GAAP vs IFRS
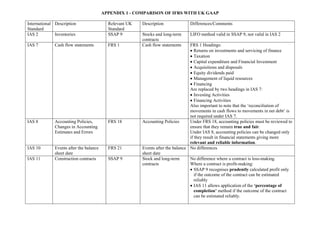
- 1. APPENDIX 1 - COMPARISON OF IFRS WITH UK GAAP International Standard Description Relevant UK Standard Description Differences/Comments IAS 2 Inventories SSAP 9 Stocks and long-term contracts LIFO method valid in SSAP 9, not valid in IAS 2 IAS 7 Cash flow statements FRS 1 Cash flow statements FRS 1 Headings: • Returns on investments and servicing of finance • Taxation • Capital expenditure and Financial Investment • Acquisitions and disposals • Equity dividends paid • Management of liquid resources • Financing Are replaced by two headings in IAS 7: • Investing Activities • Financing Activities Also important to note that the ‘reconciliation of movements in cash flows to movements in net debt’ is not required under IAS 7. IAS 8 Accounting Policies, Changes in Accounting Estimates and Errors FRS 18 Accounting Policies Under FRS 18, accounting policies must be reviewed to ensure that they remain true and fair. Under IAS 8, accounting policies can be changed only if they result in financial statements giving more relevant and reliable information. IAS 10 Events after the balance sheet date FRS 21 Events after the balance sheet date No differences IAS 11 Construction contracts SSAP 9 Stock and long-term contracts No difference where a contract is loss-making. Where a contract is profit-making: • SSAP 9 recognises prudently calculated profit only if the outcome of the contract can be estimated reliably • IAS 11 allows application of the ‘percentage of completion’ method if the outcome of the contract can be estimated reliably.
- 2. International Standard Description Relevant UK Standard Description Differences/Comments IAS 12 Income taxes FRS 16 FRS 19 Current tax Deferred tax No difference with FRS 16 Differences with FRS 19: • IAS 12 does not allow ‘discounting’ of deferred tax to present day values (irrelevant, as not practiced by HH) • FRS 19 recognises deferred tax as ‘timing differences’, while IAS 12 recognises deferred tax on the basis of ‘taxable temporary differences’. • Fundamental conceptual difference in measurement. IAS 12 calculates temporary differences by comparing the balance sheet value of items to the value attributed to them for tax assessment purposes. Therefore temporary differences include not only timing differences (as per FRS 19), but other differences between the accounting and tax bases of items, for example, revaluation of assets for which no equivalent adjustment is made for tax purposes • Reconciliation required of the total current and deferred tax charge (as opposed to just the current tax charge under UK GAAP) to the tax charge that would result from applying the standard rate of tax to the profit on ordinary activities before tax
- 3. International Standard Description Relevant UK Standard Description Differences/Comments IAS 16 Property, plant and equipment FRS 15 Tangible fixed assets FRS 15 includes fixed assets ‘held for sale’. Such assets are not covered by IAS 16, but are covered by IFRS 5. When one asset is acquired in exchange for another, IAS 16 requires the cost of the acquired asset to be measured at fair value (usually corresponding with market value). Like FRS 15, can use cost model or revaluation model. Unlike FRS 15, IAS 16 requires revaluations to be at fair value rather than current value. There is also some difference in treatment of revaluation losses. Comparison of treatment of depreciation: • IAS 16 and FRS 15 both require residual values to be reviewed at each balance sheet date • IAS 16 requires increases in an asset’s residual value, based on current prices, to reduce the ongoing depreciation charge • If the residual value equals or exceeds the asset’s carrying value, the depreciation charge is reduced to zero • FRS 15 generally requires prices at the date of acquisition or latest valuation to be used; thus increases in residual values are generally reflected in disposal profits rather than in lower depreciation
- 4. International Standard Description Relevant UK Standard Description Differences/Comments IAS 17 Leases SSAP 21 FRS 5 Accounting for leases and hire purchase contracts Reporting the substance of transactions • When classifying a lease of land and buildings, IAS 17 requires the land and buildings elements to be considered separately. Lease of land is usually considered to be an operating lease. • Difference in income recognition for lessors • IAS 17 requires more extensive disclosures than SSAP 21. The main difference is that IAS 17 requires lessees to disclose the total of future minimum lease payments; SSAP 21 requires disclosure only of details of the payments that the lessee is committed to make in the next year. IAS 18 Revenue FRS 5 Reporting the substance of transactions FRS 5 is the closest equivalent to IAS 18. No differences in treatment. IAS 19 Employee benefits FRS 17 Retirement benefits Re actuarial gains and losses, IAS 19 offers two options, one of which agrees with FRS 17. Unlike with FRS 17, pension assets and liabilities cannot be shown net of any related deferred tax (IAS 12). If defined contribution accounting is used by group entities, the allocation of net defined benefit cost among the participating entities depends on whether there is an agreement or stated policy. Re short term employee benefits, IAS 19 includes accounting for and disclosure of wages and salaries, benefits, paid leave and bonuses. IAS 20 Accounting for govt grants and disclosure of govt assistance SSAP 4 Accounting for govt grants No differences IAS 21 The effects of changes in foreign exchange rates FRS 23 The effects of changes in foreign interest rates No major differences, not relevant to HH
- 5. International Standard Description Relevant UK Standard Description Differences/Comments IAS 23 Borrowing costs FRS 15 Tangible fixed assets Where borrowings specifically relate to expenditure on an asset, IAS 23 takes the actual borrowing costs less any investment income received from the temporary reinvestment of unutilised borrowings; FRS 15 takes interest on the amount of borrowings that has been spent on the asset to date. IAS 24 Related party disclosures FRS 8 Related party disclosures • IAS 24 does not exempt subsidiaries from disclosing related party transactions. It also does not include the FRS 8 exemption whereby the related party disclosure rules do not apply if this conflict with the reporting entity’s duties of confidentiality arising by the operation of law. • IAS 24 requires disclosure of related party transactions in the separate financial statements of parent entities. • IAS 24 includes management compensation in the definition of a related party transaction, and has a wider definition of key management. IAS 26 Accounting and reporting by retirement benefit plans FRS 17 Retirement benefits No differences from existing accounting requirements for pension schemes
- 6. International Standard Description Relevant UK Standard Description Differences/Comments IAS 27 SIC-12 Consolidated and separate financial statements Consolidation – special purpose entities FRS 2 FRS 5 Accounting for subsidiary undertakings Reporting the substance of transactions Mostly similar, but some differences: • IAS 27 includes guidance on the treatment of investments in subsidiaries in the parent’s financial statements, whereas FRS 2 does not • Where reporting periods of the reporting entity and its subsidiaries are not consistent, FRS 2 allows consolidation where the subsidiary’s period end is within three months of the parent’s reporting year end. IAS 27 is more flexible, and allows consolidation where the subsidiary’s period end is after the group’s period end • IAS 27 states that the existence and effect of potential voting rights should be considered when assessing whether one entity controls another; FRS 2 states that options are taken into account only when they are exercised • FRS 2 requires a subsidiary to be excluded from consolidation where severe long-term restrictions substantially hinder the exercise of the parent’s rights over the assets or management of the subsidiary. Under IAS 27 control must be lost for exclusion to occur. • On disposal of a subsidiary, IAS 27 excludes goodwill previously written off to equity when calculating the gain or loss on disposal. FRS 2 requires that goodwill previously written off to the I&E is included in the calculation of the gain or loss. SIC-12 agrees with FRS 5
- 7. International Standard Description Relevant UK Standard Description Differences/Comments IAS 28 Investments in associates FRS 9 Associates and joint ventures • FRS 9 requires an investor’s share of its associates’ operating results be brought into the consolidated profit and loss immediately after group operating profit. IAS 28 requires only that the investors consolidated profit and loss reflect the share of the results of its investee. • Where the aggregate of the investors share in all its associates exceeds 15% of the value of the total group, FRS 9 requires additional disclosure of the aggregate of the share in investees turnover (if not already provided), fixed assets, current assets, liabilities due within one year and liabilities due after one year. Additionally where the share of associates exceeds 25% of the group total the investor should also disclose the aggregate of the share of investees profit before tax, taxation and profit after tax. These requirements do not feature in IAS 28. IAS 29 Financial reporting in hyperinflationary economies FRS 24 Financial reporting in hyperinflationary economies No differences IAS 31 Interests in joint ventures FRS 9 Associates and joint ventures The only material differences in disclosure for joint ventures (JVs) is that where the aggregate of the venturer’s share in all its JVs exceeds 15% of the value of the total group FRS 9 requires additional disclosure of the aggregate of the venture’s share in its JVs’ fixed assets, current assets, liabilities due within one year and liabilities due after one year. Additionally where the share in JVs exceeds 25% of the group total the venturer should disclose the aggregate of its share of JVs’ profit before tax, taxation and profit after tax. IAS 31 contains no such requirements.
- 8. International Standard Description Relevant UK Standard Description Differences/Comments IAS 32 Financial instruments: presentation FRS 25 FRS 29 Financial instruments: disclosure and presentation Financial instruments: disclosure No differences IAS 33 Earnings per share FRS 22 Earnings per share Not relevant to HH (company limited by guarantee) IAS 34 Interim financial reporting ASB Statement Interim financial reporting No major differences
- 9. International Standard Description Relevant UK Standard Description Differences/Comments IAS 36 Impairment of assets FRS 10 FRS 11 Goodwill and intangible assets Impairment of fixed assets and goodwill The basic recognition approach is the same, but there are some differences in subsequent treatment: • FRS 11 states that impairments of revalued assets that are clearly caused by the consumption of economic benefits should be recognised in the I&E, whereas IAS 36 requires such impairments to be recognised in the income statement only to the extent that the loss exceeds the balance on the revaluation reserve relating to the specific asset • Impairment losses are first allocated to goodwill then pro-rata to intangible and tangible assets (vs. UK GAAP order of goodwill, intangibles and then tangible assets) • Under IAS 36, goodwill impairments cannot be reversed • Under IFRS, goodwill cannot be amortised. IAS 36 requires an annual impairment review instead • Both FRS 11 and IAS 36 require that estimated cash flows from future restructuring/expenditure on enhancing the asset to which the entity is not yet committed should be excluded when determining value in use. However, FRS 11 includes an exception for newly-acquired income generating units and permits such cash flows to be included if they were anticipated at the time of performing the impairment review in the first full year after acquisition • IAS 36 does not require recognition of losses that would have arisen in the past, but which have since reversed. FRS 11 requires that any past impairment that should have been recognised is charged when actual cash flows are substituted. • IAS 36 requires more extensive and detailed disclosure of impairments and testing processes than FRS 11.
- 10. International Standard Description Relevant UK Standard Description Differences/Comments IAS 37 Provisions, contingent liabilities and contingent assets FRS 12 Provisions, contingent liabilities and contingent assets No significant differences. FRS 12 contains more guidance than IAS 37 on the discount rate to be used in determining the present value of a provision. IAS 38 Intangible assets FRS 10 SSAP 13 Goodwill and intangible assets Accounting for research and development • A wider range of intangible assets is recognised under IFRS, such as software licences (regarded as tangible fixed assets under UK standards) • Under FRS 10, an asset is identifiable when it is capable of being sold separately from the entity. IAS 38 includes this definition, and also identifies intangible assets arising from contractual or other legal rights • FRS 10 includes a presumption that the useful economic life of an intangible asset is 20 years or less. IAS 38 allows that an intangible asset can have indefinite life, and in such cases need not be amortised • IFRS requires annual impairment reviews for intangible assets with indefinite life. IAS 38 requires impairment review only if there is an indication of impairment, or for intangible assets not yet ready for use. FRS 10 requires that the useful economic lives of intangible assets should be reviewed at the end of the 20-year useful life period • Under IAS 38, research costs must be written off as incurred, whereas development costs should be capitalised where particular criteria are met. SSAP 13 allows a choice regarding capitalisation of product and service development costs.
- 11. International Standard Description Relevant UK Standard Description Differences/Comments IAS 39 Financial instruments: recognition and measurement FRS 4 FRS 5 FRS 26 Capital instruments Reporting the substance of transactions Financial instruments: recognition and measurement There is fundamental change for companies not applying FRS 26. Under IFRS: • There are restrictions on stating assets at amortised cost, broadly only applicable for assets “held to maturity”, cash, loans and other receivables. Most other assets reported at fair value. • Issued debt is recorded at amortised cost, but embedded derivatives must be separated. • Some financial assets (debtors, creditors, accruals including loans, and investments) recognised under UK GAAP at cost will be shown at fair value under IFRS. Changes in fair value will be taken to either Income or Equity. • Linked presentation of non-recourse finance arrangements is not permitted under IAS 39. • There is strict hedge accounting criteria, measurement and recognition criteria. • Detailed hedge accounting documentation and effectiveness testing is required in order to obtain hedge accounting. • Foreign currency assets hedged using forwards cannot be recognised at the contracted forward exchange rate. The forward and asset are separately recognised. Hedge accounting may be applied subject to strict criteria.
- 12. International Standard Description Relevant UK Standard Description Differences/Comments IAS 40 Investment property SSAP 19 Accounting for investment properties • IAS 40 allows an entity to choose between the fair value model and depreciated cost for all investment property. SSAP 19 requires investment properties to be carried at open market value • When the IAS 40 fair value model is applied, the carrying amount is not depreciated. Gains or losses arising from changes in the asset’s fair value are recognised in the income statement. According to SSAP 19, a revaluation gain or loss is recognised in the STRGL unless it is a permanent deficit (or reversal) in which case it is recognised in the P&L • IAS 40 has more extensive disclosure requirements than SSAP 19 IAS 41 Agriculture No equivalent Not relevant to HH IFRS 1 First time adoption of international financial reporting standards No equivalent IFRS 1 encapsulates all adoption and reconciliation requirements for the initial application for IFRS, and as such must to be followed in full when stating the year’s opening balances. IFRS 2 Share-based payment FRS 20 Share-based payment No differences, and not relevant to HH
- 13. International Standard Description Relevant UK Standard Description Differences/Comments IFRS 3 Business combinations FRS 6 FRS 7 FRS 10 Acquisitions and mergers Fair values in acquisition accounting Goodwill and intangible assets • Under IFRS 3, merger accounting is prohibited; business combinations are required to be accounted for as acquisitions using the purchase method • FRS 6 does not have scope exclusions, whereas IFRS 3 has several • When an acquisition takes place in stages, IAS 3 requires that each exchange transaction is treated separately for the purpose of determining the fair values of the identifiable assets, liabilities and goodwill. UK GAAP requires that such assets and liabilities acquired are measured at their fair value on the date the investee becomes a subsidiary. However, the FRS 2 true and fair override is consistent with IFRS 3 • Under FRS 7, adjustments made to the fair value of assets and liabilities as at the date of acquisition should be made in the first full financial year following the acquisition. This can be longer than the 12 month period allowed by IFRS 3 • Under IFRS 3, adjustments to provisional fair values should be recognised as if the initial accounting had been completed at the acquisition date (i.e. comparatives should be restated). Under UK GAAP, adjustments to provisional fair values are accounted for in the period that adjustments are made • IFRS 3 does not use the term ‘negative goodwill’ and instead calls it ‘excess of acquirer’s interest in the net fair value of acquiree’s identifiable assets’. IFRS 3 requires this to be taken into the I&E in the year of acquisition. UK GAAP requires that negative goodwill should be classified as such in the ‘capital and reserves’ section of the balance sheet. Negative goodwill up to the fair values of the non-monetary assets acquired should be recognised in the I&E in the periods in which the non-monetary assets are recovered (either through depreciation or sale)
- 14. International Standard Description Relevant UK Standard Description Differences/Comments IFRS 4 Insurance contracts No equivalent Not relevant to HH, as the standard applies to insurers rather than policyholders IFRS 5 Non-current assets held for sale and discontinued operations FRS 3 (part) Reporting financial performance • IFRS 5 and FRS 3 have different definitions of discontinued operations • IFRS 5 requires a single number to be disclosed on the face of the income statement. A breakdown of this figure is required to be given either on the face of the income statement or in the notes to the accounts. FRS 3 requires disclosure of the split in the pre-tax figures on the face of the income statement IFRS 6 Exploration for and evaluation of mineral resources No equivalent Not relevant to HH IFRS 7 Financial instruments: disclosures FRS 29 Financial instruments: disclosures No differences at present. A FRED has been issued for FRS 29, and the consultation period ended on 30th January 2009. Outcome of the consultation is expected shortly.
- 15. International Standard Description Relevant UK Standard Description Differences/Comments IFRS 8 Operating segments SSAP 25 Segmental reporting • IFRS 8 operating segments are defined in terms of the structure of the entity and how it manages itself. In the UK SSAP 25 Segmental Reporting identify two types of segment: classes of business and geographical segments. Segmental reporting based on SSAP 25’s classes of business criteria would result in reporting similar to that achieved under IFRS 8. • The segmental reporting requirements under IFRS 8 are greater than those under SSAP 25. • IFRS 8 requires entities to report: segment profit or loss; liabilities; revenue from external customers; revenue from other segments; interest revenue; interest expense; depreciation and amortisation; material items of income and expense; the entity’s interest in profit and loss of associates and joint venture’s accounted for by the equity method; and income tax expense or income and material non-cash items other than depreciation and amortisation. • SSAP 25 only requires entities to report segment: turnover distinguishing between that from external customers and that from other segments; results before taxation, minority interests and extraordinary items; and net assets. • The two standards use slightly different criteria to assess whether a segment merits separate reporting based on turnover/revenue. SSAP 25 requires this assessment to be made on third party turnover only whereas IFRS 8 requires the assessment to be based on sales to external customers and inter-segment sales or transfers.
- 16. GLOSSARY GAAP – Generally Accepted Accounting Principles IAS – International Accounting Standard SSAP – Statement of Standard Accounting Practice LIFO – Last In First Out FRS – Financial Reporting Standard IFRS – International Financial Reporting Standard HH – Hounslow Homes SIC – Standing Interpretations Committee (predecessor body to the International Financial Reporting Interpretations Committee, IFRIC) I&E – Income & Expenditure STRGL – Statement of Total Recognised Gains and Losses FRED – Financial Reporting Exposure Draft SOURCES Accounting Standards Board – www.frc.org.uk International Accounting Standards Board – www.iasb.org Government Financial Reporting Manual – www.financial-reporting.gov.uk HM Revenue & Customs – www.hmrc.gov.uk HM Treasury – www.hm-treasury.gov.uk The Chartered Institute of Public Finance and Accountancy (CIPFA) – www.cipfa.org.uk IFRS Briefings – Managing the Transition – www.audit-commission.gov.uk Association of Chartered Certified Accountants (ACCA) – www.uk.accaglobal.com The Institute of Chartered Accountants in England and Wales (ICAEW) – www.icaew.com IAS Plus, published by Deloitte – www.iasplus.com International Financial Reporting Standards, published by KPMG – www.kpmg.co.uk Public Finance, CIPFA Accountancy Age – www.accountancyage.com IFRS: Managing the Conversion, 5th December 2008, PriceWaterhouseCoopers & CIPFA International Financial Reporting Standards – The potential impact for housing associations – PriceWaterhouseCoopers & National Housing Federation