Anal cancer
- 1. Anal Carcinoma • Ranjita Pallavi, Fellow 1
- 2. Overview • Anal cancer accounts for 2.5% of all digestive system cancers. • Risk factors include HPV (anal-genital warts), a h/o of receptive anal intercourse or STD, a h/o cervical, vulvar or vaginal cancer, immunosuppression after solid organ transplantation or HIV, hematologic malignancies, certain autoimmune disorders and smoking. • The association between anal cancer and persistent infection with a high risk form of HPV like HPV-16,18 is strong.
- 3. Risk Reduction • High grade anal intraepithelial neoplasia (AIN) can be a precursor to anal cancer. Its treatment may prevent anal cancer development. • AIN can be identified by cytology, HPV testing, DRE, high resolution anoscopy and biopsy.
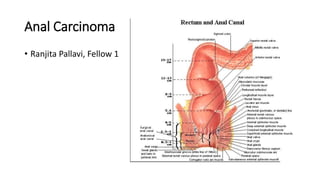
- 4. Anatomy • The anal region is comprised of anal canal and anal margin. • Anal canal is the more proximal portion of the anal region. • By histologic definition, the most superior aspect of the anal canal is a 1-2 cm zone between the anal and rectal epithelium, which has rectal, urothelial, and squamous histologic characteristics. • The most inferior aspect of the anal canal, approx. at the anal verge corresponds to the area where the mucosa, lined with modified squamous epithelium transitions to an epidermis- lined anal margin. • The anatomic anal canal begins at the anorectal ring and extends to the anal verge.
- 5. Anatomy • Functionally, the anal canal is defined by the sphincter muscles. • The superior border of the functional anal canal, separating it from the rectum, has been defined as the palpable upper border of the anal sphincter and puborectalis muscles of the anorectal ring. • It is approx. 3-5 cm in length and its inferior border starts at the anal verge, the lowermost edge of the sphincter muscles, corresponding to the introitus of the anal orifice. • The functional definition is used in the radical surgical treatment.
- 6. Anatomy • The anal margin starts at the anal verge and includes the perianal skin over a 5-6 cm radius from the squamous mucocutaneous junction. • It is covered by epidermis, not mucosa. • Tumors can involve both the anal canal and anal margin.
- 7. Sentinel nodes of the anus are inguinal nodes.
- 14. Primary treatment of non-metastatic anal cancer: Role of Chemotherapy • Journal of Clinical Oncology 1997
- 15. Purpose of the study • To investigate the potential gain of the concomitant use of radiotherapy and chemotherapy in improving local control and reducing the need for colostomy, a randomized phase III trial was performed in patients with locally advanced anal cancer.
- 16. Methods • From 1987 to 1994, 110 patients were randomized between radiotherapy alone and a combination of radiotherapy and chemotherapy. • The patients had T3-4NO-3 or T1-2N1-3 anal cancer. • Radiotherapy consisted of 45 Gy given in 5 weeks, with a daily dose of 1.8 Gy. • After a rest period of 6 weeks, a boost of 20 or 15 Gy was given in case of partial or complete response, respectively. • Surgical resection as part of the primary treatment was performed if possible in patients who had not responded 6 weeks after 45 Gy or with residual palpable disease after the completion of treatment. • Chemotherapy was given during radiotherapy: 750 mg/m2 daily fluorouracil as a continuous infusion on days 1 to 5 and 29 to 33, and a single dose of mitomycin 15 mg/m2 administered on day 1.
- 17. Results • The addition of chemotherapy to radiotherapy resulted in a significant increase in the complete remission rate from 54% for radiotherapy alone to 80% for radiotherapy and chemotherapy, and from 85% to 96%, respectively, if results are considered after surgical resections. • This led to a significant improvement of locoregional control and colostomy-free interval (P = .02 and P = .002, respectively), both in favor of the combined modality treatment. • The locoregional control rate improved by 18% at 5 years, while the colostomy-free rate at that time increased by 32% by the addition of chemotherapy to radiotherapy. • The survival rate remained similar in both treatment arms.
- 18. Results • Skin ulceration, nodal involvement, and sex were the most important prognostic factors for both local control and survival. • Event-free survival, defined as free of locoregional progression, no colostomy, and no severe side effects or death, showed significant improvement (P = .03) in favor of the combined-treatment modality.
- 19. Locoregional control/Colostomy free interval
- 20. PFS/OS
- 21. • Lancet 1996
- 22. Methods • 585 patients were randomized to receive initially either 45 Gy radiotherapy in twenty or twenty-five fractions over 4-5 weeks (290 patients) or the same regimen of radiotherapy combined with 5-fluorouracil (1000 mg/m2 for 4 days or 750 mg/m2 for 5 days) by continuous infusion during the first and the final weeks of radiotherapy and mitomycin (12 mg/m2) on day 1 of the first course (295 patients). • Clinical response was assessed 6 weeks after initial treatment: good responders were recommended for boost radiotherapy and poor responders for salvage surgery. • The main endpoint was local-failure rate (> or = 6 weeks after initial treatment); secondary endpoints were overall and cause-specific survival.
- 23. Results • After a median follow-up of 42 months, 164 of 279 (59%) radiotherapy patients had a local failure compared with 101 of 283 (36%) CMT patients. • This gave a 46% reduction in the risk of local failure in the patients receiving CMT (relative risk 0.54, 95% CI 0.42-0.69, p < 0.0001). • The risk of death from anal cancer was also reduced in the CMT arm (0.71, 0.53-0.95, p = 0.02). • There was no overall survival advantage (0.86, 0.67-1.11, p = 0.25). • Early morbidity was significantly more frequent in the CMT arm (p = 0.03), but late morbidity occurred at similar rates.
- 24. • Journal of Clinical Oncology 1996
- 25. Purpose • Definitive chemoradiation (CR) has replaced radical surgery as the preferred treatment of epidermoid carcinoma of the anal canal. • To determine the importance of mitomycin (MMC) in the standard CR regimen and to assess the role of salvage CR in patients who have residual tumor following CR, a phase III randomized trial was undertaken by the Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG)/Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG).
- 26. Patients and Methods • Between August 1988 and December 1991, 310 patients were randomized to receive either radiotherapy (RT) and fluorouracil (5-FU) or radiotherapy, 5-FU, and MMC. • Of 291 assessable patients, 145 received 45 to 50.4 Gy of pelvic RT plus 5-FU at 1,000 mg/m2/d for 4 days, and 146 received RT, 5-FU, and MMC (10 mg/m2 per dose for two doses). • Patients with residual tumor on posttreatment biopsy were treated with a salvage regimen that consisted of additional pelvic RT (9 Gy), 5- FU, and cisplatin (100 mg/m2).
- 27. Results • Posttreatment biopsies were positive in 15% of patients in the 5-FU arm versus 7.7% in the MMC arm (P = .135). • At 4 years, colostomy rates were lower (9% v 22%; P = .002), colostomy-free survival higher (71% v 59%; P = .014), and disease-free survival higher (73% v 51%; P = .0003) in the MMC arm. • A significant difference in overall survival had not been observed at 4 years. • Toxicity was greater in the MMC arm (23% v 7% grade 4 and 5 toxicity; P < or = .001).
- 28. Conclusions • Despite greater toxicity, the use of MMC in a definitive CR regimen for anal cancer is justified, particularly in patients with large primary tumors. • Salvage CR should be attempted in patients with residual disease following definitive CR before resorting to radical surgery.
- 29. • Lancet Oncology 2012
- 30. Purpose • Fluorouracil-based chemoradiotherapy is regarded as a standard perioperative treatment in locally advanced rectal cancer. • This study evaluated the efficacy and safety of substituting fluorouracil with the oral prodrug capecitabine.
- 31. Methods • This was a randomised, open-label, multicentre, non-inferiority, phase 3 trial that began in March, 2002, as an adjuvant trial comparing capecitabine-based chemoradiotherapy with fluorouracil-based chemoradiotherapy, in patients aged 18 years or older with pathological stage II–III locally advanced rectal cancer from 35 German institutions. • Patients in the capecitabine group were scheduled to receive two cycles of capecitabine (2500 mg/m2 days 1–14, repeated day 22), followed by chemoradiotherapy (50·4 Gy plus capecitabine 1650 mg/m2 days 1–38), then three cycles of capecitabine. • Patients in the fluorouracil group received two cycles of bolus fluorouracil (500 mg/m2 days 1–5, repeated day 29), followed by chemoradiotherapy (50·4 Gy plus infusional fluorouracil 225 mg/m2 daily), then two cycles of bolus fluorouracil.
- 32. Methods • The protocol was amended in March, 2005, to allow a neoadjuvant cohort in which patients in the capecitabine group received chemoradiotherapy (50·4 Gy plus capecitabine 1650 mg/m2 daily) followed by radical surgery and five cycles of capecitabine (2500 mg/m2 per day for 14 days) and patients in the fluorouracil group received chemoradiotherapy (50·4 Gy plus infusional fluorouracil 1000 mg/m2days 1–5 and 29–33) followed by radical surgery and four cycles of bolus fluorouracil (500 mg/m2 for 5 days). • The primary endpoint was overall survival. Non-inferiority of Capecitabine was tested.
- 33. Results • 5-year overall survival in the capecitabine group was non-inferior to that in the fluorouracil group (76% [95% CI 67–82] vs 67% [58–74]; p=0·0004. • Similar numbers of patients had local recurrences in each group (12 [6%] in the capecitabine group vs 14 [7%] in the fluorouracil group, p=0·67), but fewer patients developed distant metastases in the capecitabine group (37 [19%] vs 54 [28%]; p=0·04). • Diarrhoea was the most common adverse event in both groups. • Patients in the capecitabine group had more hand-foot skin reactions, fatigue and proctitis than did those in the fluorouracil group, whereas leucopenia was more frequent with fluorouracil than with capecitabine.
- 34. Conclusion • Thus, Capecitabine could replace fluorouracil in adjuvant or neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy regimens for patients with locally advanced rectal cancer.
- 35. • Lancet Oncology 2013
- 36. Purpose • Chemoradiation became the standard of care for anal cancer after the ACT I trial. • However, only two-thirds of patients achieved local control, with 5- year survival of 50%; therefore, better treatments are needed. • The investigators studied whether replacing mitomycin with cisplatin in chemoradiation improves response, and whether maintenance chemotherapy after chemoradiation improves survival.
- 37. Methods • Patients were randomly assigned to one of four groups, to receive either mitomycin (12 mg/m2 on day 1) or cisplatin (60 mg/m2 on days 1 and 29), with fluorouracil (1000 mg/m2 per day on days 1–4 and 29–32) and radiotherapy (50·4 Gy in 28 daily fractions); with or without two courses of maintenance chemotherapy (fluorouracil and cisplatin at weeks 11 and 14). • Primary endpoints were complete response at 26 weeks and acute toxic effects (for chemoradiation), and progression-free survival (for maintenance).
- 38. Findings • 472 patients were assigned to mitomycin, of whom 246 were assigned to no maintenance, 226 to maintenance; 468 were assigned to cisplatin, of whom 246 were assigned to no maintenance, 222 to maintenance. • Median follow-up was 5·1 years. • 90·5% patients in the mitomycin group versus 89·6% in the cisplatin group had a complete response at 26 weeks (difference −0·9%, 95% CI −4·9 to 3·1; p=0·64). • Overall, toxic effects were similar in each group. • The most common grade 3–4 toxic effects were skin, pain, haematological, and gastrointestinal. • 3-year progression-free survival was 74% (95% CI 69–77; maintenance) versus 73% (95% CI 68–77; no maintenance; hazard ratio 0·95, 95% CI 0·75–1·21; p=0·70).
- 40. Methods All patients received CX (400 mg/m2 loading, then 250 mg/m2/wk IV x 6-8 wks) plus CDDP (75 mg/m2 IV q28 days x 2) and 5-FU (1000 mg/m2/day IV infusion days 1-4 q 28 days x 2) concurrently with RT (45-54 Gy) beginning with CX dose 2. Patients in E3205 also received 2 cycles of CDDP/5-FU alone prior to CX/CDDP/5-FU/RT; this was discontinued on recommendation of the NCI Anorectal Task Force after 28 patients. Both trials were powered to detect a reduction in 3-year local-regional failure (LRF) rate from 35% to 17.5% (alpha=0.10, beta=0.10), the primary end point. Other endpoints included progression free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS). The results below include complete toxicity and preliminary efficacy data (including only the first 28 patients from E3205).
- 41. Results • CX plus CDDP/5-FU/RT is feasible in patients with SCAC, including patients with HIV infection.
- 42. • Annals of Oncology 2013
- 43. Methods • Immunocompetent patients with histologically confirmed LAACC received CRT [45 gray (Gy)] in 25 fractions over 5 weeks, fluorouracil and cisplatin during weeks 1 and 5), in combination with weekly dose of cetuximab (250 mg/m2 with a loading dose of 400 mg/m21 week before irradiation), and a standard dose boost (20 Gy). • The trial was originally designed to include 81 patients to detect a 15% of objective response increase with the new combination in comparison with CRT.
- 44. Results • The trial was prematurely stopped after the declaration of 15 serious adverse events (SAEs) in 14 out of 16 patients. • Among the 15 SAEs, 6 were unexpected. Grade (G) 3/4 acute toxic effects, observed in 88% patients, were general (n = 13, 81%), digestive (n = 9, 56%), dermatological (n = 5, 31%), infectious (n = 4, 25%), haematological (n = 3, 19%), and others (n = 9); and three patients suffered from six G3/4 late toxic effects. • No treatment-related death was reported. • All 11 assessable patients had an objective response consisting of six complete (55%) and five partial (45%) response 2 months after the end of the treatment. • Thirteen patients were followed up with a median of 22 months [95% confidence interval (CI ): 18–27] and had a 1-year colostomy-free survival, progression-free and overall survival rate of 67% (95% CI: 40%–86%), 62% (95% CI: 36%–82%), and 92% (95% CI: 67%–99%), respectively.
- 45. NCCN Recommendations for Primary treatment of anal canal cancer: Summary • Currently, concurrent chemoRT is the recommended primary treatment for patients with nonmetastatic anal canal cancer. • Mitomycin and 5-FU or mitomycin and capecitabine are administered concurrently with radiation. • Most studies have delivered 5-FU as a protracted 96-120 hour infusion during the first and fifth weeks of RT, and bolus injection of mitomycin is typically given on the first or second day of 5-FU infusion. • Capecitabine is given orally, Mon through Fri for 4-6 weeks, with bolus injecvtion of mitomycin and concurrent radiation.
- 46. Treatment of metastatic anal cancer • Most common sites of anal cancer metastasis outside of the pelvis include liver, lung and extrapelvic lymph nodes. • Metastatic disease is usually treated with cisplatin based chemotherapy. • No evidence supporting resection of metastatic disease. • Palliative RT can be given in case of a symptomatic bulky primary. • If cisplatin based therapy fails, no other regimens have shown to be effective.
- 48. • Thank You
