C5e Gas Volumes
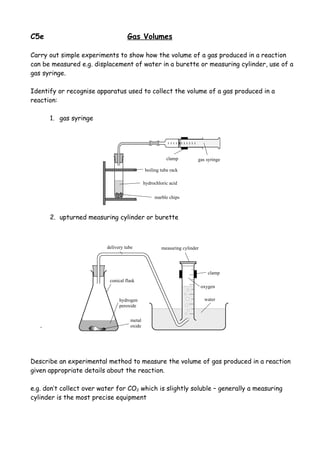
- 1. C5e Gas Volumes Carry out simple experiments to show how the volume of a gas produced in a reaction can be measured e.g. displacement of water in a burette or measuring cylinder, use of a gas syringe. Identify or recognise apparatus used to collect the volume of a gas produced in a reaction: 1. gas syringe clamp gas syringe boiling tube rack hydrochloric acid marble chips 2. upturned measuring cylinder or burette delivery tube measuring cylinder clamp conical flask oxygen hydrogen water peroxide metal . oxide Describe an experimental method to measure the volume of gas produced in a reaction given appropriate details about the reaction. e.g. don’t collect over water for CO2 which is slightly soluble – generally a measuring cylinder is the most precise equipment
- 2. Reactions Involving Gases Examples Mg + 2HCl MgCl2 + H2 CaCO3 + 2HCl CaCl2 + H2O + CO2 • A reaction stops when one of the reactants is all used up. • The more reactant you use the higher the volume of gas made • The limiting reactant is the one that is used up first • The other reactant is said to be in excess i.e. more than enough • A reaction stops when the limiting reactant has been used up • The volume of gas produced is directly proportional to the amount of the limiting reactant present Questions 1 gram of magnesium is reacted in excess hydrochloric acid. It took 30s for the reaction to stop and 52 cm3 of gas was collected. 1. What would you observe that tells you a reaction is taking place? 2. How would you know when the reaction had finished? Give 2 observations. 3. Why does the reaction stop? 4. Which is the limiting reactant? 5. How much gas would be collected after 60s? 6. If 2 grams of magnesium were used (and the acid was still in excess) how much gas would be collected by the time the reaction stopped? 20cm3 of hydrochloric acid was reacted with excess marble chips. 75cm3 of gas had been collected when the reaction stopped 7. Which is the limiting reactant? 8. How much gas would be collected if marble powder was used instead of marble chips? 9. How much gas would be collected 10cm3 of acid were used?
- 3. Reactions Involving Gases Examples Mg + 2HCl MgCl2 + H2 CaCO3 + 2HCl CaCl2 + H2O + CO2 • A reaction stops when _________________________________________ • The more reactant you use the __________________ the volume of gas made • The _____________________ reactant is the one that is used up first • The other reactant is said to be in ________________ i.e. more than enough • A reaction stops when the ____________________ reactant has been used up • The volume of gas produced is __________________ proportional to the amount of the limiting reactant present Questions 1 gram of magnesium is reacted in excess hydrochloric acid. It took 30s for the reaction to stop and 52 cm3 of gas was collected. 1. What would you observe that tells you a reaction is taking place? 2. How would you know when the reaction had finished? Give 2 observations. 3. Why does the reaction stop? 4. Which is the limiting reactant? 5. How much gas would be collected after 60s? 6. If 2 grams of magnesium were used (and the acid was still in excess) how much gas would be collected by the time the reaction stopped? 20cm3 of hydrochloric acid was reacted with excess marble chips. 75cm3 of gas had been collected when the reaction stopped 7. Which is the limiting reactant? 8. How much gas would be collected if marble powder was used instead of marble chips? 9. How much gas would be collected if 10cm3 of acid were used?
- 4. Investigating Rates of Reaction CaCO3 + 2HCl CaCl2 + H2O + CO2 Here are the results for the above reaction where HCl was reacted with excess marble chips, CaCO3, using different concentrations of acid. Concentration (mol/dm3) Time 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 (seconds) 0 0 0 0 0 15 18 8 4 4 30 30 15 9 7 45 42 21 11 12 60 49 22 13 15 75 50 30 15 20 90 59 34 20 21 105 62 37 23 23 120 66 39 27 24 135 67 40 30 24 150 68 41 31 24 165 69 42 33 24 180 70 43 34 24 1. Plot a graph using the results put time on the x axis 2. Describe the shape of the curves. 3. For the 0.8mol/dm3 solution label the fastest point on the graph? 4. How do we know the rate decreases (slows down) near the end? 5. How do we know when the reaction as stopped? 6. The gradient of this graph gives the rate of reaction at any point. Draw a tangent to the initial slope of your curve 7. Work out the gradient (y/x) of this tangent – this is your initial rate Now, given the results shown in the table below, determine the initial rates of reaction for the 4 different concentrations:
- 5. HIGHER Given the knowledge that one mole of gas molecules occupy a volume of 24 dm3 at room temperature and pressure, use it to calculate the volumes of samples of gases. Perform calculations involving gas volumes and number of moles.
- 6. Drawing Graphs and Making Predictions 1. Hydrochloric acid reacting with magnesium ribbon: a) Sketch a curve to show what happens to the volume of gas collected over a period of time when there is an increase in temperature. low temperature b) What factors must be kept constant? c) Explain the shape of the curve that you have drawn in as much detail as you can, refer to the gradient and final volume. d) What has happened to the rate? Explain why in terms of the collision theory in as much detail as you can. 2. Marble chips reacting in acid: a) Sketch a curve to show what happens to small marble the volume of gas collected over a period chips of time when larger marble chips are used. b) What factors must be kept constant? c) What has happened to the rate? Explain why in terms of the collision theory.
- 7. 3. Hydrochloric acid reacting with magnesium ribbon: a) Sketch 2 curves. One to show what happens to the volume of gas collected over a period of time when a more dilute solution is used and one to show a more concentrated solution. c) What has happened to the rate? Explain why in terms of the collision theory. 4. a) The graph below shows the volume of gas collected when 20cm3 of HCl were reacted with a large excess of marble chips. Sketch the shape of the graph that you would get if 40cm3 of HCl was reacted with a large excess. 40 Volume of CO2 30 produced (cm3) 20 10 Time (s) b) Explain your answer
- 8. Carry out experiments to measure the mass of a gas being produced during a reaction e.g. marble and acid and/or thermal decomposition of zinc carbonate. Describe that measurement of change of mass may be used to monitor the amount of gas made in a reaction. Describe an experimental method to measure the mass of gas produced in a reaction given appropriate details about the reaction. NO HIGHER