Set hw
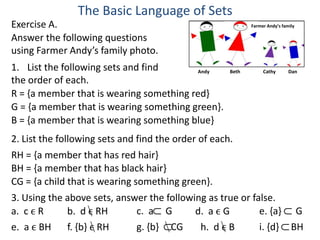
- 1. The Basic Language of Sets Exercise A. Farmer Andy’s family Answer the following questions using Farmer Andy’s family photo. 1. List the following sets and find Andy Beth Cathy Dan the order of each. R = {a member that is wearing something red} G = {a member that is wearing something green}. B = {a member that is wearing something blue} 2. List the following sets and find the order of each. RH = {a member that has red hair} BH = {a member that has black hair} CG = {a child that is wearing something green}. 3. Using the above sets, answer the following as true or false. a. c ϵ R b. d ϵ RH c. a G d. a ϵ G e. {a} G ∩ ∩ ∩ e. a ϵ BH f. {b} ϵ RH g. {b} CG h. d ϵ B i. {d} BH ∩
- 2. The Basic Language of Sets Exercise A. Farmer Andy’s family R = {wearing something red} G = {wearing something green}. B = {wearing something blue} Andy Beth Cathy Dan List the following set, find the order of each and answer the T or F questions. 4. W = {wearing both something red and something green} W R? R W? W G? G W? Explain your answer. ∩ ∩ ∩ ∩ 5. V = {wearing something red or something green, or both} R V? V R? G V? V G? Explain your answers. ∩ ∩ ∩ ∩ 6. X = {wearing something blue or something green, or both} X B? B X? X G? G X? Explain your answer. ∩ ∩ ∩ ∩ 7. Y = {wearing something blue and something green} B Y? Y B? Y G? G Y? Explain your answer. ∩ ∩ ∩ ∩
- 3. The Basic Language of Sets Exercise A. Farmer Andy’s family R = {wearing something red} G = {wearing something green}. B = {wearing something red} Andy Beth Cathy Dan Recall that a sample of size n from a set A is a subset of n elements selected from A. 8. G has 2 elements. List all the possible size 1 sample(s) of G, then list all size 2 sample(s) Why can’t there be any size 3 sample? 9. R has 3 elements. List all the possible size 1 sample(s) of G, then list all the size 2 sample(s) and the size 3 sample(s). Why can’t there be any size 4 sample? 10. If Farmer Andy’s family decide to take all the possible photos consist of exactly three members of the family, how may photos would be taken? List the members in each photo.
- 4. The Basic Language of Sets Let the universal set U = {0, 1, 2,.., 9}. List and find the order of each of the following subsets of each. Express each answer as an inequality. 11. A = {x | x is more than 6} 12. B = {x | x is no less than 6} 13. C = {x | x is less than 3} 14. D = {x | x is no more than 3} 15. E = {x | x is even} Following sample measurements are taken, classify each measurement is discrete or continuous. 16. Your weight w 17. Your height h 18. The number of your siblings n 19. The amount of time you took to do last night’s homework t 20. The number of times you washed your hands today f
- 5. More on the Language of Sets Exercise A. From the photo of Farmer Andy’s family in their new dresses, we define the following sets U = { the family} Farmer Andy’s family in new dresses R = {red} G = {green} B = {blue} F = {female} M = {male} Andy Beth Cathy Dan T = {has triangular decoration} C = {has circular decoration} Exercise A. 1. a. List each set defined above and pick out all the mutually exclusive pairs by inspection. List the elements of each of the the following sets. Name and describe each set in the form of {x | x is ###}. b. FC c. MC d. CC e. TC f. GC g. UC h. T U F i. F ∩ M j. B U C k. C U FC l. GC ∩ T k. TC ∩ CC
- 6. More on the Language of Sets 2. From Example C. we have the table as shown. Let A = {Adult} ,T = {Teen}, Adult Teen Child C = {Child}, F = {Female}, Male 5 17 18 M = {Male}, Female 15 26 19 Which pair of sets are mutually exclusively? Name and describe each of the following sets in the form of {x | x is ###} and find its order. b. TC c. CC d. MC e. FC f. AC g. A U F h. T ∩ C i. F ∩ MC j. AC U C k. CC U FC 3. Given intervals I, J , and K, do the set operation. Draw. Put the answer in the interval and the inequality notations. I: –8 –2 0 J: x < –3½ K: –5 ≤ x < 2 a. K U J b. K ∩ I c. I U J d. K U I e. I ∩ J f. K ∩ J g. (K ∩ J) U I h. (K U J) ∩ I
- 7. More on the Language of Sets 4. Given following shapes and their areas, find the total area if we glue them together as shown. a. 10 cm2 20 cm2 A B AUB b. 8 12 A B AUB c. Each overlap is 1 A 20 A B 20 C B AUBUC C 20
- 8. More on the Language of Sets 5. Farmer Andy produces nuts and sells them in three types of bags. These are: peanuts only, cashews only, and mixed peanuts–cashews. We bought many bags of each type. Draw a diagram that reflects each of the following questions. Answer the question if possible. If not, explain why not. a. Out of the bags we bought, 30 contain peanut and 12 contain cashews only. How many bags we bought in total? How many peanuts only bags did we buy? How many mixed begs did we buy? b. Out of the bags we bought, 30 contain peanut only and 12 contain cashews only. How many bags we bought in total? c. Out of the bags we bought, 30 contain peanut, 12 contain cashews and there are 6 of mixed type. How many bags did we buy in total and how may of each type did we buy? d. Out of the 40 bags we bought, 30 contain peanut and 12 are of mixed type. How many bags of each type did we buy?
- 9. More on the Language of Sets 6. Everyone in an extended family of 100 people have either genetic traits A or B, or both. Answer each of the following questions with the given information. Define and draw each set. a. There are 85 people who have trait A. Out of the people with trait A , 27 people have both traits A and B. How many people of each type did we have? b. There are 85 people who have trait A and there 27 people with B. How many people of each type did we have? c. Is it possible to have 85 people not having trait A and there 15 people with both traits A, B? What may we conclude? d. Is it possible to have 85 people who don’t have trait B and there 16 people with both traits A, B? What may we conclude?
- 10. Trees and Factorials Exercise A. There are multiple buses from the park to the mall where we may change bus and go to downtown. Draw the tree diagram of all the possible bus trips from the park to downtown given the following information. Red bus, Green bus, Bus No. 3 1 . park Blue bus, mall Bus No. 7 downtown Red bus, Green bus, Bus No. 3 2 . park Blue bus, Yellow bus mall Bus No. 7 downtown 3. Continuing with problem 1, after downtown we are going straight home either by the metro train or have Joe pick us up. Draw the tree that represents all the possible trips from the park to downtown, then home. 4. How many different bus trips are possible if we are going from the park to downtown and back to the park. Do not draw the tree.
- 11. Trees and Factorials 5. Dan wants to take a math class in the morning then go directly to a PE class. There are five choices for the math classes and for PE, Dan can like do swimming, rock climbing or hole digging. How many different possible morning class schedules Dan can have? 6. The Banana Inc. produces and sell tablets with different configurations. There are 4 possible storage capacities: 100 TB, 10 TB, 1 TB, or 500 GB, three different types of processors: the BS–super X, BS–super XX, and the Double BS. The tablets come in black, white, and zebra stripes. How may different types of Banana tablets are there? 7. This Friday night, Farmer Andy’s family can go out to eat at a one out of the local five restaurants or eat yesterday’s leftover, afterwards they can go to one of the three movies or to the library; after that they can either go for boat ride or paint the garage. How many different arrangements are possible for Friday nights? Which is the least desirable?
- 12. Trees and Factorials 9. For Cathy, an outfit consists of a hat, a shirt, a pair of pant or a skirt, and a pair of shoes. If Cathy has 3 hats, 3 pairs of shoes, 4 skirts, 4 shirts, and 5 pants, does Cathy have enough to have a different outfit for each day of the year? 10. At the Marx’s Senior hamburger store, a Junior combo special meal consists of a choice of a Lardy Burger, with or without cheese, with or without bacons, a choice of an order of fry Cheese balls or fry cookie, then a small diet C or diet P for drink. How many different Junior combos are possible? 11. The music directory in Maria’s computer has 12 subdirectories for 12 types of music, in each subdirectory there are 12 artists’ recordings and for each artist there are 12 songs stored. How many songs does Maria have? 12. Frank is writing a math book which consists of 8 chapters, each chapter has 6 sections and each section has 30 homework problems, how many homework problems does Frank have to come up with?
- 13. Trees and Factorials 13. The main trunk of an Andy–berry tree, grows and splits into 3 boughs, each bough splits into 3 more branches, each branch splits into 2 twigs, at the end of each twig it produce 5 small berries, how many Andy–berries are there on one tree? Suppose each acre can grow 120 trees, and Farmer Andy’s has 80 acres of the berry–trees, and each berry can be sold for 5¢, how much money will Andy earn if he harvest and sell each one of them? 14. What’s 0!? 1!? 2!? 3!? 4!? 5!? 6!? 7!? 8!? Calculate the following by cancelling as much as possible first. 15. Find a. 3! b. 4! c. 5! d. 7! e. 8! 2! 2! 3! 4! 3! 3! 16. Find a. b. 4! c. 5! d. 7! e. 8! 2!1! 2!2! 2!3! 4!3! 3!5! 12! 17. Find a. 5!7! b. 14! c. 25! d. 17! e. 18! 12!2! 22!3! 9!5! 9!9!
- 14. Permutations and Combinations Translate each of the following expressions into the nPr notation or the factorial notation, then calculate the outcome by cancelling as much as possible first. 1. a. 3! b. 3P2 c. 5! d. 6P2 e. 8! 2! 3! 3! 2. a. 3P1 b. 3! c. 5P2 d. 6! e. 8P5 1! 4! Translate each of the following expressions into the nCr notation or the factorial notation, then calculate the outcome by cancelling as much as possible first. 3. a. 3! b. 3C1 c. 5! d. 6 C2 e. 8! 2!1! 2!3! 3!5! 4. a. 3C2 b. 3! c. 5C2 d. 6! e. 8C5 1!2! 2!4! 5. Farmer Andy’s family {a, b, c, d} is Farmer Andy’s family taking family photos. They are to sit in four chairs in a row. How many different sitting arrangements are possible? Andy Beth Cathy Dan
- 15. Permutations and Combinations 6. For the dinner cleaning duty, one member of Farmer Andy’s family does the dishes and another member dries them. How many different cleaning arrangements are there? List them. 7. From 6, if we meet a third person to take out the garbage, how many different after dinner cleaning arrangements are possible? 8. For the after dinner cleaning duty, two members of Farmer Andy’s family are in charge of dish duty. How many different after dinner cleaning 2–person teams are possible? List them. 9. From 8, if we need three members of Farmer Andy’s family in charge of dish&garbage duty. How many different 3–person teams are possible? List them. 10. Farmer Andy’s family are to draw lots to determine the order of the bathroom usages in the morning. How many different lineups of the bathroom usage are possible? (Everyone uses the only bathroom in the morning.)
- 16. Permutations and Combinations 11. From problem 6, if the dish–washing job may be done by anyone but the drying job must be done by a boy, how many arrangements are possible? List them. (Hint: Fill the drying job first) 12. From problem 11, besides that the drying job must be done by a boy, the dish–washing job has to be done by a girl, how many arrangements are possible? List them. 13. From problem 6, if the dish–washing job and the drying job must be done by members from different genders, how many arrangements are possible? List them. 14. From 6, Andy could participate in the drying but he can’t wash dishes because he is allergic to dish–washing, how many arrangements are possible? List them. 15. Back to problem 13, besides that Andy is allergic to dish– washing that Beth is allergic to dish–drying but can participate in washing, how many arrangements are possible? List them.
- 17. Permutations and Combinations 16. From the set of digits D = {0, 1, 2, .. 9} we are to line up seven different digits. How many different numbers we may have? 17. How many 7–digit phone numbers are possible if the first digit can’t be 0 and that no digit is repeated? 18. How many 7–digit phone numbers are possible if digit may be repeated? 19. How many 7–digit phone numbers are possible if the first digit can’t be 0 and that digit may be repeated? A B We have two boxes A and B each contains different gifts as shown. Answer the following questions. 20. We are to select two items to keep, how many different two–item gifts are possible?
- 18. Permutations and Combinations 21. We are to select three items to keep, how many different three–item gifts are possible? 22. We are to select two items to keep but they must be from different boxes, how many such two–item gifts are possible? 23. We are to select two items to keep but they must be from the same boxes, how many such two–item gifts are possible? 24. Why is the sum of the answers from 22 and 23 is the answer of problem 19? 25. We are to select three items to keep but they must be from the same boxes, how many such three–item gifts are possible? 26. We are to select three items to keep but they can’t be all from box A, how many such three–item gifts are possible? (Use the complementary counting principle) 27. We are to select three items to keep but they can’t be all from box B, how many such three–item gifts are possible? (Use the complementary counting principle)
- 19. Permutations and Combinations Translate each of the following expressions into the nPr notation / or the factorial notation, then calculate the outcome by cancelling as much as possible first. 1. a. 3! b. 3P2 c. 5! d. 6P2 e. 8! 2! 3! 3! 2. a. 3P1 b. 3! c. 5P2 d. 6! e. 8P5 1! 4! Translate each of the following expressions into the nCr notation / or the factorial notation, then calculate the outcome of each by cancelling as much as possible first. 3. a. 3! b. 3C1 c. 5! d. 6 C2 e. 8! 2!1! 2!3! 3!5! 4. a. 3C2 b. 3! c. 5C2 d. 6! e. 8C5 1!2! 2!4! 5. Farmer Andy’s family {a, b, c, d} is Farmer Andy’s family taking family photos. They are to sit in four chairs in a row. How many different sitting arrangements are possible? Andy Beth Cathy Dan
- 20. Permutations and Combinations 6. For the dinner cleaning duty, one member of Farmer Andy’s family does the dishes and another member dries them. How many different cleaning arrangements are there? List them. 7. From 6, if we meet a third person to take out the garbage, how many different after dinner cleaning arrangements are possible? List them. 8. For the after dinner cleaning duty, two members of Farmer Andy’s family are in charge of dish duty. How many different after dinner cleaning 2–person teams are possible? List them. 9. From 8, if we need three members of Farmer Andy’s family in charge of dish&garbage duty. How many different 3–person teams are possible? List them. 10. Farmer Andy’s family are to draw lots to determine the order of the bathroom usages in the morning. How many different lineups of the bathroom usage are possible? (Everyone uses the only one bathroom in the morning.)
- 21. Permutations and Combinations 11. From problem 6, if the dish–washing job may be done by anyone but the drying job must be done by a boy, how many arrangements are possible? List them. (Hint: Fill the drying job first) 12. From problem11, besides that the drying job must be done by a boy, the dish–washing job has to be done by a girl, how many arrangements are possible? List them. 13. From problem 6, if the dish–washing job and the drying job must be done by members from different genders, how many arrangements are possible? List them. 14. From 6, Andy could participate in the drying but he can’t wash dishes because he is allergic to dish–washing, How many arrangements are possible? List them. 15. Back to problem 13, besides that Andy is allergic to dish– washing that Beth is allergic to dish–drying but can participate in washing, how many arrangements are possible? List them.
- 22. Permutations and Combinations 16. From the set of digits D = {0, 1, 2, .. 9} we to line up 7 different digits. How many different numbers we may have? 17. How many 7–digit phone numbers are possible if the first digit can’t be 0 and that no digit is repeated? 18. How many 7–digit phone numbers are possible if digit may be repeated? 19. How many 7–digit phone numbers are possible if the first digit can’t be 0 and that digit may be repeated? A B We have two boxes A and B each contains different gifts as shown. Answer the following questions. 20. We are to select two items to keep, how many different two–item gifts are possible?
- 23. Permutations and Combinations 21. We are to select three items to keep, how many different three–item gifts are possible? 22. We are to select two items to keep but they must be from different boxes, how many such two–item gifts are possible? 23. We are to select two items to keep but they must be from the same boxes, how many such two–item gifts are possible? 24. We are to select three items to keep but they must be from the same boxes, how many such three–item gifts are possible? 25. Why is the sum of the answers from 23 and 25 is the answer of problem 19? 26. We are to select three items to keep but they can’t be all from box A, how many such three–item gifts are possible? (Use the complementary counting principle) 27. We are to select three items to keep but they can’t be all from box B, how many such three–item gifts are possible? (Use the complementary counting principle)