Bhu 19 pet_solved_3
- 1. Ans – 2
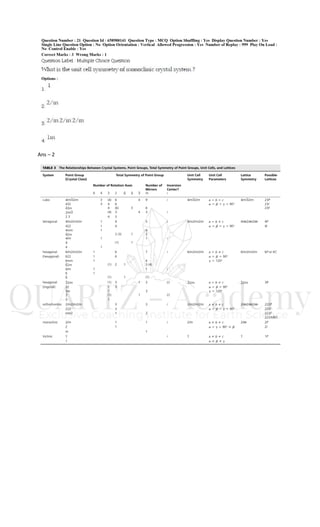
- 2. Ans – 3
- 3. Ans – 1 (Link is in description)
- 4. Ans – 2
- 7. Ans- 3 Double Refraction • In most modern polarizing microscopes, polarized light leaves the lower polarizer vibrating in the east-west direction. • If it encounters an isotropic mineral on the stage, it slows as it passes through the mineral, but is still east-west polarized when it emerges. • Upon entering an anisotropic crystal, however, light is normally split into two polarized rays, each traveling through the crystal along a slightly different path with a slightly different velocity and refractive index. • For uniaxial minerals, we call the two rays the ordinary ray (O ray), symbolized by ω and the extraordinary ray (E ray), symbolized by ε. • The O ray travels a path predicted by Snell’s Law, while the E ray does not. • The directions of the O-ray and E-ray vibrations depend on the direction the light is traveling through the crystal structure, but the vibration directions of the two rays are always perpendicular to each other. • We call the splitting of a light beam into two perpendicularly polarized rays double refraction. • All randomly oriented anisotropic minerals cause double refraction. • We can easily observe it by placing clear calcite over a piece of paper on which a line, dot, or other image has been drawn. • Two images appear, one corresponding to each of the two rays. A thin piece of polarizing film placed over the calcite crystal would verify that the two rays are polarized and vibrating perpendicular to each other. • If we rotate either the film or the crystal, every one ray becomes extinct, and we will see only one image. • Calcite is one of the few common minerals that exhibit double refraction easily seen without a microscope, but even minerals that exhibit subtler double refraction can be tested using polarizing filters. • Glass, like all isotropic substances, does not exhibit double refraction OR
- 8. ISOTROPIC AND ANISOTROPIC MINERALS • The majority of minerals polarise the light that passes through them. • In general, two rays of light are produced; their vibration directions are both at right angles to the direction of propagation of the light and at right angles to each other (this is not strictly true, but such an assumption simplifies the following explanations without detracting from the essential principles). • Minerals that affect light in such a way are termed anisotropic. • All crystals except those that belong to the cubic system are anisotropic (though a few anisotropic minerals may in practice appear to be isotropic, e.g. perovskite). • Cubic minerals do not polarise light passing through them, and they do not vary directionally in their effect on light. • Cubic minerals are therefore termed isotropic. Glass and amorphous substances are also isotropic. • Isotropism directly reflects the high degree of regularity in the atomic structure of cubic minerals. • The specific details of anisotropic optical properties also reflect the particular symmetry of the crystals. Double refraction • If a small clear cleavage rhomb of calcite is placed over a small dot, two images of the dot will be seen. • The two images represent the two separately polarised rays of light produced by the anisotropic calcite. • The fact that two images are seen demonstrates that each ray represents a different refractive index for the crystal (and also a different velocity of light). This phenomenon is known as double refraction, and is characteristic of all anisotropic minerals, although the amount of double refraction is unusually large in calcite. • The refractive index of all anisotropic minerals varies continuously depending on the vibration direction of the light within the crystal. ISOTROPIC MINERALS IN CROSSED-POLARISED LIGHT • Light is not polarised by cubic minerals. • Therefore, when light travels through such a mineral placed on the microscope stage, the vibration direction of light produced by the polariser is not changed, regardless of how we rotate the stage. • The light that reaches the analyser is thus polarised at right angles to the vibration direction of the analyser and is completely absorbed. • In other words, all cubic minerals (and glass) will appear black whenever observed in crossed-polarised light. • Only special sections of anisotropic minerals have this property.
- 9. ANISOTROPIC MINERALS IN CROSSED-POLARISED LIGHT Anisotropic minerals generally polarise light into two rays vibrating at right angles to each other. In the general situation, where these vibration directions are not parallel to those of the polariser and analyser, light from the polariser is resolved into two rays by the mineral (Fig. 14). These two rays are resolved by the analyser so that the light reaching the eye is only vibrating in the one direction allowed by the analyser. If the stage is rotated through 360°, there are four positions in which the two vibration directions of the mineral are parallel to those of the polariser and analyser (Fig. 15). In these positions light from the polariser cannot be resolved into two rays and passes through the mineral unchanged in vibration direction. This light is vibrating at right angles to the direction allowed by the analyser, which completely absorbs it. In general, therefore, all anisotropic minerals will go black (or will extinguish) in these four positions when the stage is rotated through 360°. As we shall see later, there are special sections of anisotropic minerals that remain black or very dark when the stage is rotated, and it is then necessary to make further tests to distinguish them from isotropic mineral sections.
- 10. Ans – 3 Birefringence (value). The difference between the greatest and least indices of refraction of a crystalline substance. (nslow - nfast) Ans – 4 Calcite – CaCO3 – Trigonal Magnesite – MgCO3 – Trigonal Siderite – FeCO3 – Hexagonal Cerussite – PbCO3 – Orthorhombic • Siderite is iron carbonate (FeCO3) with the same structure as calcite and is very difficult to distinguish between iron and calcium carbonates on mineralogical grounds. It is rarely pure, often containing some magnesium or manganese substituted for iron in the lattice. Siderite forms within sediments as an early diagenetic mineral.
- 12. Ans – 4
- 15. Ans – 1 Ans – 1 (Leucite is Feldspathoid) others are amphibole & pyroxene, link is in description.
- 17. Join us - Telegram – https://t.me/joinchat/F0YSxRk74GYHjhjMJVL6Nw WhatsApp Group 1 – https://chat.whatsapp.com/IP8aQw3hsTvEdWQvvwwzSt WhatsApp Group 2 - https://chat.whatsapp.com/LQmvgO8WXWX45kRh0cU3me Instagram – https://www.instagram.com/geologistical/ Facebook – https://www.facebook.com/Quartz-Exclusive-Coaching-Institute-for-earth-Sciences- 507962722965703 Slideshare – https://www.slideshare.net/nikhilsherekar LinkedIn - https://www.linkedin.com/in/nikhil-sherekar-8b179a9b/
