Larval Stage in Different Animal
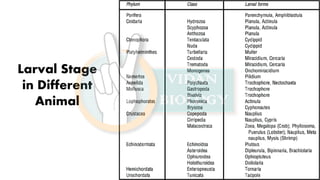
- 2. one of the free swimming larval stages of sponges and numerous coelenterates. The elongated oval body consists of flagellate ectodermal cells and a mass of entodermal cells (parenchyma). In sponges, the parenchymula settles to the bottom and becomes attached; in coelenterates, it changes into the planula stage. Amphiblastula larva is found in some of the sponges. It is a free-swimming larva with the front half having flagellated cells and the other half having cells without flagella Parenchymula Parenchymula Amphiblastula
- 3. Actinula A larval stage of some hydrozoans that has tentacles and a mouth; attaches and develops into a hydroid in some species, or metamorphoses into a medusa. planula, plural planulae, free-swimming or crawling larval type common in many species of the phylum Cnidaria (e.g., jellyfish, corals, and sea anemones). The planula body is more or less cylindrical or egg-shaped and bears numerous cilia (tiny hairlike projections), which are used for locomotion.
- 4. Cydippid muller larva cydippid larva A free-swimming, larval stage of a ctenophorid (Ctenophora) which resembles adults of the order Cydippidea Müller's larva or Mulleria is a larva of some Polycladida.[It has 8-fold symmetry and is somewhat like a ctenophore.[Müller’s larva is ciliated and has several paired and unpaired lobes.
- 5. The Miracidium is the second stage in the life cycle of trematodes. When trematode eggs are laid and come into contact with fresh water, they hatch and release miracidium. In this phase, miracidia are ciliated and free- swimming. A cercaria (plural cercariae) is the larval form of the trematode class of parasites. It develops within the germinal cells of the sporocyst or redia.] A cercaria has a tapering head with large penetration glands. It may or may not have a long swimming "tail", depending on the species.
- 6. An oncomiracidium is the ciliated and free- living larva of a monogenean, a type of parasitic flatworm commonly found on fish. It is similar to the miracidium of Trematoda, but has sclerotised (hardened) hooklets not found in the latter. The free-swimming hat-shaped larva of various nemertean worms in whose interior the young worm develops
- 7. Trochophore, also called trochosphere, small, translucent, free-swimming larva characteristic of marine annelids and most groups of mollusks. Trochophores are spherical or pear-shaped and are girdled by a ring of cilia (minute hairlike structures), the prototroch, that enables them to swim. The smallest Amphisamytha larvae fall in the size range of the nectochaetes and have a similar number of chaetigers. Nectochaete larvae have a ciliary band behind the head and are generally thinner for their length than Amphisamytha.
- 8. The cyphonautes larva is the planktonic propagule of benthic bryozoans. Usually found in shallow-water and can be common in some seasons.
- 9. In crustaceans the larva, called nauplius, does not differ substantially in mode of life or means of locomotion from the adult but has fewer appendages than the adult. A typical crustacean nauplius has three pairs of legs and an unpaired simple eye. Additional pairs of appendages and paired compound eyes appear in the course of a sometimes prolonged development.
- 10. •It is the larvae of Sacculina, Balanus and Lepas. •It develops from nauplius •It is a free swimming larva. •It is triangular in shape with bivalent shell. •The larva has seven pairs of appendages, namely a pair of antennules and six pair of thoracic appendages. •A median eye is present. •The larva contains a mass of germ cells. •It undergoes a remarkable series of metamorphoses to become the sessile adult form.
- 11. zoea A free-swimming planktonic larval form of many decapod crustaceans and especially crabs that has a relatively large cephalothorax, conspicuous eyes, and fringed antennae and mouthparts.
- 12. Megalopa larva •In true crabs, the zoaea larva or metazoaea larva passes through successive moults into the post larval megalopa stage. •It has a broad and crab-like unsegmented cephalothorax. •The carapace is produced anteriorly into a median spine. •The eyes are large, stalked and compound. •All the thoracic appendages are well formed of which the last 5 pairs are uniramous. •The abdomen is also well formed, straight and bears biramous pleopods.
- 13. Phyllosoma larva •In the rock- lobster (Palinurus), the newly hatched larva is called the phyllosoma larva or glass- crab •It is a greatly modified mysis stage. •It is a remarkable for its large size, extremely flattened and leaf- like delicate form and glassy transparency. •A narrow constriction demarcates the head from thorax. •A large oval carapace covers the head and the first two thoracic segments. •The eyes are compound and borne by large stalks. •Only anterior 6 pairs of thoracic appendages are present in the newly hatched larva. •The first thoracic appendages or maxillipedes are rudimentary (Palinurus) or absent (Scyllarus) and the second are uniramous; succeed by 4 pairs of very long and biramous legs with exopodites. •Last two pairs of thoracic appendages are usually absent. •Abdomen, though indistinctly segmented is very small and limbless. •Phyllosoma undergoes several moults before reaching the adult form
- 15. Metanauplius larva •It is the larva of Apus. •It is the second larval stage which develops from the nauplius larva. •The body has an anterior oval cephalothorax, an elongated trunk-region and an abdomen terminating in a caudal fork provided with setae. •The anterior end has a pair of frontal sense organs. •Dorsal shield of the head grows back to form carapace. •The larvae has three pair of appendages just as in nauplius, it also develops the rudiments of 4 pairs of appendages, which later become the maxillae and 2 pairs of maxillipedes of the adults.
- 16. Mysis larva •In Penaeus, the zoaea larva, instead of converting into the megalopa stage, moults into the post larval mysis larva. •It has 13 pairs of appendages. All the thoracic appendages are biramous. Even the 5 pairs of posterior thoracic legs are biramous with flagellar exopodites which take up the locomotory function. •The abdomen develops similar to that of the adult form, with 5 pairs of biramous pleopods and a pair of uropods and a telson. •The mysis larva metamorphosis in to the adult prawn by the loss of the exopodites on the thoracic legs.
- 18. •Sea urchins; the small and spiny creatures found in the oceans of the world. •Planktonic larva is called pluteus larva.
- 19. Dipluirula A hypothetical bilaterally symmetrical echinoderm larva sometimes regarded as a common ancestor of echinoderms and chordates 2: a larval echinoderm (such as a bipinnaria or an echinopluteus) —not used technically
- 20. Bipinnaria A bipinnaria is the first stage in the larval development of most starfish, and is usually followed by a brachiolaria stage. Movement and feeding is accomplished by the bands of cilia. Starfish that brood their young generally lack a bipinnaria stage, with the eggs developing directly into miniature adults The bipinnaria is free-living, swimming as part of the zooplankton. When it initially forms, the entire body is covered by cilia, but as it grows, these become confined to a narrow band forming a number of loops over the body surface.
- 22. A brachiolaria is the second stage of larval development in many starfishes. It follows the bipinnaria. Brachiolaria have bilateral symmetry, unlike the adult starfish, which have a pentaradial symmetry The brachiolaria develops from the bipinnaria larva when the latter grows three short arms at the underside of its anterior end. These arms each bear sticky cells at the tip, and they surround an adhesive sucker.
- 23. The larva of echinoderms of the class Ophiuro idea. An ophiopluteus has four pairs of long pr ocesses, or arms, enclosing calcareous rods. These arms, which are covered with a strip of ciliate epithelium, enable the larva to swim. Th ree pairs of coelomic sacs extend from the int estine; the left anterior sac opens to the outsid e through an interstitial canal. The adult form develops from the anterior part of the larva onl y.
- 25. A tornaria is the planktonic larva of some species of Hemichordata such as the acorn worms.It is very similar in appearance to the bipinnaria larvae of starfishes, with convoluted bands of cilia running around the body. It is an oval shaped, transparent larva. The diameter of the body is about 3 mm. It has an apical plate, which is a thickened region provided by a tuft of cilia and a pair of eye spots. The larva has a complete alimentary canal. The ciliary band stretches throughout the anterior and posterior region, and also the postoral region. References
