Bacterial Cell structure and Function (1).ppt
- 2. Robert Hooke (1635-1703) English Scientist First to use the microscope to observe cells Coined the term “cell”
- 3. Anton van Leeuwenhoek 1632-1723 Dutch scientist Invented the first compound microscope First to observe LIVING cells Blood cells and protists
- 4. Robert Brown 1773-1858 Scottish botanist In 1831 he was the first person to observe the nucleus of a cell
- 5. Schleiden & Schwann 1804-1881 1810-1882
- 6. Developing Cell Theory 1838 Schleiden Said “all plants are made up of cells” Schwann Said “all animals are made up of cells”
- 7. Cell Theory Overview 1. All organisms are made of one or more cells [Unicellular or Multicellular]. 2. All cells carry on life activities. 3. New cells arise only from other living cells.
- 8. Prokaryotic vs Eukaryotic PROKARYOTIC Simplest form Lack membrane bound structures Lack true nucleus Example: bacteria and cyanobacteria EUKARYOTIC Most common Possess membrane bound structures and a nucleus Found in most living things
- 9. Sizes of Cells Eukaryotic are usually larger than prokaryotic Both nutrients and wastes are constantly entering and exiting cells Vary in size and shape
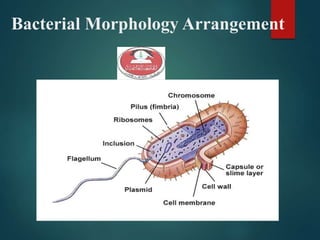
- 11. Bacterial Morphology Arrangement 1. Rod or Bacilli a.Streptobacilli b. Bacilli 2. Cocci a. Cocci b. Diplococci ( e.g. Neisseria meningitidis) c. Streptococci ( e.g. Streptococcus pyogenes) d. Staphylococci (e.g. Staphylococcus aureus) e. Sarcina f. tetrads ( Micrococcus species)
- 12. 12 Bacterial Shapes, Arrangements, and Sizes Variety in shape, size, and arrangement but typically described by one of three basic shapes: coccus - spherical bacillus – rod coccobacillus – very short and plump ( Brucella abortus) Streptobacilli ( Bacillus subtilus) diplobacilli spirillum - helical, comma, twisted rod, spirochete – spring-like- flexible ( Treponema pallidum) vibrio – gently curved ( Vibrio cholera) Spirilla- rigid ( Borrelia species) Pleomorphic : variable in shape ( Corynebacterium)
- 13. 13
- 14. 14 Bacterial Shapes, Arrangements, and Sizes Arrangement of cells is dependent on pattern of division and how cells remain attached after division: cocci: singles diplococci – in pairs tetrads – groups of four irregular clusters chains cubical packets bacilli: chains
- 15. 15
- 20. Bacterial Morphology Arrangement 3 Spirl a. Vibrio b. Spirillum c. Spirochete
- 24. Bacterial Cell Structures & Functions Pili
- 25. Bacterial Cell Structure Appendages - flagella, pili or fimbriae Surface layers - capsule, cell wall, cell membrane Cytoplasm - nuclear material, ribosome, mesosome, inclusions etc. Special structure - endospore
- 26. Appendages 1. flagella Some rods and spiral form have this. a). function: motility b). origin : cell membrane flagella attach to the cell by hook and basal body which consists of set(s) of rings and rods Gram - : 2 sets of ring and rods, L, P, S, M rings and rods . e.g. E. coli Gram + : S, M rings and rods .e.g. B. megaterium
- 27. Flagella Motility - movement Swarming occurs with some bacteria Spread across Petri Dish Proteus species most evident Arrangement basis for classification Monotrichous; 1 flagella Lophotrichous; tuft at one end Kophotrichous; tuft at both ends Amphitrichous; both ends Peritrichous; all around bacteria
- 29. Structure of the flagellum
- 30. c).Origin (continued) – The structure of the bacterial flagella allows it to spin like a propeller and thereby propel the bacterial cell; clockwise or counter clockwise wave like motion. – Bacterial flagella provides the bacterium with mechanism for swimming toward or away from chemical stimuli, a behavior is knows as CHEMOTAXIX, chemosenors in the cell envelope can detect certain chemicals and signal the flagella to respond. d). structure protein in nature: subunit flagellin ( globular protein)
- 33. 2. Fimbriae and Pili Fimbriae: Shorter than flagella and straighter , smaller, hairlike appendages . Only on some gram- bacteria. a). function: adhere. Not involve in motility. One of the invasive mechanism on bacteria. Some pathogens cause diseases due to this (Antigenic characteristic). Prevent phagocytosis.
- 34. pili - sex factor. If they make pili, they are + or donors of F factor. It is necessary for bacterial conjugation resulting in the transfer of DNA from one cell to another. It have been implicated in the ability of bacteria to recognize specific receptor sites on the host cell membrane.
- 35. Conjugation in E. coli
- 36. b). Origin: Cell membrane c). Position: common pili , numerous over the cell, usually called sex pile, 1-4/cell d). Structure: composed of proteins which can be dissociated into smaller unit Pilin . It belongs to a class of protein Lectin which bond to cell surface polysaccharide.
- 37. II. CELL SURFACE LAYER 1. Glycocalyx: Capsule or slime layer Many bacteria are able to secrete material that adheres to the bacterial cell but is actually external to the cell. It consists of polypeptide and polysaccharide on bacilli. Most of them have only polysaccharide. It is a protective layer that resists host phagocytosis. Medically important ( Streptococcus pneumonia).
- 38. Capsule and Slime layer The layer is well organized and not easily washed off, it is capsule Slime layer, unorganized material that is easily removed. They give mucoid growth on agar plate B. anthracis has a capsule of poly-D-glutamic acid, while S. pyogenes made of Hyaluronic acid. Function: Resistant phagocytosis, Protect against desiccation, Attachment to surface of solid objects.
- 39. Axial Filaments Present in spirochetes ( Treponema pallidum cause syphilis) Function is motility – gliding motility Bundles of fibrils that arise at the ends of the cell
- 40. Spirochetes Axial filament Structurally similar to flagella Unique location under an outer membrane
- 41. 2. Bacterial Cell Wall General structure: mucopolysaccharide i.e. peptidoglycan. It is made by N- acetylglucosamine and N-acetylmuramic acid. tetrapeptide ( L-alanine- isoglutamine-lysine- alanine) is attached. The entire cell wall structure is cross linked by covalent bonds. This provide the rigidity necessary to maintain the integrity of the cell. N-acetylmuramic acid is unique to prokaryotic cell.
- 42. Cell walls of bacteria(2)
- 43. Cell walls of bacteria(3)
- 44. Cell walls of bacteria(4)
- 45. Cell walls of bacteria(1)
- 48. a). Gram positive bacterial cell wall Thick peptidoglycan layer pentaglycin cross linkage. Teichoic acid (TA): Polymer of ribitol & glycerol joined by phosphate groups Some have peptioglycan teichoic acid. All have lipoteichoic acid.
- 49. Function of Teichoic acids: * Antigenic determinant * Participate in the supply of Mg to the cell by binding Mg++ * regulate normal cell division. For most part, protein is not found as a constituent of the G+ cell wall except M protein on group streptococci
- 50. Structure of the Gram-positive Cell Wall
- 51. (b) Gram negative bacterial cell wall: Thin peptidoglycan Tetrapeptide cross linkage A second membrane structure: protein and lipopolysaccharide (LPS). Toxicity : endotoxin on lipid A of LPS. glucosamine- glucosamine-long polysaccharide- repeated sequences of a few sugars (e.g. gal- mann-rham) n=10-20 O antigen
- 53. Toxicity : endotoxin on lipid A of lipopolysaccharide. glucosamine- glucosamine-long FA FA FA FA polysaccharide- repeated sequences of a few sugars (e.g. gal- mann-rham) n=10-20 O antigen
- 54. Chemistry of LPS
- 55. The Gram-negative outer membrane(1)
- 56. The Gram-negative outer membrane(2)
- 58. 58 Atypical Cell Walls Some bacterial groups lack typical cell wall structure i.e. Mycobacterium and Nocardia Gram-positive cell wall structure with lipid mycolic acid (cord factor) pathogenicity and high degree of resistance to certain chemicals and dyes basis for acid-fast stain used for diagnosis of infections caused by these microorganisms Some have no cell wall i.e. Mycoplasma cell wall is stabilized by sterols pleomorphic
- 59. 2. Cell Membrane Function: a. control permeability b. transporte’s and protons for cellular metabolism c. contain enzymes to synthesis and transport cell wall substance and for metabolism d. secret hydrolytic enzymes e. regulate cell division. Fluid mosaic model. phospholipid bilayer and protein (structure and enzymatic function). Similar to eukaryotic cell membrane but some differs. e.g.
- 60. 60
- 61. Functions of the cytoplasmic membrane(1)
- 62. Functions of the cytoplasmic membrane(2)
- 64. Classes of membrane transporting systems(1)
- 65. Classes of membrane transporting systems(2)
- 66. 66 Bacterial Internal Structures Cell cytoplasm: dense gelatinous solution of sugars, amino acids, and salts 70-80% water serves as solvent for materials used in all cell functions
- 67. 67 Bacterial Internal Structures Chromosome single, circular, double-stranded DNA molecule that contains all the genetic information required by a cell DNA is tightly coiled around a protein, aggregated in a dense area called the nucleoid.
- 68. The bacterial chromosome and supercoiling
- 69. 69 Bacterial Internal Structures Plasmids small circular, double-stranded DNA free or integrated into the chromosome duplicated and passed on to offspring not essential to bacterial growth and metabolism may encode antibiotic resistance, tolerance to toxic metals, enzymes and toxins used in genetic engineering- readily manipulated and transferred from cell to cell
- 70. 70 Bacterial Internal Structures Ribosomes (70 S) made of 60% ribosomal RNA and 40% protein consist of two subunits: large and small procaryotic differ from eucaryotic ribosomes in size and number of proteins site of protein synthesis present in all cells
- 71. 71
- 72. 3. Mesosomes ( mostly in Gram +ve) A large invaginations of the plasma membrane, irregular in shape. a. increase in membrane surface, which may be useful as a site for enzyme activity in respiration and transport. b. may participate in cell replication by serving as a place of attachment for the bacterial chromosome.
- 73. 4. Inclusions Not separate by a membrane but distinct. Granules of various kinds: * glycogen ( used as carbon source), *polyhydroxybutyric acid droplets (PHB) i.e. fat droplets and have Lipid inclusion * inorganic metaphosphate (metachromatic granules or Volutin granules) - in general, starvation of cell for almost any nutrients leads to the formation of this to serve as an intracellular phosphate reservoir ( Corynebacterium).
- 74. PHB
- 75. 5. Chromatophores Only in photosynthetic bacteria and blue green algae. Prok. no chloroplast, pigment found in lamellae located beneath the cell membrane. Sulfur Granules: Mainly in Thiobacillus, convert H2S to S
- 76. 76
- 77. IV. Special Structure * Endospores Spore former: Sporobactobacilli and Sporosarcinae (Gram + cocci)- no medical importance. Bacillus and Clostridium ( Gram + Rod) have medical importance. Coxiella ( Gram –ve Rod) cause Q fever. * Position: median, sub-terminal and terminal have small water, high calcium content and dipicolinic acid (calcium dipicolinate) Extremely resistant to heat, UV, chemicals etc. may be due to many S containing A.A for disulfide groups.
- 78. • After the active growth period approaching the stationary growth phase, a structure called forespore develops within the cells. • It consists of coat, cortex and nuclear structure. The process of endospore formation
- 80. Negatively Stained Bacillus: (A) Vegetative Cell (B) Endospore
- 81. Dipicolinic acid
- 82. 82
- 83. Detailed steps in endospore formation(1)
- 84. Detailed steps in endospore formation(2)
- 85. Detailed steps in endospore formation(3)
- 87. PROCARYOTIC vs. EUCARYOTIC CELLS Property Procaryotes Eucaryotes Membrane-bound nucleus Absent Present DNA complexed with histones No Yes Number of chromosomes One > One Nucleolus Absent Present Mitosis No Yes Genetic recombination Partial Meiosis unidirectional fusion of gametes
- 88. PROCARYOTIC vs. EUCARYOTIC CELLS Property Procaryotes Eucaryotes Mitochondria Absent Present Chloroplasts Absent Present Endoplasmic reticulum Absent Present Golgi apparatus Absent Present
- 89. PROCARYOTIC vs. EUCARYOTIC CELLS Property Procaryotes Eucaryotes Plasma membrane sterols Usually no Yes Flagella Submicroscopic Membrane bound (1 fiber) 20 microtubules (9+2) Microtubules Absent or rare Present
- 90. PROCARYOTIC vs. EUCARYOTIC CELLS Property Procaryotes Eucaryotes 70S (30S+50S) 80S (40S+60S) Lysosomes, peroxisomes Absent Present Cell walls Ribosomes Complex; peptidoglycan Simple; no peptidoglycan 70S (30S+50S)