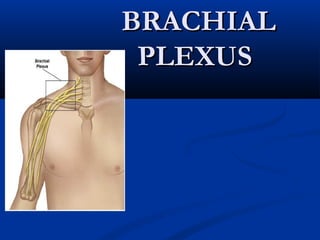
Brachial plexus
- 2. plexus is a latin word meaning "braid"; axonsplexus is a latin word meaning "braid"; axons from spinal cord levels C5-T1 are mixedfrom spinal cord levels C5-T1 are mixed (braided) in the brachial plexus and repackaged(braided) in the brachial plexus and repackaged into terminal branches so that each branchinto terminal branches so that each branch contains axons from several spinal cordcontains axons from several spinal cord segmental levelssegmental levels
- 4. The plexus is formed by the ventral rami ofThe plexus is formed by the ventral rami of spinal nerves C5–8 and T1.spinal nerves C5–8 and T1. These are the roots of the brachial plexus thatThese are the roots of the brachial plexus that supplies the upper limb.supplies the upper limb. C5–8 emerge into the neck between scalenusC5–8 emerge into the neck between scalenus anterior and medius.anterior and medius. T1 emerges inferior to the neck of the first rib,T1 emerges inferior to the neck of the first rib, but joins the plexus above the apex of the lung.but joins the plexus above the apex of the lung.
- 5. C5 and C6 form the upper trunk, C7 continuesC5 and C6 form the upper trunk, C7 continues as the middle trunk, while C8 and T1 form theas the middle trunk, while C8 and T1 form the lower trunklower trunk The trunks pass laterally and lie around theThe trunks pass laterally and lie around the subclavian artery while passing over the first ribsubclavian artery while passing over the first rib to enter the axilla, between the clavicle and theto enter the axilla, between the clavicle and the scapula.scapula.
- 6. Behind the clavicle, each trunk splits intoBehind the clavicle, each trunk splits into anterior and posterior divisions.anterior and posterior divisions. These recombine to form the posterior , lateralThese recombine to form the posterior , lateral and medial cords around the axillary arteryand medial cords around the axillary artery The upper roots (C5–7) tend to stay lateral, theThe upper roots (C5–7) tend to stay lateral, the lower roots (C8,T1) tend to stay medial.lower roots (C8,T1) tend to stay medial.
- 7. All roots contribute to the posterior cord, andAll roots contribute to the posterior cord, and therefore also to the radial nerve.therefore also to the radial nerve. The median nerve is formed from both lateralThe median nerve is formed from both lateral and medial cords, therefore also contains alland medial cords, therefore also contains all roots.roots.
- 8. Proximal muscles tend to be supplied by nerveProximal muscles tend to be supplied by nerve roots that emerge from higher segments of theroots that emerge from higher segments of the spinal cord.spinal cord. Distal muscles are supplied by nerves arisingDistal muscles are supplied by nerves arising from the lower segmentsfrom the lower segments
- 9. The five main branches of the brachial plexusThe five main branches of the brachial plexus are median , ulnar , radial , axillary andare median , ulnar , radial , axillary and musculocutaneous nervesmusculocutaneous nerves Branches from both lateral and medial cordsBranches from both lateral and medial cords supply the pectoral muscles. After supplying thesupply the pectoral muscles. After supplying the pectorals and contributing to the median nerve,pectorals and contributing to the median nerve, the lateral cord becomes the musculocutaneousthe lateral cord becomes the musculocutaneous nerve.nerve.
- 10. subscapularis, teres major and latissimus dorsisubscapularis, teres major and latissimus dorsi are supplied by the posterior cord, which alsoare supplied by the posterior cord, which also gives the axillary nerve to deltoid and teresgives the axillary nerve to deltoid and teres minor before continuing as the radial nerve.minor before continuing as the radial nerve. The medial cord contributes to the medianThe medial cord contributes to the median nerve, and also gives cutaneous nerves to thenerve, and also gives cutaneous nerves to the medial arm and forearm before continuing asmedial arm and forearm before continuing as the ulnar nerve.the ulnar nerve.
- 12. Upper trunk injuryUpper trunk injury removes C5 and C6, whichremoves C5 and C6, which supply the shoulder abductors and externalsupply the shoulder abductors and external rotators, and the elbow flexors and supinators.rotators, and the elbow flexors and supinators. Consequently, the upper limb lies at the sideConsequently, the upper limb lies at the side adducted and internally rotated. . The elbow isadducted and internally rotated. . The elbow is extended and pronated. The fingers may flexextended and pronated. The fingers may flex slightly and the condition , Erb’s palsy, is oftenslightly and the condition , Erb’s palsy, is often called ‘waiter’s tip’ palsycalled ‘waiter’s tip’ palsy
- 13. Lower trunk injuryLower trunk injury (Klumpke’s paralysis)(Klumpke’s paralysis) removes C8 and T1, therefore all the thenar andremoves C8 and T1, therefore all the thenar and hypothenar muscles are affected, along with thehypothenar muscles are affected, along with the lumbricals and interossei. The hand is flattenedlumbricals and interossei. The hand is flattened and the fingers clawed.and the fingers clawed.
- 14. Brachial plexusBrachial plexus dorsal scapular,dorsal scapular, long thoracic,long thoracic, n. to subclavius,n. to subclavius, suprascapular,suprascapular, lateral and medial pectoral,lateral and medial pectoral, medial brachial and antebrachial cutaneous,medial brachial and antebrachial cutaneous, upper, middle and lower subscapular,upper, middle and lower subscapular, musculocutaneous,musculocutaneous, ulnar,ulnar, median,median, axillary,axillary, radialradial
- 15. Brachial plexus lesion, superior trunkBrachial plexus lesion, superior trunk EtiologyEtiology traffic accidents, birth injuries; these injuries aretraffic accidents, birth injuries; these injuries are normally combined with lesions of otherproximalnormally combined with lesions of otherproximal structures (other trunks, root avulsions)structures (other trunks, root avulsions) humerus luxations (unusual, may engage distal parts ofhumerus luxations (unusual, may engage distal parts of plexus)plexus) brachial plexus neuritisbrachial plexus neuritis stab and bullet woundsstab and bullet wounds tumors (especially lung cancer and metastasis of thetumors (especially lung cancer and metastasis of the lymph nodes in the axilla)lymph nodes in the axilla)
- 16. Brachial plexus lesion, superior trunkBrachial plexus lesion, superior trunk Clinical featuresClinical features weakness and/or atrophy of shoulderweakness and/or atrophy of shoulder abduction, elbow flexion, upper arm outwardabduction, elbow flexion, upper arm outward rotationrotation loss of sensation over the lateral side of theloss of sensation over the lateral side of the upper arm and the thumbupper arm and the thumb
- 17. Brachial plexus lesion, medial trunkBrachial plexus lesion, medial trunk EtiologyEtiology traffic accidents, birth injuries; these injuries aretraffic accidents, birth injuries; these injuries are normally combined with lesions of otherproximalnormally combined with lesions of otherproximal structures (other trunks, root avulsions)structures (other trunks, root avulsions) humerus luxations (unusual, may engage distal parts ofhumerus luxations (unusual, may engage distal parts of plexus)plexus) acute idiopathic mononeuropathy (brachial plexusacute idiopathic mononeuropathy (brachial plexus neuritis, neuralgic amyotrophy)neuritis, neuralgic amyotrophy) stab and bullet woundsstab and bullet wounds tumors (especially lung cancer and metastasis of thetumors (especially lung cancer and metastasis of the lymf nodes in the axilla)lymf nodes in the axilla)
- 18. Brachial plexus lesion, medial trunkBrachial plexus lesion, medial trunk Clinical featuresClinical features weakness of elbow extension, wrist flexion andweakness of elbow extension, wrist flexion and extensionextension numbness and/or loss of sensation in fingers 2-numbness and/or loss of sensation in fingers 2- 33
- 19. Brachial plexus lesion, inferior trunkBrachial plexus lesion, inferior trunk EtiologyEtiology cervical rib, fibrous band from C7 (neurogenic thoracic outletcervical rib, fibrous band from C7 (neurogenic thoracic outlet syndrome)syndrome) traffic accidents, birth injuries. these injuries are normallytraffic accidents, birth injuries. these injuries are normally combined with lesions of other proximalstructures (other trunks,combined with lesions of other proximalstructures (other trunks, root avulsions)root avulsions) humerus luxations (unusual, may engage distal parts of plexus)humerus luxations (unusual, may engage distal parts of plexus) acute idiopathic mononeuropathy (brachial plexus neuritis,acute idiopathic mononeuropathy (brachial plexus neuritis, neuralgic amyotrophy)neuralgic amyotrophy) stab and bullet woundsstab and bullet wounds tumors (especially lung cancer and metastasis of the lymf nodestumors (especially lung cancer and metastasis of the lymf nodes in the axilla)in the axilla)
- 20. Brachial plexus lesion, inferior trunkBrachial plexus lesion, inferior trunk Clinical featuresClinical features weakness and/or atrophy of intrinsic handweakness and/or atrophy of intrinsic hand musclesmuscles numbness and/or loss of sensation in fingers 4-numbness and/or loss of sensation in fingers 4- 55
- 21. Brachial plexus lesion, lateral fascicleBrachial plexus lesion, lateral fascicle EtiologyEtiology traffic accidents, birth injuries; these injuries aretraffic accidents, birth injuries; these injuries are normally combined with lesions of other proximalnormally combined with lesions of other proximal structures (other trunks, root avulsions)structures (other trunks, root avulsions) humerus luxations (unusual, may engage distal parts ofhumerus luxations (unusual, may engage distal parts of plexus)plexus) acute idiopathic mononeuropathy (brachial plexusacute idiopathic mononeuropathy (brachial plexus neuritis, neuralgic amyotrophy)neuritis, neuralgic amyotrophy) stab and bullet woundsstab and bullet wounds tumors (especially lung cancer and metastasis of thetumors (especially lung cancer and metastasis of the lymf nodes in the axilla)lymf nodes in the axilla)
- 22. Brachial plexus lesion, lateral fascicleBrachial plexus lesion, lateral fascicle Clinical featuresClinical features weakness and atrophy of muscles innervated byweakness and atrophy of muscles innervated by n.medianus and n.musculocutaneusn.medianus and n.musculocutaneus numbness and/or loss of sensation of fingers 1-numbness and/or loss of sensation of fingers 1- 33
- 23. Brachial plexus lesion, posterior fascicleBrachial plexus lesion, posterior fascicle EtiologyEtiology traffic accidents, birth injuries; these injuries aretraffic accidents, birth injuries; these injuries are normally combined with lesions of other proximalnormally combined with lesions of other proximal structures (other trunks, root avulsions)structures (other trunks, root avulsions) humerus luxations (unusual, may engage distal parts ofhumerus luxations (unusual, may engage distal parts of plexus)plexus) acute idiopathic mononeuropathy (brachial plexusacute idiopathic mononeuropathy (brachial plexus neuritis, neuralgic amyotrophy)neuritis, neuralgic amyotrophy) stab and bullet woundsstab and bullet wounds tumors (especially lung cancer and metastasis of thetumors (especially lung cancer and metastasis of the lymf nodes in the axilla)lymf nodes in the axilla)
- 24. Brachial plexus lesion, posterior fascicleBrachial plexus lesion, posterior fascicle Clinical featuresClinical features weakness and atrophy of muscles innervated byweakness and atrophy of muscles innervated by n.axillaris and n.radialisn.axillaris and n.radialis
- 25. Brachial plexus lesion, medial fascicleBrachial plexus lesion, medial fascicle EtiologyEtiology traffic accidents, birth injuries; these injuries aretraffic accidents, birth injuries; these injuries are normally combined with lesions of other proximalnormally combined with lesions of other proximal structures (other trunks, root avulsions)structures (other trunks, root avulsions) humerus luxations (unusual, may engage distal parts ofhumerus luxations (unusual, may engage distal parts of plexus)plexus) acute idiopathic mononeuropathy (brachial plexusacute idiopathic mononeuropathy (brachial plexus neuritis, neuralgic amyotrophy)neuritis, neuralgic amyotrophy) stab and bullet woundsstab and bullet wounds tumors (especially lung cancer and metastasis of thetumors (especially lung cancer and metastasis of the lymf nodes in the axilla)lymf nodes in the axilla)
- 26. Brachial plexus lesion, medial fascicleBrachial plexus lesion, medial fascicle Clinical featuresClinical features weakness of muscles innervated by n.ulnaris andweakness of muscles innervated by n.ulnaris and n.medianusn.medianus numbness and/or loss of sensation in fingers 4-numbness and/or loss of sensation in fingers 4- 55
- 27. Erb's Palsy (Brachial PlexusErb's Palsy (Brachial Plexus Birth Palsy)Birth Palsy) Erb's palsy is a form of brachial plexus palsy. ItErb's palsy is a form of brachial plexus palsy. It is named for one of the doctors who firstis named for one of the doctors who first described this condition, Wilhelm Erb.described this condition, Wilhelm Erb. The brachial plexus is a network of nerves nearThe brachial plexus is a network of nerves near the neck that give rise to all the nerves of thethe neck that give rise to all the nerves of the arm. These nerves provide movement andarm. These nerves provide movement and feeling to the arm, hand, and fingers. Palsyfeeling to the arm, hand, and fingers. Palsy means weakness, and brachial plexus birth palsymeans weakness, and brachial plexus birth palsy causes arm weakness and loss of motion.causes arm weakness and loss of motion.
- 28. One or two of every 1,000 babies have thisOne or two of every 1,000 babies have this condition. It is often caused when an infant'scondition. It is often caused when an infant's neck is stretched to the side during a difficultneck is stretched to the side during a difficult delivery.delivery. Most infants with brachial plexus birth palsy willMost infants with brachial plexus birth palsy will recover both movement and feeling in therecover both movement and feeling in the affected arm. Parents must be watchful andaffected arm. Parents must be watchful and active participants in the treatment process toactive participants in the treatment process to make sure their child recovers maximummake sure their child recovers maximum function in the affected arm.function in the affected arm.
- 29. In most cases of brachial plexus birth palsy, it isIn most cases of brachial plexus birth palsy, it is the upper nerves that are affected. This is knownthe upper nerves that are affected. This is known as Erb's palsy. The infant may not be able toas Erb's palsy. The infant may not be able to move the shoulder, but may be able to move themove the shoulder, but may be able to move the fingers. If both the upper and lower nerves arefingers. If both the upper and lower nerves are stretched, the condition is usually more severestretched, the condition is usually more severe than just Erb's palsy. This is called a "global," orthan just Erb's palsy. This is called a "global," or total, brachial plexus birth palsy.total, brachial plexus birth palsy.
- 30. In general, there are four types of nerve injuries.In general, there are four types of nerve injuries. All can occur at the same time in the sameAll can occur at the same time in the same infant. The symptoms of a nerve injury are theinfant. The symptoms of a nerve injury are the same (loss of feeling and partial or completesame (loss of feeling and partial or complete paralysis), regardless of the type of injury. It isparalysis), regardless of the type of injury. It is the severity of the injury that affects boththe severity of the injury that affects both treatment decisions and the extent of recoverytreatment decisions and the extent of recovery possible.possible.
- 31. NeurapraxiaNeurapraxia A stretch injury that "shocks," but does not tearA stretch injury that "shocks," but does not tear the nerve is the most common type. This isthe nerve is the most common type. This is called a neurapraxia. Normally, these injuriescalled a neurapraxia. Normally, these injuries heal on their own, usually within 3 months.heal on their own, usually within 3 months. Neurapraxia can happen in adults, as well asNeurapraxia can happen in adults, as well as infants. For example, when it happens toinfants. For example, when it happens to football players who are injured during play, it isfootball players who are injured during play, it is called "burners and stingers."called "burners and stingers."
- 32. NeuromaNeuroma A stretch injury that damages some of the nerveA stretch injury that damages some of the nerve fibers may result in scar tissue. This scar tissuefibers may result in scar tissue. This scar tissue may press on the remaining healthy nerve. Thismay press on the remaining healthy nerve. This condition is called a "neuroma." Some, but notcondition is called a "neuroma." Some, but not total, recovery usually occurstotal, recovery usually occurs
- 33. RuptureRupture A stretch injury that causes the nerve to be tornA stretch injury that causes the nerve to be torn apart (ruptured) will not heal on its own. Aapart (ruptured) will not heal on its own. A rupture happens when the nerve itself is torn.rupture happens when the nerve itself is torn.
- 34. AvulsionAvulsion An avulsion happens when the nerve is tornAn avulsion happens when the nerve is torn from the spinal cord. Nerve ruptures andfrom the spinal cord. Nerve ruptures and avulsions are the most serious types of nerveavulsions are the most serious types of nerve injury. It may be possible to repair a rupture byinjury. It may be possible to repair a rupture by "splicing" a donor nerve graft from another"splicing" a donor nerve graft from another nerve of the child. It is not possible to repair annerve of the child. It is not possible to repair an avulsion from the spinal cord. In some cases, itavulsion from the spinal cord. In some cases, it may be possible to restore some function in themay be possible to restore some function in the arm by using a nerve from another muscle as aarm by using a nerve from another muscle as a donor.donor.
- 35. CauseCause Brachial plexus stretch injuries in newbornsBrachial plexus stretch injuries in newborns usually occur during a difficult delivery, such asusually occur during a difficult delivery, such as with a large baby, a breech presentation, or awith a large baby, a breech presentation, or a prolonged labor. It may also happen when aprolonged labor. It may also happen when a birth becomes complicated and the personbirth becomes complicated and the person assisting the delivery must deliver the babyassisting the delivery must deliver the baby quickly and exert some force to pull the babyquickly and exert some force to pull the baby from the birth canal. If one side of the baby'sfrom the birth canal. If one side of the baby's neck is stretched, the nerves may also beneck is stretched, the nerves may also be stretched, and injury may result.stretched, and injury may result.
- 36. SymptomsSymptoms Weakness in one armWeakness in one arm Loss of feeling in the armLoss of feeling in the arm Partial or total paralysis of the armPartial or total paralysis of the arm
- 37. DIAGNOSISDIAGNOSIS A pediatrician is usually the one to make theA pediatrician is usually the one to make the diagnosis of a brachial plexus palsy injury, baseddiagnosis of a brachial plexus palsy injury, based on weakness of the arm and physicalon weakness of the arm and physical examination.examination. Your doctor may order an x-ray or otherYour doctor may order an x-ray or other imaging study to learn whether there is anyimaging study to learn whether there is any damage to the bones and joints of the neck anddamage to the bones and joints of the neck and shoulder. He or she may also do some tests toshoulder. He or she may also do some tests to learn whether any nerve signals are present inlearn whether any nerve signals are present in the muscle of the upper arm. These tests maythe muscle of the upper arm. These tests may include an electromyogram (EMG) or a nerveinclude an electromyogram (EMG) or a nerve conduction study (NCS).
- 38. TreatmentTreatment Because most newborns with brachial plexusBecause most newborns with brachial plexus birth palsy recover on their own, the doctor willbirth palsy recover on their own, the doctor will re-examine the child frequently to see if there-examine the child frequently to see if the nerves are recovering. It may take up to 2 yearsnerves are recovering. It may take up to 2 years for complete recovery.for complete recovery. Nonsurgical TreatmentNonsurgical Treatment Daily physical therapy isDaily physical therapy is the main treatment method for Erb's palsy.the main treatment method for Erb's palsy. Because a baby cannot move the affected arm allBecause a baby cannot move the affected arm all alone, parents must take an active role inalone, parents must take an active role in keeping the joints limber and the functioningkeeping the joints limber and the functioning muscles fit.muscles fit.
- 39. Daily physical therapy and range of motionDaily physical therapy and range of motion exercises, done as often as possible during theexercises, done as often as possible during the day, begin when a baby is about 3 weeks old.day, begin when a baby is about 3 weeks old. The exercises will maintain the range of motionThe exercises will maintain the range of motion in the shoulder, elbow, wrist, and hand. This willin the shoulder, elbow, wrist, and hand. This will prevent the joint from becoming permanentlyprevent the joint from becoming permanently stiff, a condition called joint contracture.stiff, a condition called joint contracture.
- 40. Surgical TreatmentSurgical Treatment If there is no change overIf there is no change over the first 3 to 6 months, doctors may suggestthe first 3 to 6 months, doctors may suggest exploratory surgery on the nerves to improveexploratory surgery on the nerves to improve the potential outcome. Nerve surgery will notthe potential outcome. Nerve surgery will not restore normal function, and is usually notrestore normal function, and is usually not helpful for older infants. Because nerves recoverhelpful for older infants. Because nerves recover very slowly, it may take several months, or evenvery slowly, it may take several months, or even years, for nerves repaired at the neck to reachyears, for nerves repaired at the neck to reach the muscles of the lower arm and hand. Manythe muscles of the lower arm and hand. Many children with brachial plexus injuries willchildren with brachial plexus injuries will continue to have some weakness in the shoulder,continue to have some weakness in the shoulder, arm, or hand. There may be surgical proceduresarm, or hand. There may be surgical procedures that can be performed at a later date that mightthat can be performed at a later date that might