Introduction on Circle
•Transferir como PPTX, PDF•
5 gostaram•6,296 visualizações
Denunciar
Compartilhar
Denunciar
Compartilhar
Recomendados
Mais conteúdo relacionado
Mais procurados
Mais procurados (20)
Math10 q2 mod3of8_theorems on chords, arcs, central angles and inscribed angl...

Math10 q2 mod3of8_theorems on chords, arcs, central angles and inscribed angl...
Destaque
Destaque (13)
Semelhante a Introduction on Circle
Semelhante a Introduction on Circle (20)
Grade 10_Math-Chapter 3_Lesson 3-1 Central Angles and Inscribed Angles a.pptx

Grade 10_Math-Chapter 3_Lesson 3-1 Central Angles and Inscribed Angles a.pptx
CIRCLES and its parts: Tangent, secant ,radius, diameterptx

CIRCLES and its parts: Tangent, secant ,radius, diameterptx
Grade 9 (Alternate) Mathematics III - Learning Modules for EASE Program of DepEd

Grade 9 (Alternate) Mathematics III - Learning Modules for EASE Program of DepEd
Mais de rey castro
Mais de rey castro (20)
Último
Último (20)
Presentation by Andreas Schleicher Tackling the School Absenteeism Crisis 30 ...

Presentation by Andreas Schleicher Tackling the School Absenteeism Crisis 30 ...
Measures of Central Tendency: Mean, Median and Mode

Measures of Central Tendency: Mean, Median and Mode
Measures of Dispersion and Variability: Range, QD, AD and SD

Measures of Dispersion and Variability: Range, QD, AD and SD
Mixin Classes in Odoo 17 How to Extend Models Using Mixin Classes

Mixin Classes in Odoo 17 How to Extend Models Using Mixin Classes
SECOND SEMESTER TOPIC COVERAGE SY 2023-2024 Trends, Networks, and Critical Th...

SECOND SEMESTER TOPIC COVERAGE SY 2023-2024 Trends, Networks, and Critical Th...
Z Score,T Score, Percential Rank and Box Plot Graph

Z Score,T Score, Percential Rank and Box Plot Graph
Russian Escort Service in Delhi 11k Hotel Foreigner Russian Call Girls in Delhi

Russian Escort Service in Delhi 11k Hotel Foreigner Russian Call Girls in Delhi
Beyond the EU: DORA and NIS 2 Directive's Global Impact

Beyond the EU: DORA and NIS 2 Directive's Global Impact
Unit-IV; Professional Sales Representative (PSR).pptx

Unit-IV; Professional Sales Representative (PSR).pptx
Introduction on Circle
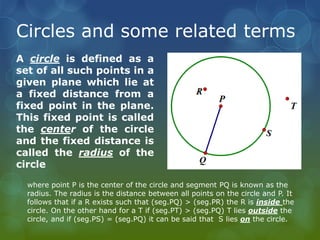
- 1. Circles and some related terms A circle is defined as a set of all such points in a given plane which lie at a fixed distance from a fixed point in the plane. This fixed point is called the center of the circle and the fixed distance is called the radius of the circle where point P is the center of the circle and segment PQ is known as the radius. The radius is the distance between all points on the circle and P. It follows that if a R exists such that (seg.PQ) > (seg.PR) the R is inside the circle. On the other hand for a T if (seg.PT) > (seg.PQ) T lies outside the circle, and if (seg.PS) = (seg.PQ) it can be said that S lies on the circle.
- 2. Lines of a Circle The lines in the plane of the circle are classified into three categories. a) Lines like l which do not intersect the circle. b) Lines like m which intersect the circle at only one point. c) Lines like n which intersect the circle at two points..
- 3. Lines of a Circle Lines like m are called tangents. A tangent is a line that has one of its points on a circle and the rest outside the circle. Thus K is the point of tangency. Line n is called a secant of the circle. A secant is defined as any line that intersects a circle in two distinct points. K
- 4. Lines of a Circle A segment whose end points lie on a circle is called a Chord . In a figure AB is a chord of the circle. Thus a chord is always a part of secant. Thus the other chords are;
- 5. Lines of a Circle The longest chord of the circle passes through its center and is called as the diameter. In the figure chord CD is the diameter. It can be noticed immediately that the diameter is twice the radius of the circle. The center of the circle is the midpoint of the diameter.
- 6. Example 1 Refer to ⊙ 𝑂. 1. Name the center of ⊙ 2. Name the longest chord 3. Name three radii 4. Name a secant 5. Name a tangent and the point of tangency. 6. If OC=12, find SI. 7. Is OS a chord of ⊙ 𝑂. 8. Is SI>ER? Explain.
- 7. Arcs The angle described by any two radii of a circle is called the central angle. Its vertex is the center of the circle. ∠APB is a central angle. The part of the circle that is cut by the arms of the central angle is called an arc. AB is an arc And the other arcs are;
- 8. Arcs arcAB is called the minor arc and is the arcAOB is a major arc. The minor arc is always represented by using the two end points of the arc on the circle. However it is customary to denote the major arc using three points. The two end points of the major arc and a third point also on the arc.
- 9. Arcs If a circle is cut into two arcs such that there is no minor or major arc but both the arcs are equal then each arc is called a semicircle.
- 10. Arcs An arc is measured as an angle in degrees and also in units of length. The measure of the angle of an arc is its central angle and the length of the arc is the length of the portion of the circumference that it describes. If ∠𝐴𝑃𝐵 is a central angle, then 𝑚∠𝐴𝑃𝐵 = 𝐴𝐵
- 11. The Arc Addition Postulate Given point B on 𝐴𝐶, then 𝑚 𝐴𝐶=mAB + mBC.
- 12. Example 2 Identify the following. 1. 2 major arcs 2. 2 minor arcs 3. An acute central angle 4. An obtuse central angle 5. A radius which is not a part of a diameter 6. A semicircle
- 13. Inscribed angles An inscribed angles are formed by chords. the vertex O of the inscribed ∠ AOB is on the circle. The minor arc AB cut on the circle by an inscribed angle is called as the intercepted arc.
- 14. The Inscribed Angle Theorem The measure of an inscribed angle is half the measure of its intercepted arc. If ∠𝐴𝑂𝐵 is an inscribed angle, then 𝑚∠𝐴𝑂𝐵 = 1 2 𝐴𝐵
- 15. Example 3 In the figure at the right, 𝑚∠𝐴𝑇𝑀=72. Find a. 𝑚 𝐴𝑀 b. 𝑚∠𝑈 c. 𝑚∠𝑂
- 16. Inscribed Angle Theorem: If two inscribed angles intercept the same arc or arcs of equal measure then the inscribed angles have equal measure. If ∠𝐶𝐴𝐷 and ∠𝐶𝐵𝐷 are inscribed angles with same intercepted arc CD, then ∠𝐶𝐴𝐷 ≅ ∠𝐶𝐵𝐷.
- 17. Example 4 Given m∠𝐺𝑂𝐹 = 7𝑥 + 10, 𝑚∠𝐺𝐹𝑂 = 8𝑥 + 20, 𝑚∠𝐷𝑂𝐹 = 3𝑦 − 12, 𝑚∠𝐿𝐹𝑂 = 2𝑦 − 3, and 𝑂𝐿 ≅ 𝐷𝐹. Find 𝑚∠𝐺𝑂𝐹, 𝑚∠𝐷𝑂𝐹, 𝑚∠𝐿𝐹𝑂.
- 18. The Semicircle Theorem An angle inscribed in a semicircle is a right angle. If ∠ACB is inscribed at arc AXB, then m∠ACB = 90o
- 19. Example 5 Solve the value of x.
