How enzymes work
- 1. How Enzymes Work Click here for audio
- 3. Lock and Key Analogy Click here for audio
Notas do Editor
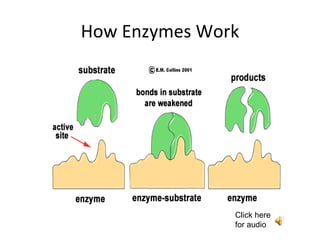
- A substrate binds to an enzyme’s active site. An example of a substrate could be a disaccharide, which means two sugars stuck together. This forms an enzyme-substrate complex. While attached to the substrate, the enzyme causes a weakening of certain chemical bonds in the substrate molecule, resulting in a breakdown (hydrolysis) of the substrate into two smaller product molecules (such as monosaccharides). The enzyme is unaltered during the reaction and is free to catalyze the breakdown of another substrate molecule.
- A substrate binds to an enzyme’s active site. An example of a substrate could be a polysaccharide. This forms an enzyme-substrate complex. While attached to the substrate, the enzyme causes a weakening of certain chemical bonds in the substrate molecule, resulting in a breakdown (hydrolysis) of the substrate into smaller product molecules (such as monosaccharides). The enzyme is unaltered during the reaction and is free to catalyze the breakdown of another substrate molecule.
- The active site has a unique geometric shape that is complementary to the geometric shape of a substrate molecule, similar to the fit of puzzle pieces. This means that enzymes specifically react with only one or a very few similar compounds. In this analogy, the lock is the enzyme and the key is the substrate. Only the correctly sized key (substrate) fits into the key hole (active site) of the lock (enzyme) . (incorrectly shaped or sized substrate molecules) do not fit into the lock (enzyme) and a chemical reaction will not occur.
- The active site has a unique geometric shape that is complementary to the geometric shape of a substrate molecule, similar to the fit of puzzle pieces. This means that enzymes specifically react with only one or a very few similar compounds.