The gas laws
- 1. The Gas Laws Pressure, volume and temperature
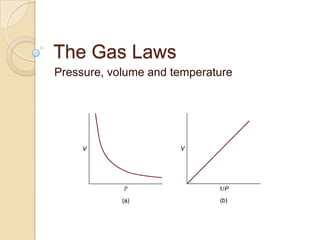
- 2. Boyle’s Law Robert Boyle (1627 – 1691) was a chemist and philosopher. He discovered that gases can be compressed. Boyle took great care to ensure that the trapped gas he was studying stayed at the same temperature. He noticed that when he doubled the pressure, the volume halved. This discovery is called Boyle’s Law.
- 3. Boyle’s Law Boyle’s Law can be expressed using the following equation: p1V1 = p2V2 This means that if you take a fixed mass of gas at pressure p1 and volume V1, and change either the pressure or the volume, the product of the pressure and the volume will not change.
- 5. Temperature Boyle took great care to carry out his experiment at a constant temperature. He was aware that temperature also has an effect on the pressure of a gas. If we heat a gas up the pressure increases and if we cool it down, the pressure decreases. There is a linear correlation between temperature and pressure.
- 6. Temperature The relationship between temperature and pressure can be summed up as follows: p1 p2 = T1 T2 (T must be measured in Kelvin) YOU NEED TO KNOW THIS!