DIGESTIVE SYSTEM.pdf
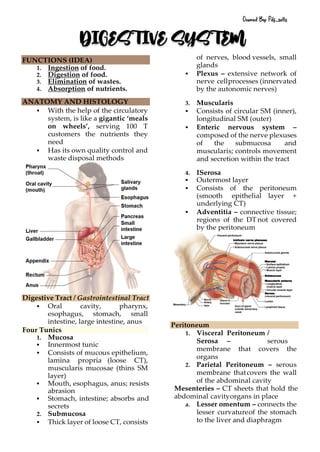
- 1. FUNCTIONS (IDEA) 1. Ingestion of food. 2. Digestion of food. 3. Elimination of wastes. 4. Absorption of nutrients. ANATOMY AND HISTOLOGY ▪ With the help of the circulatory system, is like a gigantic ‘meals on wheels’, serving 100 T customers the nutrients they need ▪ Has its own quality control and waste disposal methods Digestive Tract / Gastrointestinal Tract ▪ Oral cavity, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, anus Four Tunics 1. Mucosa ▪ Innermost tunic ▪ Consists of mucous epithelium, lamina propria (loose CT), muscularis mucosae (thins SM layer) ▪ Mouth, esophagus, anus; resists abrasion ▪ Stomach, intestine; absorbs and secrets 2. Submucosa ▪ Thick layer of loose CT, consists of nerves, blood vessels, small glands ▪ Plexus – extensive network of nerve cellprocesses (innervated by the autonomic nerves) 3. Muscularis ▪ Consists of circular SM (inner), longitudinal SM (outer) ▪ Enteric nervous system – composed of the nerve plexuses of the submucosa and muscularis; controls movement and secretion within the tract 4. ISerosa ▪ Outermost layer ▪ Consists of the peritoneum (smooth epithelial layer + underlying CT) ▪ Adventitia – connective tissue; regions of the DT not covered by the peritoneum Peritoneum 1. Visceral Peritoneum / Serosa – serous membrane that covers the organs 2. Parietal Peritoneum – serous membrane thatcovers the wall of the abdominal cavity Mesenteries – CT sheets that hold the abdominal cavityorgans in place a. Lesser omentum – connects the lesser curvatureof the stomach to the liver and diaphragm DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Owned By: Pdf_sells
- 2. b. Greater omentum – connects the greater curvature of the stomach to the transverse colon and posterior body wall ❖ Omental bursa – a long, double fold of mesentery that extends inferiorly from the stomach before looping back to the transverse colon to create a cavity/pocket ❖ Mesentery proper – attaches the small intestine to the posterior abdominal wall Retroperitoneal – abdominal organs that have no mesenteries; duodenum, pancreas, ascending + descending colon, rectum, kidneys, adrenal glands,urinary bladder ORAL CAVITY, PHARYNX, AND ESOPHAGUS Anatomy of Oral Cavity ▪ Bounded by the lips and cheeks ++ contains the teeth and tongue Lips – muscular structures formed by the orbicularis oris muscle Cheeks – buccinators muscles flatten the cheeks against teeth Mastication – begins the process of mechanical digestion Tongue – plays a major role in the process of swallowing; major sensory organ for taste; one of the major organs of speech ❖ Frenulum – thin fold of tissue inferior to thetongue Teeth ▪ 32 teeth in normal adult mouth ▪ Located in the mandible and maxillae 1. Incisor – to cut 2. Canine – to tear 3. Premolars 4. Molars 5. Wisdom teeth – third molars Permanent teeth – secondary teeth Primary teeth – deciduous teeth; milk or baby teeth Parts a. Crown b. Cusps c. Neck d. Root Pulp cavity – center of the tooth; contains blood vessels nerves, and pulp (connective tissue) Dentin – bonelike tissue that surrounds the pulp cavity Enamel – extremely hard, acellular substance that coversthe dentin of the tooth drown Cementum – covers the surface of the dentin in the root; anchors the tooth in the jaw Alveoli (along the alveolar process of mandible x maxillae) – where the teeth are rooted Gingiva – dense fibrous CT and most stratified squamous epithelium that covers the alveolar processes Periodontal ligaments – CT fibers that extend from the alveolar walls that hold the teeth in place Dental caries / Tooth decay – result of the breakdown of enamel by acids produced by bacteria on tooth surface Owned By: Pdf_sells
- 3. Periodontal disease – inflammation x degeneration of the periodontal ligaments, gingiva, alveolar bone Palate and Tonsils Palate – roof of the oral cavity; prevents food from passing into the nasal cavity during chewing and swallowing a. Hard palate – anterior part that contains bone b. Soft palate – posterior portion that consists of skeletal muscle _ CT • Uvula – grape-like; posterior extension of the soft palate Tonsils – protect against pathogens from entering the nose and mouth Salivary Glands • Produce saliva (serous + mucous fluids) 3 Pairs of SG 1. Parotid glands – largest; serous glands located anterior to each ear 2. Submandibular glands – produce more serous than mucous secretions 3. Sublingual glands– smallest; produce primarily mucous secretions Mumps – inflammation of the parotid gland caused by viral infection Saliva ▪ Helps keep the oral cavity moist ▪ Contains enzymes that begin the process of digestion Salivary amylase – a digestive enzyme that breaks the covalent bonds bet. glucose molecules (starch) and other polysaccharides; enhances the sweet taste of food Lysozyme – enzyme that has weak antibacterial action Tongue – house taste buds and mucus Mastication • Breaks large food particles into many small ones • Increases the efficiency of digestion Pharynx • Throat • Connects the mouth with the esophagus • Oropharynx + laryngopharynx – transmit food • Contains pharyngeal constrictor muscles Esophagus ▪ Muscular tube that ransports food from thepharynx to the stomach ▪ Esophageal sphincters – regulate the movementof food into and out of the esophagus ▪ Cardiac sphincter – lower ES Swallowing / Deglutition 1. Voluntary Phase Owned By: Pdf_sells
- 4. ▪ Bolus (mass of food) us formed in the mouth ▪ Bolus is pushed by the tongue forcing in into theoropharynx 2. Pharyngeal Phase ▪ A reflex initiated when a bolus of food stimulates receptors in the oropharynx ▪ Epiglottis – tipped posteriorly to cover thelarynx 3. Esophageal Phase ▪ Responsible for moving food form the pharynx to the stomach ▪ Peristaltic waves – muscular contractions of theesophagus STOMACH ▪ Functions primarily as a storage and mixing chamber for ingested food Anatomy Gastroesophageal opening– opening from theesophagus into the stomach Cardiac region – region of around the gastroesophageal opening; near the heart Fundus – most superior part of the stomach Body – largest part of the stomach ❖ Greater curvature ❖ Lesser curvature Pyloric opening – opening from the stomach into thesmall intestine Pyloric sphincter – thick ring of smooth muscle Owned By: Pdf_sells
- 5. Pyloric region – region near the pyloric opening Outer longitudinal, middle circular, and inner oblique layer – produce a churning action in the stomach Rugae – large folds where the submucosa and mucosaare thrown into when the stomach is empty Gastric pits – openings for the gastric glands; formed by simple columnar epithelium Epithelial cells of the Stomach 1. Surface mucous cells – inner surface of stomach & lining the gastric pits; coats and protects the stomach lining 2. Mucous neck cells – produce mucus 3. Parietal cells – produce hydrochloric acid &intrinsic factor 4. Endocrine cells – produce regulatory chemicals 5. Chief cells – produce pepsinogen (precursor ofthe protein digesting enzyme pepsin) Secretions of the Stomach Chyme – semifluid mixture (food + stomach secretions) 1. Hydrochloric acid kills microorganisms and activates pepsin 2. Pepsin breaks covalent bond of proteins to form smaller peptide chains. 3. Mucus lubricates and protects epithelial cells from the damaging effect of acidic chime + pepsin 4. Intrinsic factor binds with vit. B12 (DNA synthesis and RBC prod.) and makes it more readily absorbed in the small intestine Regulation of Stomach Secretions 1. Cephalic phase – stomach Owned By: Pdf_sells
- 6. secretions are initiated by the sight, smell, taste, or thought of food 2. Gastric phase – partially digested proteins and distention of the stomach promote secretion ➢ Gastrin – hormone that enters the circulation and is carried back to the stomach 3. Intestinal phase – acidic chime in the duodenum stimulates neuronal reflexes and the secretion of hormones that inhibit gastric secretions by negative feedback loops ➢ Secretin – hormone that inhibits gastric secretions; released from the duodenum in response to low pH ➢ Cholecystokinin – major inhibitor of gastric motility; released from the duodenum initiated by fatty acids and peptides Movement in the Stomach ▪ Increased motility = increases emptying ▪ Distention of stomach = increases gastricmotility A. Mixing waves – thoroughly mix ingested foodwith stomach secretions to form chime ➢ Fluid part of chime – pushed towardthe pyloric sphincter ➢ Solid center – moves back toward thebody of the stomach B. Peristaltic waves – force the chime toward and through the pyloric sphincter SMALL INTESTINE ▪ Major site of digestion and absorption of food ▪ Major function is the absorption of nutrients Anatomy 1. Duodenum – 12 in. long; contains absorptive cells, goblet cells. Granular cells and endocrine cells 2. Jejunum – 2.5 m long; makes up 2/5 3. Ileum – 3.5 m long; makes up 3/5 Owned By: Pdf_sells
- 7. Common bile duct (liver) and pancreatic duct (pancreas) – join and empty into the duodenum Increased surface area 1. Circular folds – formed by mucosa and submucosa that run perpendicular to the long axis of the digestive tract 2. Villi – formed by tiny, fingerlike projections of the mucosa 3. Microvilli – numerous cytoplasmic extensions on the surface of the villi Lacteal – lymphatic capillary Simple Columnar Epithelium 1. Absorptive cells – have microvilli, producedigestive enzymes, absorb digested food 2. Goblet cells – produce a protective mucus 3. Granular cells – help protect the intestinalepithelium from bacteria 4. Endocrine cells – produce regulatory hormones Intestinal glands – epithelial cells produced within tubular galnds of mucosa Duodenal glands – mucous glands in the submucosa of the duodenum Peyer patches – clusters of lymphatic nodules along the digestive tract; collection of lymphatic tissue Ileocecal junction – where the ileum connects to thelarge intestine Ileocecal sphincter – ring of smooth muscle Ileocecal valve – allow intestinal contents to move from the ileum to the large intestine; but not in opposite direction Secretions of the Small Intestine 1. Peptidases – break peptide bonds in proteins toform amino acids 2. Disaccharidases – break down disaccharides(maltose) into monosaccharides (glucose) Movement of the Small Intestine A. Peristaltic contractions – proceed along the length of the intestine for variable distances; causes the chime to move along the small intestine B. Segmental contractions – propagate for shotdistances; mix intestinal contents LIVER AND PANCREAS Anatomy of Liver Major Lobes 1. Right lobe 2. Left lobe Falciform ligament – CT septum that separates the right and left lobe of the liver Smaller Lobes 1. Caudate lobe 2. Quadrate lobe Porta – gate through which blood vessels, ducts, andnerves enter and exit the liver Owned By: Pdf_sells
- 8. Sources of Blood in the Liver 1. Hepatic artery – takes oxygen- rich blood to theliver; supplies liver with oxygen 2. Hepatic portal vein – oxygen- poor blood butrich in nutrients Hepatic veins – where blood exits the liver and emptyinto the inferior vena cava Portal Triads 1. Hepatic artery 2. Hepatic portal vein 3. Hepatic duct Hepatic cords – located bet. the center and margins ofeach lobule Hepatocytes – platelike groups that form the hepaticcords Hepatic sinusoids – blood channels that separates thehepatic cords from one another Central vein – where mixed blood flows toward thecenter of each lobule Bile canaliculus – a cleftlike lumen bet. the cells of eachhepatic cord Common hepatic duct – right + left hepatic ducts Common bile duct – common hepatic duct + cystic duct Gallbladder – stores and concentrates bile Duodenal papilla – where the common bile duct joindthe pancreatic duct and opens into the duodenum Functions of the Liver 1. Digestion 2. Excretion 3. Nutrient storage 4. Nutrient conversion 5. Detoxification of harmful chemicals 6. Synthesis of new molecules Bile – dilutes and neutralizes stomach acid; dramatically increases the efficiency of fat digestion and absorption; stimulated by secretin Bile salts – emulsify fats Bilirubin – bile pigment that results from the breakdown of hemoglobin Anatomy of Pancreas 1. Head – near the midline of the body 2. Tail – extends to the left Pancreatic islet / Islets of Langerhans – endocrine part;produce insulin and glucagon Compound acinar gland – exocrine part Acini – produce digestive enymes Pancreatic duct – formed by larger ducts from clustersof acini Functions of the Pancreas Major Proteolytic enzymes – continue protein digestionthat began in the stomach 1. Trypsin 2. Chymotrypsin 3. Carboxypeptidase Owned By: Pdf_sells
- 9. Pancreatic amylase – continues polysaccharide digestionthat began in the oral cavity Lipase – lipid-digesting enzyme Nucleases – enzymes that degrade DNA and RNA totheir component nucleotides LARGE INTESTINE Anatomy Cecum ▪ Proximal end of the large intestine Appendix – 9 cm tube attached to the cecum Colon 1. Ascending colon 2. Transverse colon 3. Descending colon 4. Sigmoid colon Crypts – straight, tubular glands in the mucosal lining of the colon Teniae coli – three bands Rectum ▪ Straight, muscular tube that begins at the termination of sigmoid colon & ends at the anal canal Anal Canal ▪ Begins at the inferior end of the rectum and ends at the anus (external digestive tract opening) Internal anal sphincter – smooth muscle layer at superior end External anal sphincter – skeletal muscle at inferior end Hemorrhoids – enlarged or inflamed rectal or hemorrhoidal, veins that supply the anal canal; may cause pain, itching, bleeding around anus Functions of Large Intestine 1. Feces production 2. Water absorption Feces – converted chyme Defecation – elimination of feces from the colon Mass movements – strong contractions in the large partsof the colon; propel the colon contents a considerable distance towards the anys Defecation reflex – local (weak contractions) +parasympathetic (strong contractions) reflexes DIGESTION, ABSORPTION, AND TRANSPORT Digestion - breakdown of food to molecules tha are small enough to be absorbed into the circulation a. Mechanical digestion – breaks large good particles into smaller ones b. Chemical digestion – breaking of covalent chemical bonds in organic molecules by digestive enzymes Absorption - begin in stomach; lipid-soluble molecules diffuse through the stomach epithelium into the circulation Transport - requires carrier molecules and includes facilitated diffusion, cotransport, and active transport Carbohydrates ▪ Consist primarily of starches, cellulose, sucrose (table sugar), small amounts of fructose (fruit Owned By: Pdf_sells
- 10. sugar), and lactose (milk sugar) Polysaccharides – large carbohydrates that consist of many sugars linked by chemical bonds Salivary amylase – begins the digestion of carbohydrates in the mouth Pancreatic amylase – continues digestion of carbohydrates Disaccharides – two sugars; broken down polysaccharide Disaccharidase – group of enzymes that break the disaccharides to monosaccharides Monosaccharides – single sugars; glucose, galactose, and fructose Lipids ▪ Molecules which are insoluble or slightlysoluble in water Triglycerides – most common type of lipid; 3 fatty acids bound to glycerol Saturated – fatty acids have only single bonds Unsaturated – fatty acids have one or more double bonds Emulsification – large lipid droplets are transformed into much smaller droplets Lipase – secreted by pancreas; digests lipid molecules Micelles – aggregated bile salts around small droplets ofdigested lipids Chylomicrons – packaged lipid- protein complexes (lipoproteins) Chyle – lymph containing late amounts of absorbed lipid Proteins ▪ Chains of amino acids Pepsin – enzyme secreted by stomach that breaks down proteins Polypeptides – shorter amino acid chains Trypsin, Chymotrypsin, Carboxypeptidase – enzymes produced by pancreas that continue the digestive process Peptidases – small peptides Water and Minerals ▪ Approximately 9 L of water enters the digestivetract ▪ Approximately 2 L from food & drink &remaining 7 liters is from digestive secretions Owned By: Pdf_sells