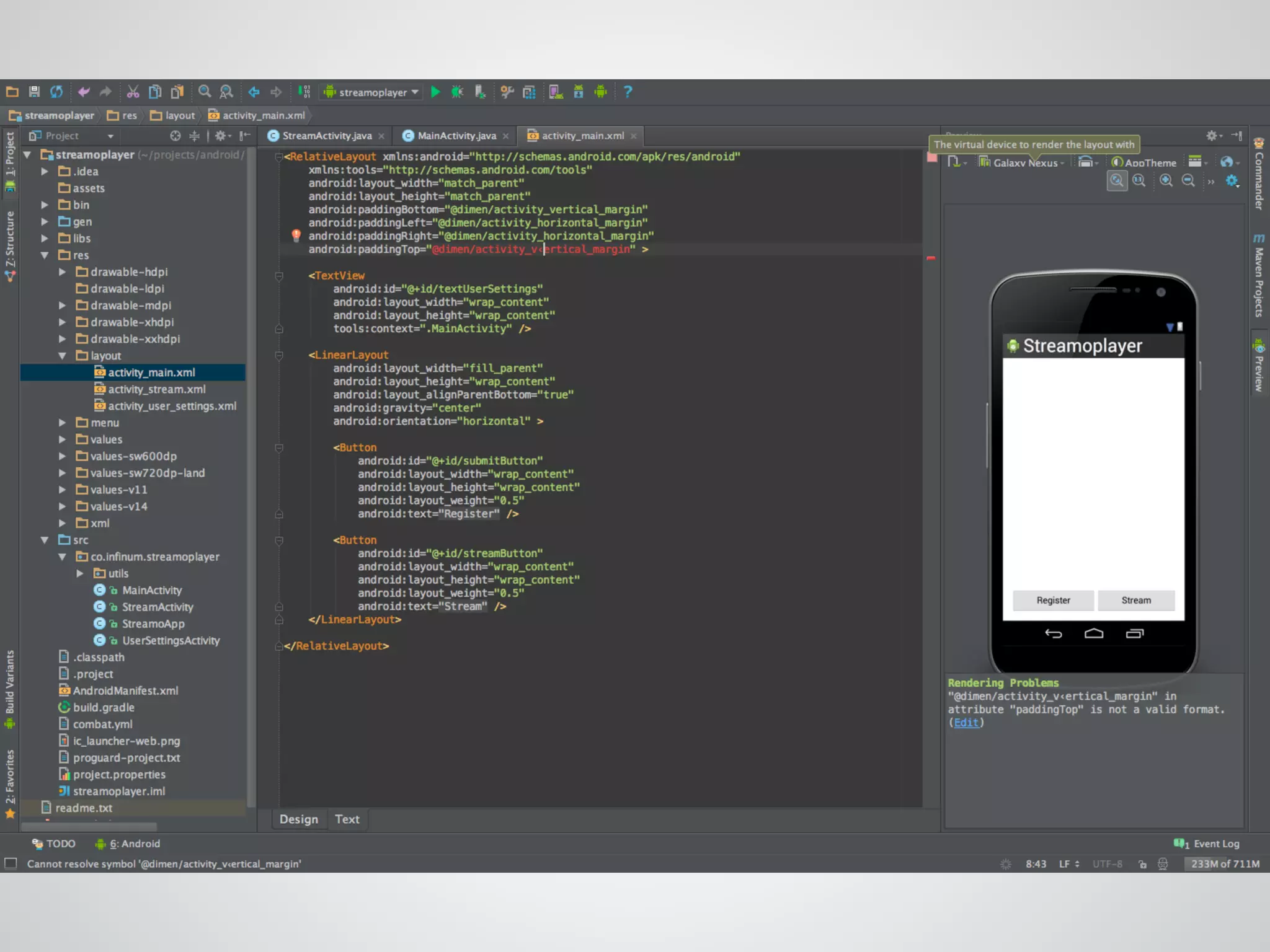
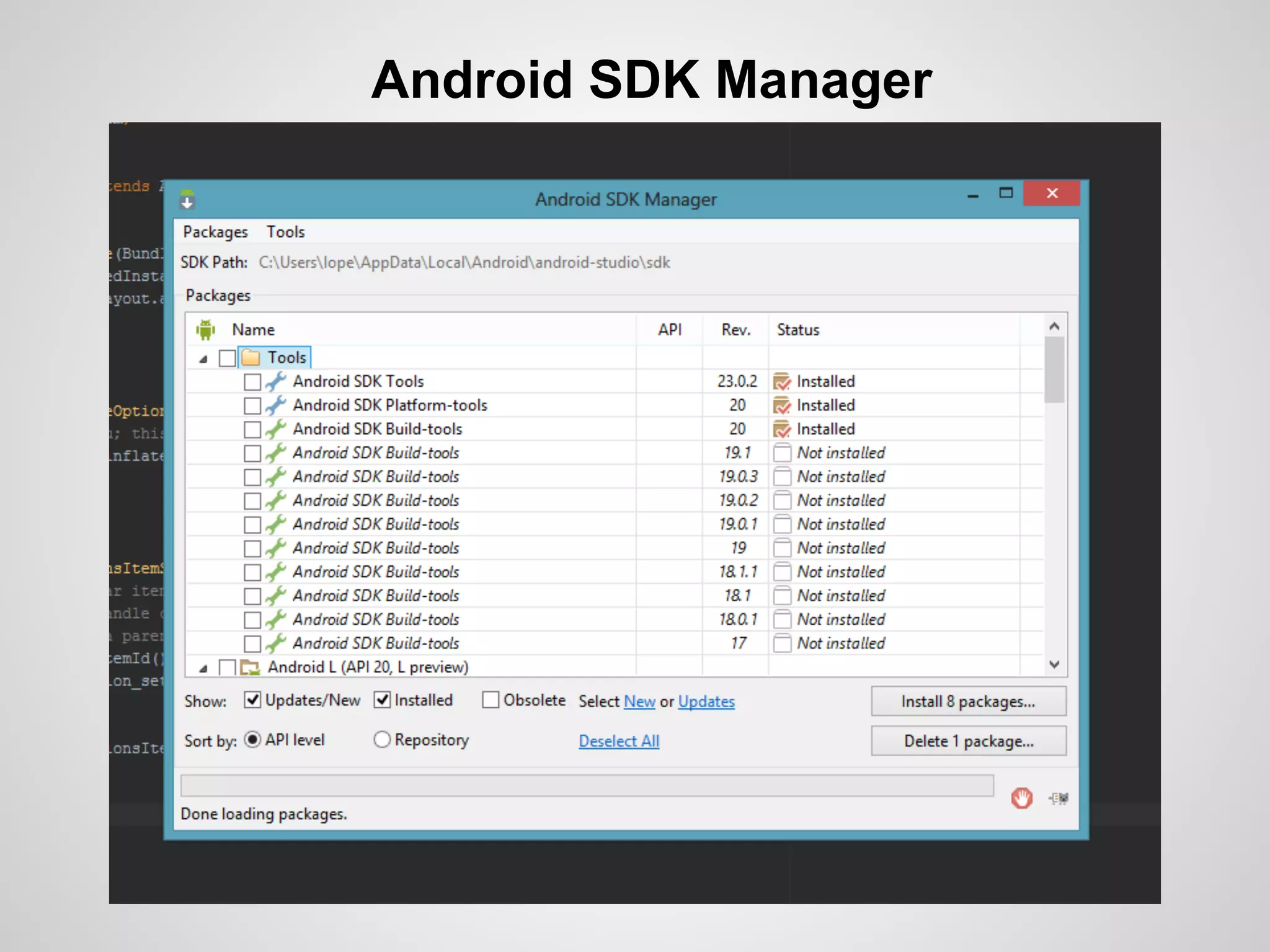
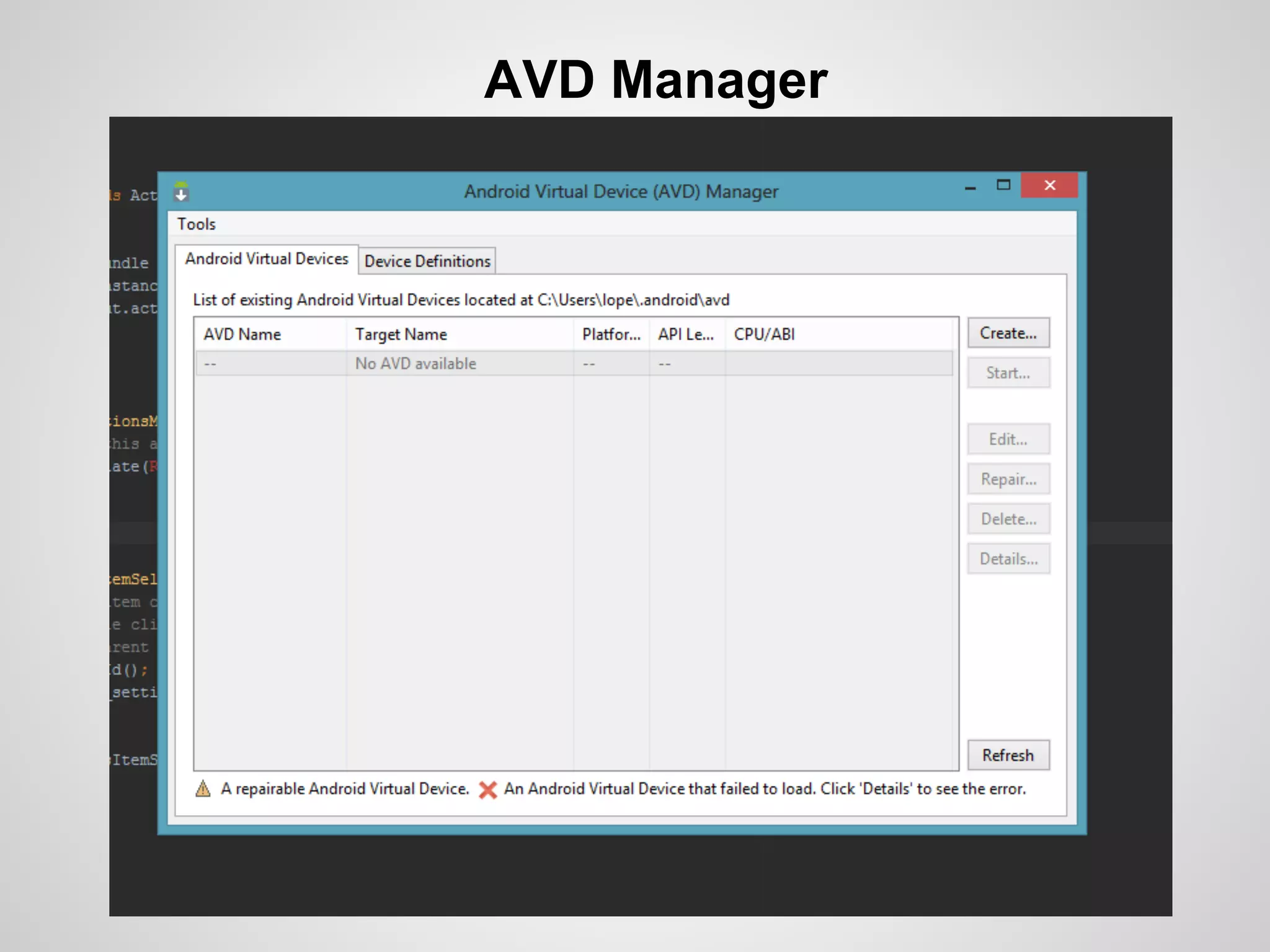
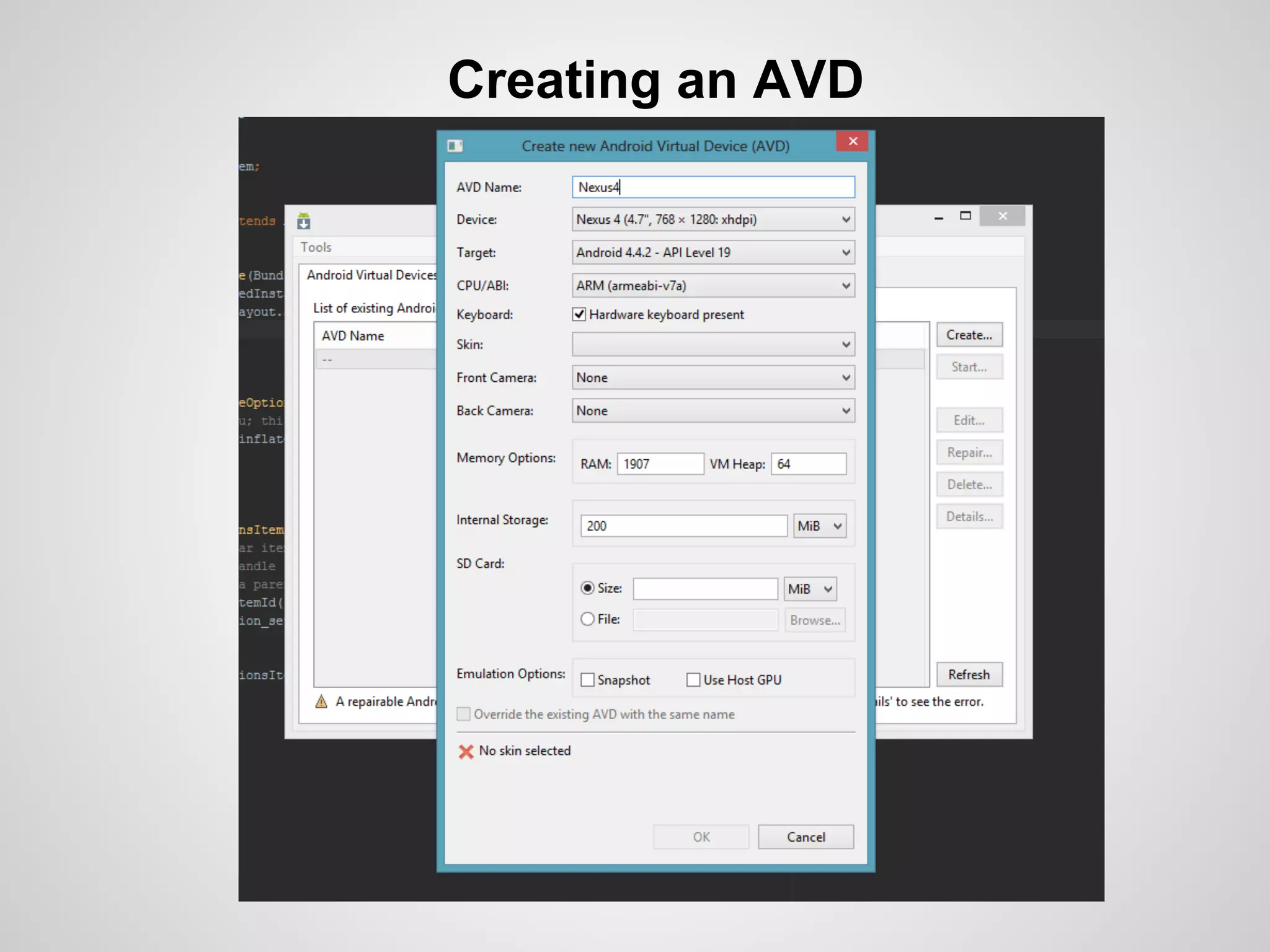
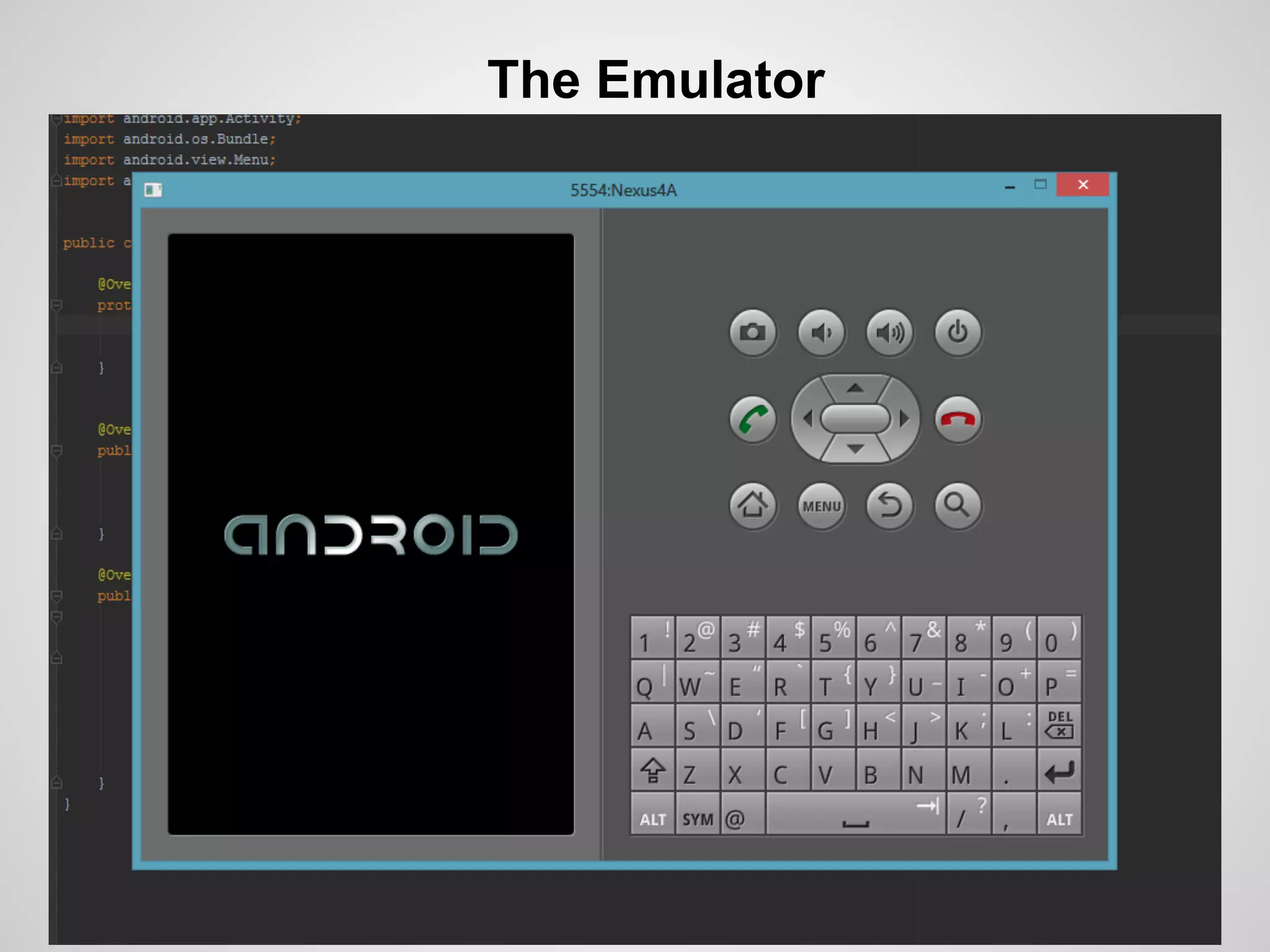
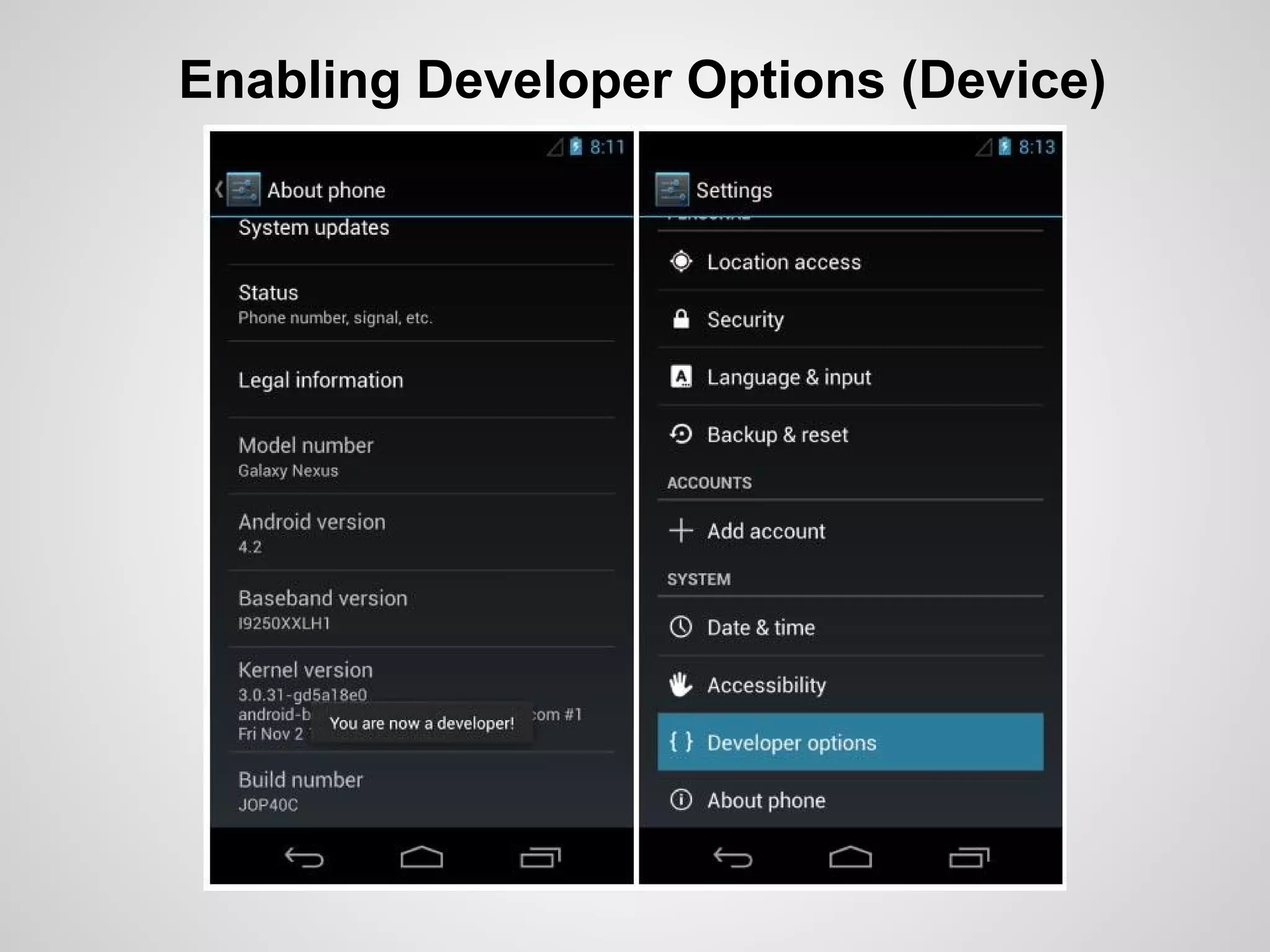
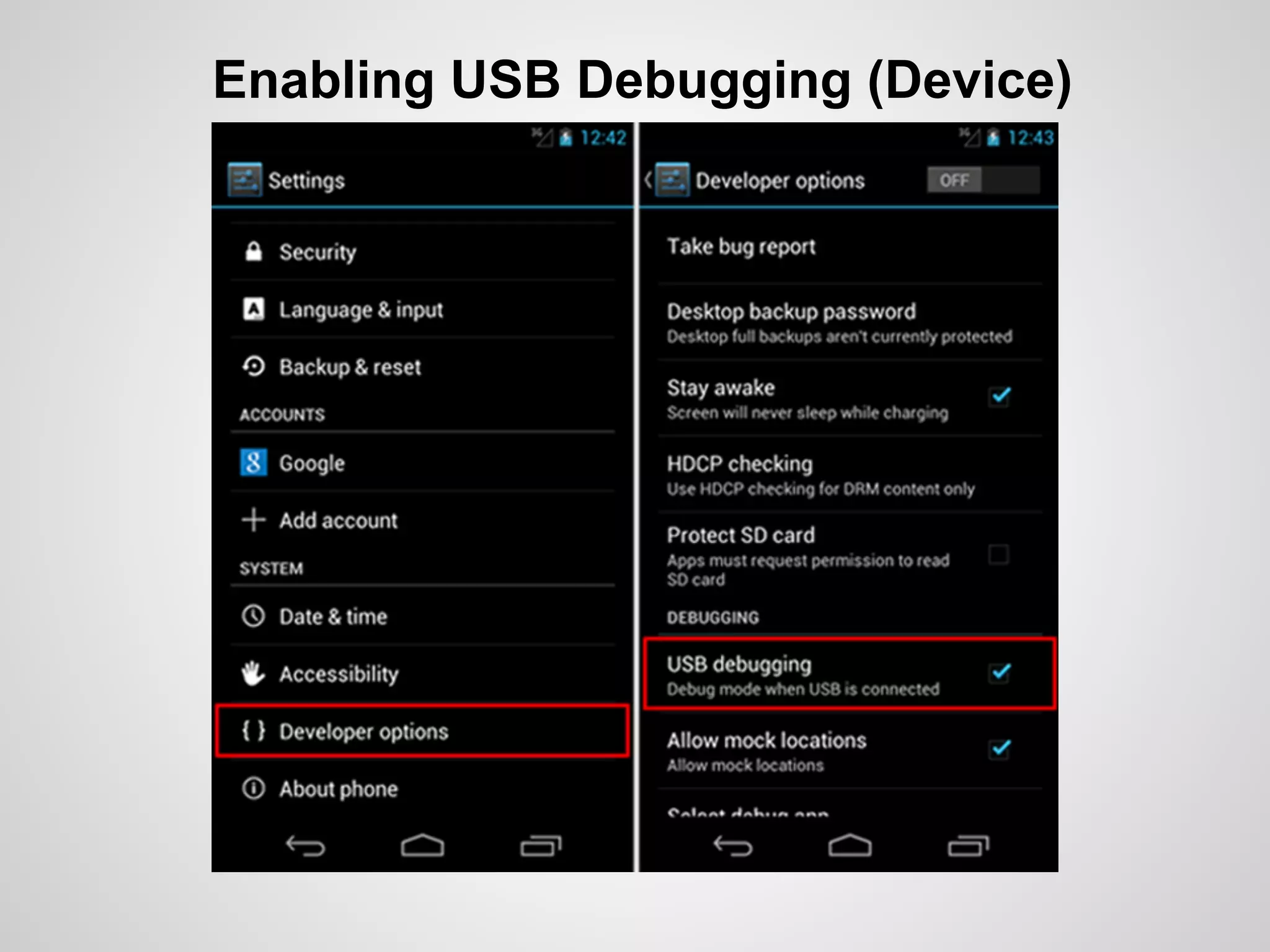
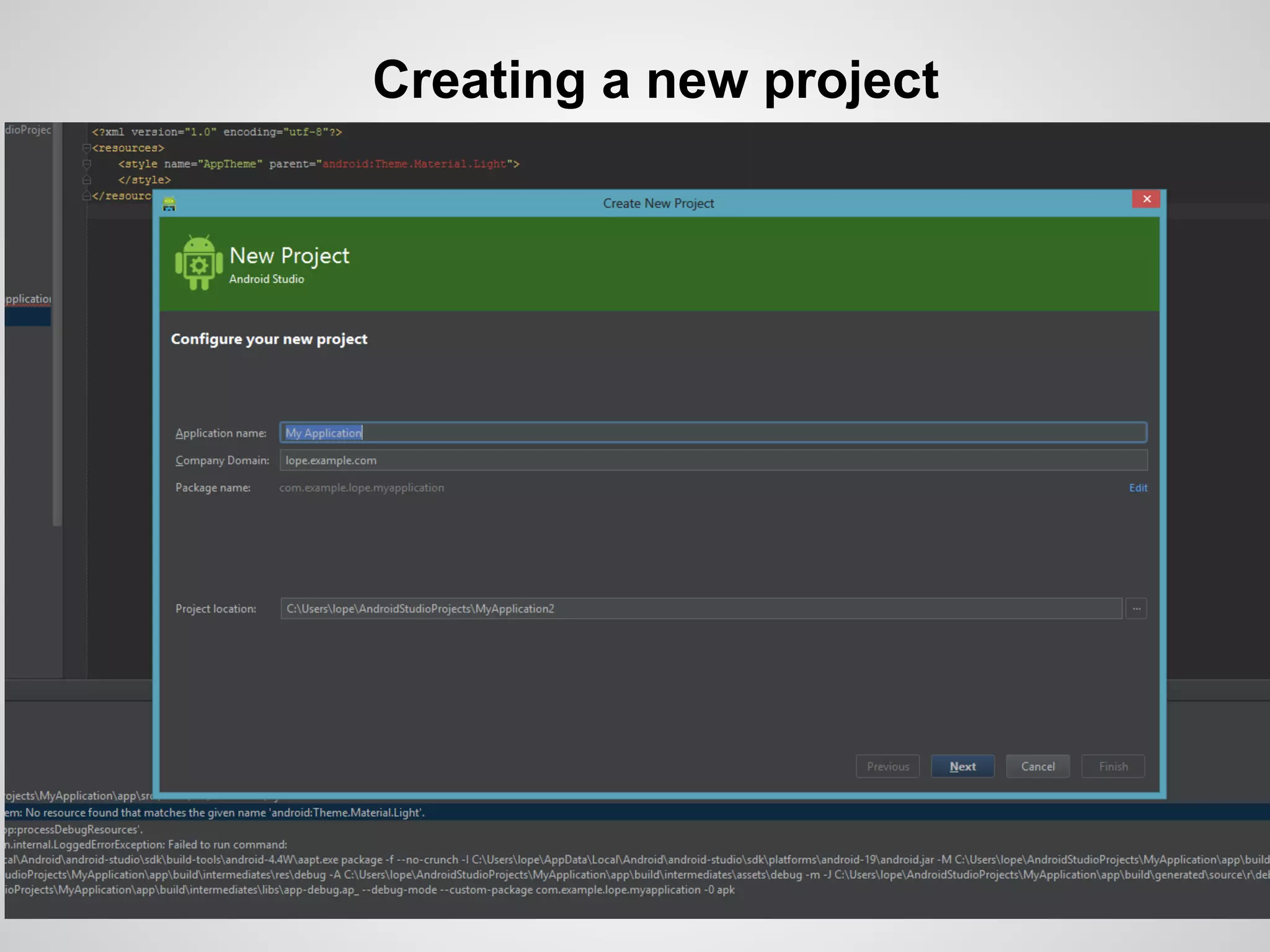
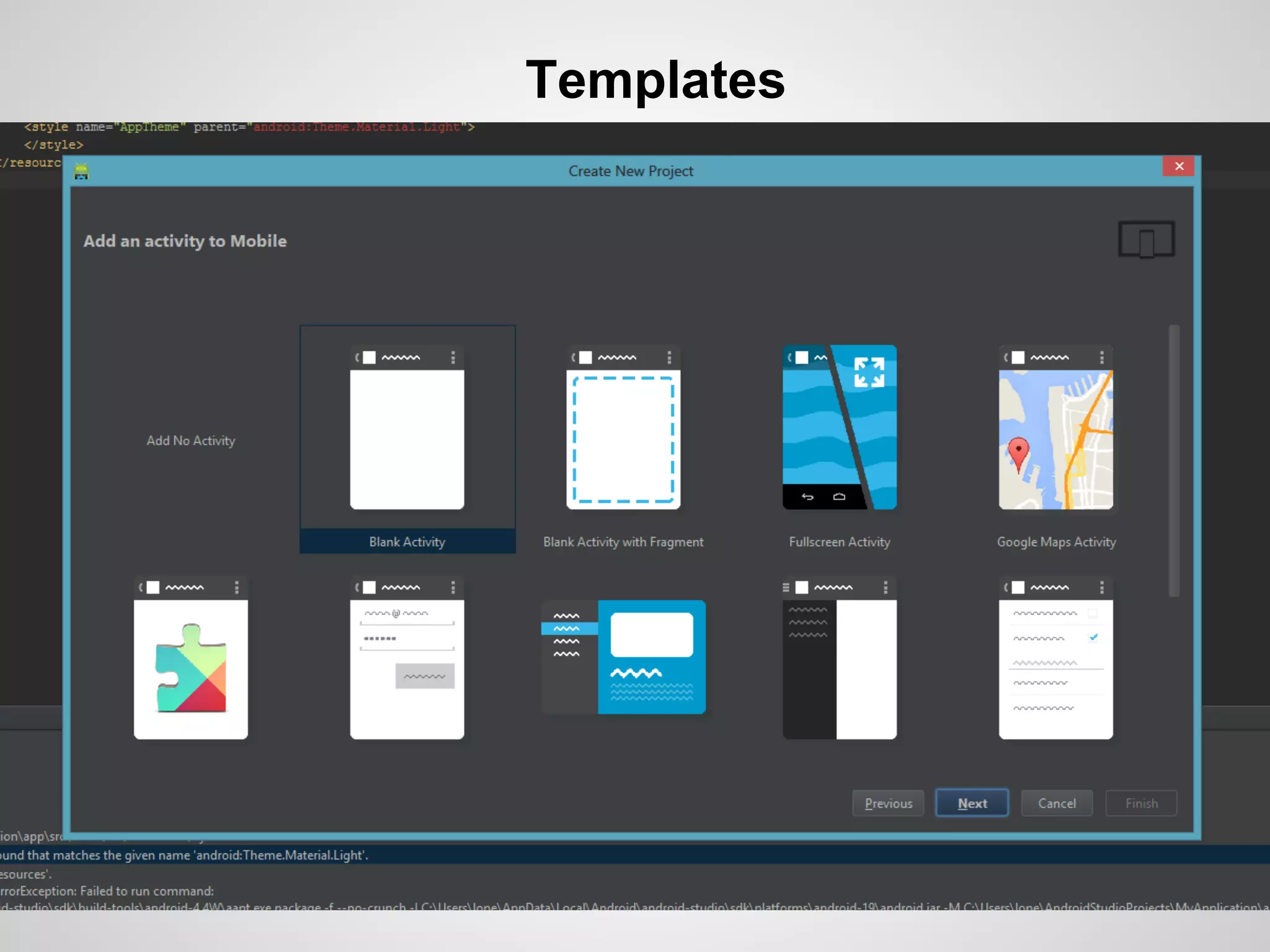
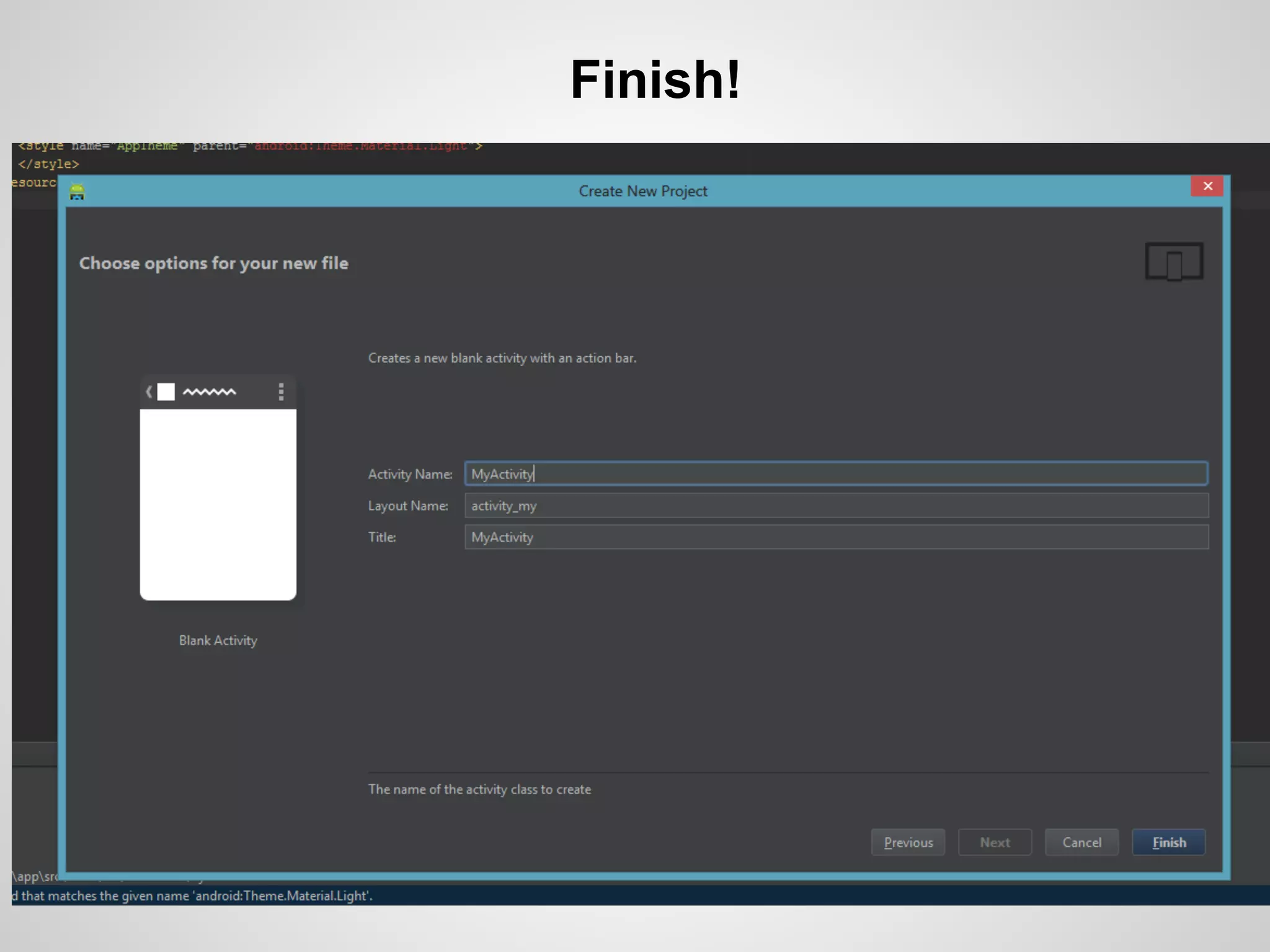
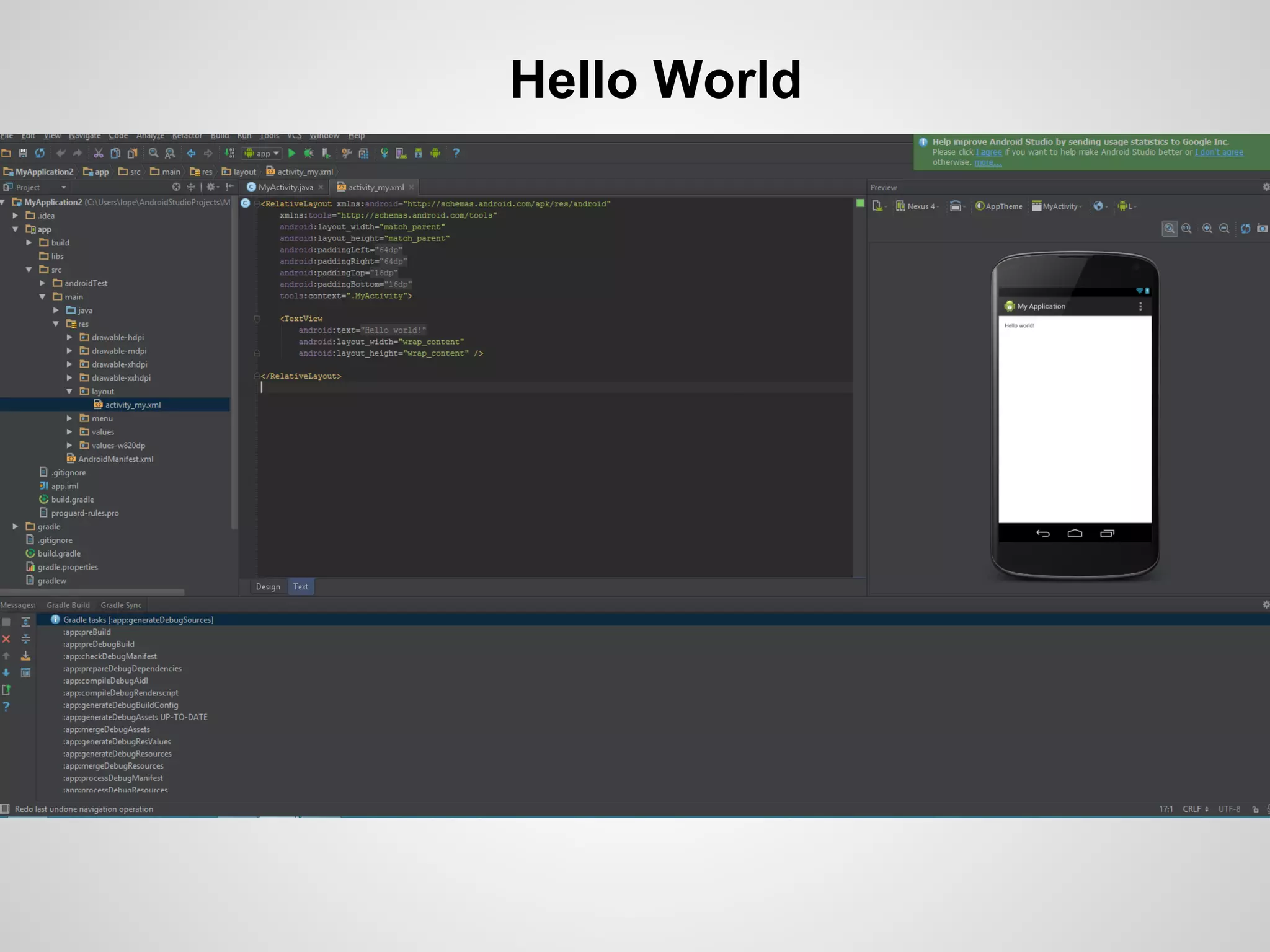
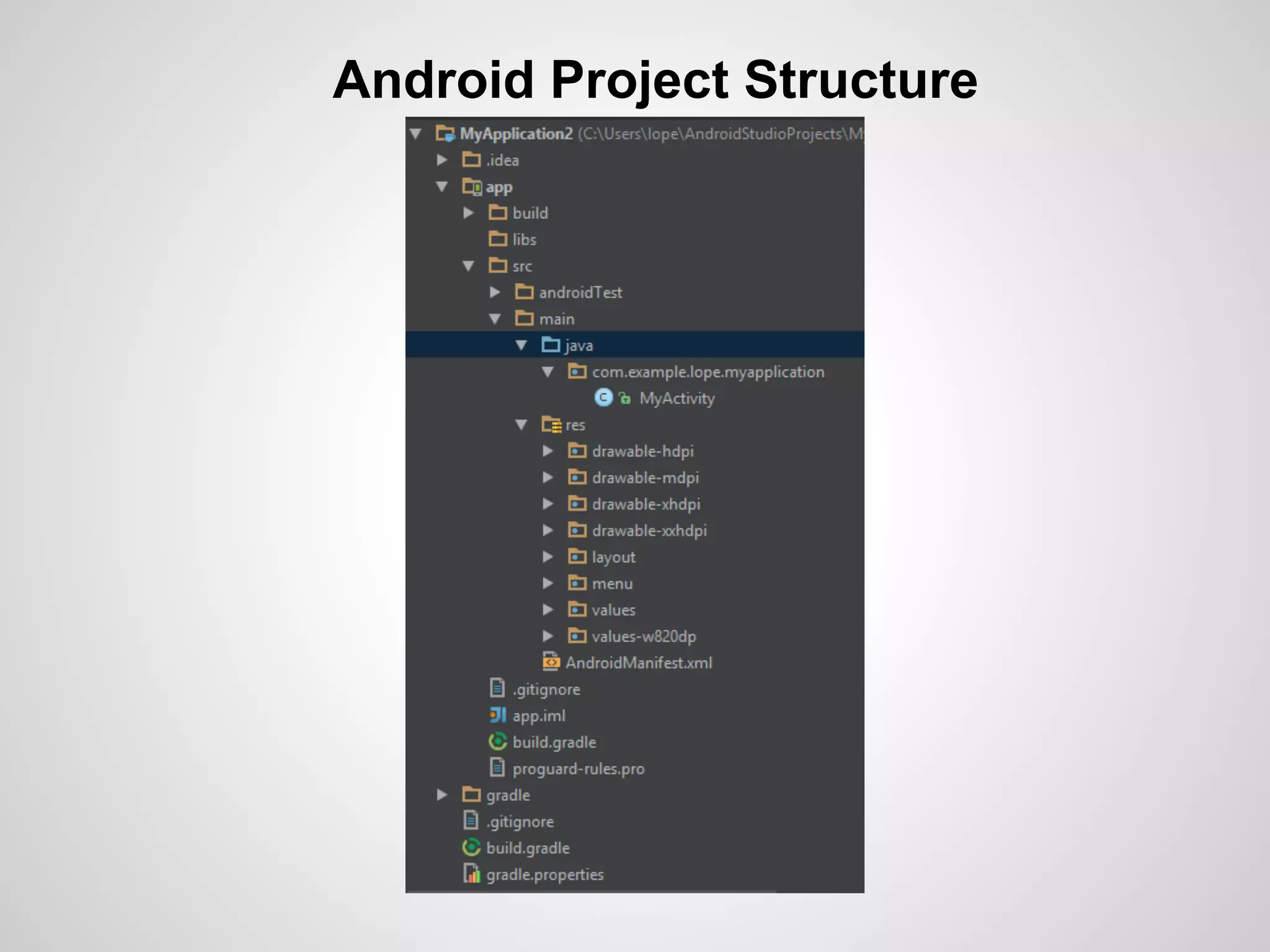
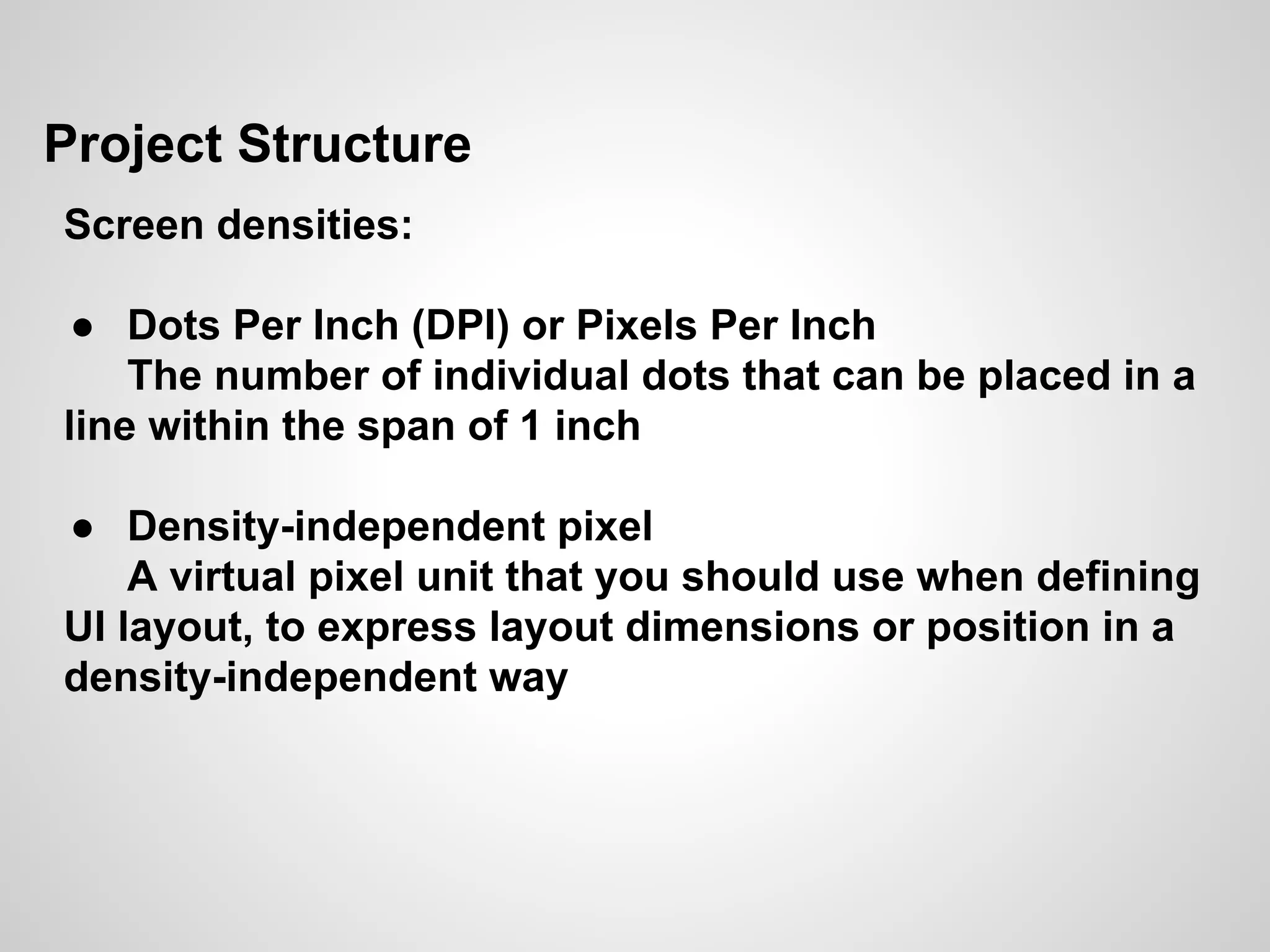
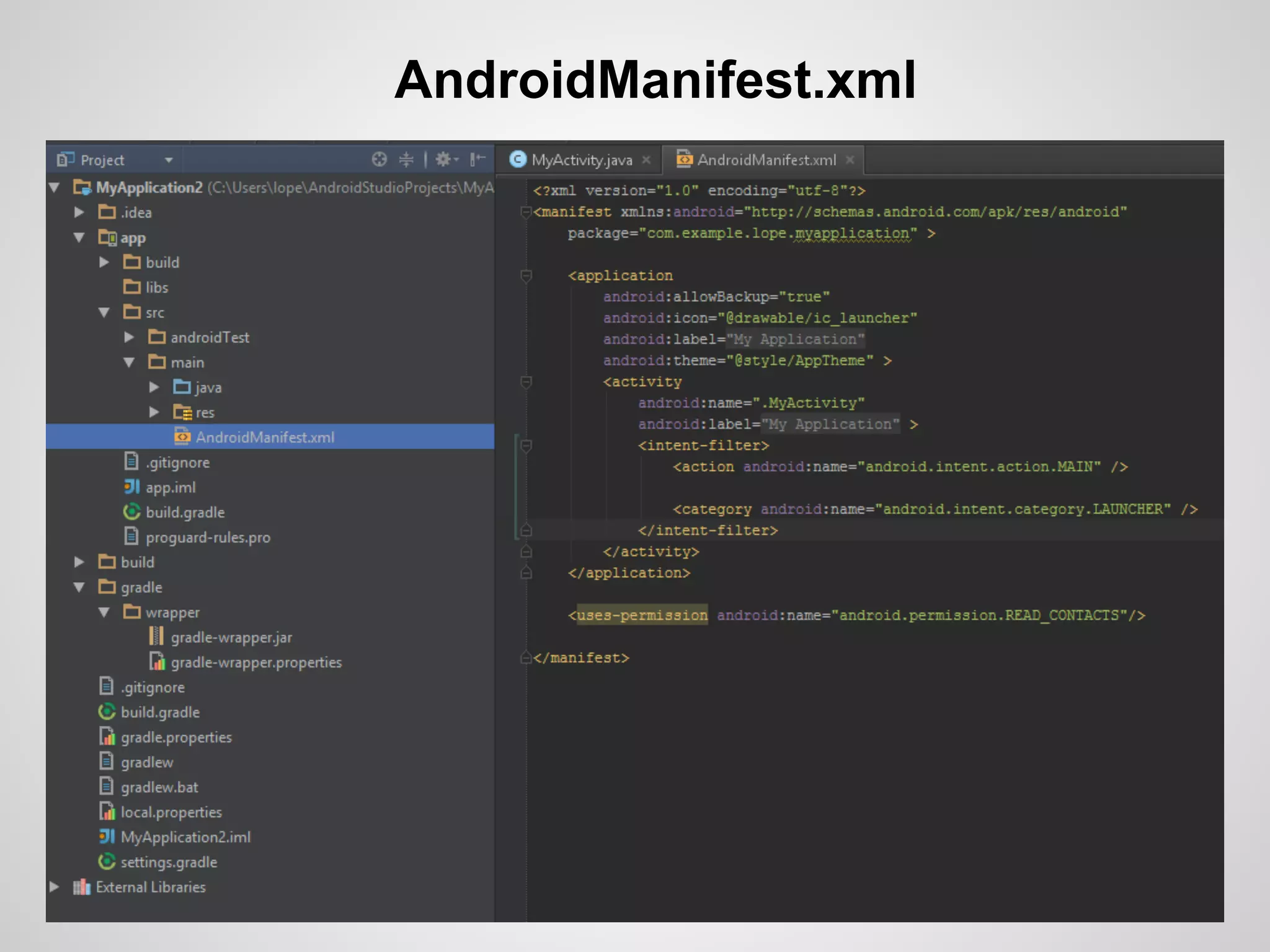
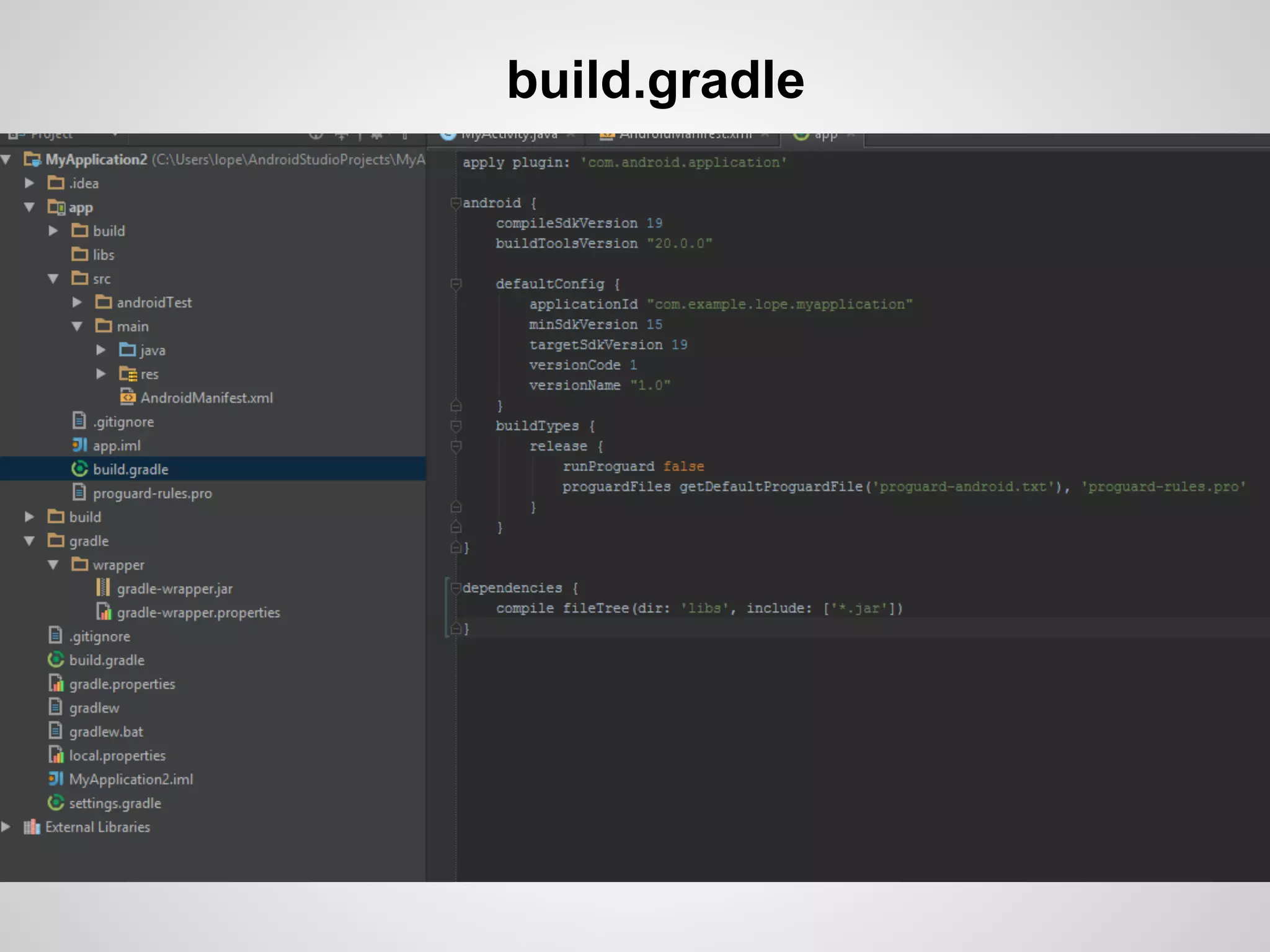
The document discusses the process and tools for Android development. It covers setting up the development environment with Java JDK, Android Studio, Android SDK Manager, and AVD Manager. It then explains creating an Android project structure with the main Java source code folder and resource folder. The document also discusses the AndroidManifest.xml file, build.gradle file, and creating a "Hello World" app.