Lesson 11 3 theoretical probability
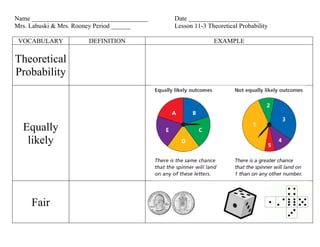
- 1. Name ____________________________________ Date ______________________ Mrs. Labuski & Mrs. Rooney Period ______ Lesson 11-3 Theoretical Probability VOCABULARY DEFINITION EXAMPLE Theoretical Probability Equally likely Fair
- 2. Finding Theoretical Probability What is the probability that a fair coin will and heads up? number or ways event can occur P(heads) = Total number of possible outcomes There are ________ outcomes: _______________ and _____________ number or ways event can occur P(heads) = 2 possible outcomes There is only one way for the coin to land heads up 1 way event can occur = P(heads) = 2 possible outcomes What is the probability of rolling a number less than 5 on a fair number cube? number or ways event can occur P(number less than 5) = Total number of possible outcomes There are six outcomes: ____________________________ P(number less than 5) = number or ways event can occur 6 possible outcomes There four ways to roll less than 5: ________________________ P(number less than 5) = 4 way event can occur = 6 possible outcomes Finding the probabilities of Events Not Happening To find the probability of an event not happening, find the probability that it will happen and subtract from 100%. Suppose there is a 10% chance that it will rain tonight. What is the probability that it will not rain? P(rain) + P(not rain)=100% + P(not rain)= 100%
- 3. Find the probability of each event using the spinner. 1. landing on blue ___________________ 2. landing on red____________________ 3. landing on green _________________ 4. not landing on blue ________________ Find the probability of each event using the bag of marbles. 5. picking a black marble ________________ 6. picking a striped marble ________________ 7. picking a white marble ________________ 8. not picking a white marble ________________ A standard number cube is rolled. Find each probability. 9. P(2) ________________ 10. P(even number) ________________ 11. P(4 or 5) ________________ 12. P(odd number) ________________ 13. Out of 10 fair coin tosses, a coin landed tails up 4 times. How does this experimental probability of a fair coin landing tails up compare to the theoretical probability of the same event? ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ 14. The probability of a spinner landing on blue is ¾. What is the probability of it not landing on blue written as a percent?
- 4. A standard number cube is rolled. Find each probability 1. P(5) ________________ 2. P(1, 2, or 3) ________________ 3. P(1 or 4) ________________ 4. P(negative number) ________________ 5. P(even number) ____________ 6. P(odd number) ________________ 7. P(positive number) ___________ 8. P(number less than 3) _______________ 9. P(not 2) ________________ 10. P(not 3 or 4) ________________ Seven pieces of paper with the numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, 4, 5, and 6 printed on them are placed in a bag. A student chooses one without looking. Compare the probabilities. Write <, >, or = . 11. P(1) ______P(5) 12. P(2) ________P(4) 13. P(4 or 5) _______P(1 or 3) 14. P(less than 4) _______P(greater than 3) 15. Explain why this spinner could not be used for a fair experiment. ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ 16. There is a 62% chance of rain tomorrow and a 19% chance of sleet. What is the probability that neither event will occur?
- 5. Name _____________________________ Date ______________________ Mrs. Labuski & Mrs. Rooney Per ______ Lesson 11-3 Theoretical Probability VOCABULARY DEFINITION EXAMPLE Probability when Theoretical all outcomes have Theoretical probability ≈ number or ways event can occur the same chance of Total number of possible outcomes Probability occurring When all Equally outcomes have the likely same chance of occurring An experiment Fair with equally likely outcomes
- 6. Finding Theoretical Probability What is the probability that a fair coin will and heads up? number or ways event can occur P(heads) = Total number of possible outcomes There are 2 outcomes: heads and tails number or ways event can occur P(heads) = 2 possible outcomes There is only one way for the coin to land heads up 1 way event can occur = 1 P(heads) = 2 possible outcomes 2 What is the probability of rolling a number less than 5 on a fair number cube? P(number less than 5) = number or ways event can occur Total number of possible outcomes There are six outcomes: 1,2,3,4,5,6 P(number less than 5) = number or ways event can occur 6 possible outcomes There four ways to roll less than 5: 1,2,3,4 P(number less than 5) = 4 way event can occur = 4 = 2 6 possible outcomes 6 3 Finding the probabilities of Events Not Happening To find the probability of an event not happening, find the probability that it will happen and subtract from 100%. Suppose there is a 10% chance that it will rain tonight. What is the probability that it will not rain? P(rain) + P(not rain)=100% 10% + P(not rain)= 100% -10% -10% P(not rain)= 90%
- 7. Find the probability of each event using the spinner. 1. landing on blue 3/5 2. landing on red 1/5 3. landing on green 1/5 4. not landing on blue 2/5 Find the probability of each event using the bag of marbles. 5. picking a black marble 4/9 6. picking a striped marble 1/3 7. picking a white marble 2/9 8. not picking a white marble 7/9 A standard number cube is rolled. Find each probability. 9. P(2) 1/6 10. P(even number) 3/6 = ½ 11. P(4 or 5) 2/6 = 1/3 12. P(odd number) 3/6 = ½ 13. Out of 10 fair coin tosses, a coin landed tails up 4 times. How does this experimental probability of a fair coin landing tails up compare to the theoretical probability of the same event? experimental probability = 4/10 = 40% theoretical probability = ½ =50% The experimental probability is 40%, which is less than the theoretical probability which is 50%. 14. The probability of a spinner landing on blue is ¾. What is the probability of it not landing on blue written as a percent? ¼ = 25%
- 8. A standard number cube is rolled. Find each probability 1. P(5) 1/6 2. P(1, 2, or 3) 3/6 = ½ 3. P(1 or 4) 1/3_____________ 4. P(negative number) 0 5. P(even number) 3/6 = ½ ______ 6. P(odd number) 3/6 = ½ 7. P(positive number) 1 or 100% 8. P(number less than 3) 1/3 9. P(not 2) 5/6 10. P(not 3 or 4) 4/6 = 2/3 Seven pieces of paper with the numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, 4, 5, and 6 printed on them are placed in a bag. A student chooses one without looking. Compare the probabilities. Write <, >, or = . 11. P(1) = P(5) 12. P(2) < P(4) 1 1 1 2 7 7 7 7 13. P(4 or 5) > P(1 or 3) 14. P(less than 4) > P(greater than 3) 3 2 3 4 7 7 7 7 15. Explain why this spinner could not be used for a fair experiment. There is a greater chance of the spinner landing on red than on any other color because there are two red sections and only one section of every other color. 16. There is a 62% chance of rain tomorrow and a 19% chance of sleet. What is the probability that neither event will occur? 62% 100% + 19% -81% 19% 81% 19%