The black and blue marble: whole Earth views from space
- 1. The black and blue marble: Whole Earth views from space 9/11/2013
- 2. Apollo 17’s iconic “blue marble” view in 1972 9/11/2013 2Source: NASA
- 3. First color photograph of whole Earth in 1967 9/11/2013 3Source: NASA
- 4. Blue marble: next generation 9/11/2013 4Source: NASA
- 5. 9/11/2013 5Source: NASA Blue marble: next generation
- 6. 9/11/2013 6Source: NASA Blue marble: next generation
- 7. 9/11/2013 79/11/2013 7Source: NASA Feb. 1, 2004
- 8. 9/11/2013 8Source: NASA The world turned on its head
- 9. The world turned on its head 9/11/2013 9Source: NASA
- 10. The view from the the top: Arctic and high latitudes 9/11/2013 10Source: NASA
- 11. Night lights of the Western hemisphere 9/11/2013 11Source: NASA
- 12. The Earth at night 9/11/2013 12Source: NASA
- 13. The United States of Light 9/11/2013 13Source: NASA
- 14. Lights in the American West 9/11/2013 14Source: NASA
- 15. Moon in orbit: the view from the Galileo spacecraft 9/11/2013 15Source: NASA/JPL
- 16. Looking back toward Earth on way to Jupiter 9/11/2013 16Source: NASA/JPL/Doug Ellison
- 17. View of Earth and moon from Saturn 9/11/2013 17Source: NASA/JPL/SSI You are here
- 18. Lunar transit of Earth 9/11/2013 18Source: NASA/JPL/UMD
- 19. Lunar transit of Earth 9/11/2013 19Source: NASA/JPL/UMD
- 20. Solar eclipse viewed from lunar orbiter 9/11/2013 20Source: NASA/GSFC/ASU
- 21. ecowest.org Download more slides and other resources 9/11/2013 21
Notas do Editor
- In this EcoWest presentation, we share some images of the whole Earth taken from space.
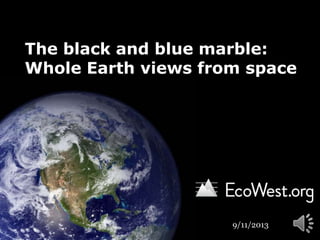
- Narrative: The iconic blue marble photo was taken on December 7, 1972, as the Apollo 17 spacecraft departed Earth for the moon. The imagewas snapped 5 hours after liftoff and 2 hours after the spacecraft left its parking orbit around Earth. The spacecraft was already 28,000 miles away from the planet, and situated perfectly for the photo with the sun behind it. Source: NASAURL: http://visibleearth.nasa.gov/view.php?id=55418Notes: Original caption:View of the Earth as seen by the Apollo 17 crew traveling toward the moon. This translunar coast photograph extends from the Mediterranean Sea area to the Antarctica south polar ice cap. This is the first time the Apollo trajectory made it possible to photograph the south polar ice cap. Note the heavy cloud cover in the Southern Hemisphere. Almost the entire coastline of Africa is clearly visible. The Arabian Peninsula can be seen at the northeastern edge of Africa. The large island off the coast of Africa is the Malagasy Republic. The Asian mainland is on the horizon toward the northeast.
- Narrative: But the 1972 photo wasn’t the first view of the whole Earth. Five years earlier, in 1967, the ATS-3 communications satellite snapped this image.Source: Wikipedia, NASAURL: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:ATSIII_10NOV67_153107.jpgNotes: First color photograph of the whole Earth (western Hemisphere), shot from the ATS-3 satellite on 10 November 1967
- Narrative: More recently, NASA has produced much higher resolution images of the planet, in a series it calls “Blue Marble.” Source: NASAURL: http://visibleearth.nasa.gov/view.php?id=57723Notes: NASA Goddard Space Flight Center Image by Reto Stöckli (land surface, shallow water, clouds). Enhancements by Robert Simmon (ocean color, compositing, 3D globes, animation). Data and technical support: MODIS Land Group; MODIS Science Data Support Team; MODIS Atmosphere Group; MODIS Ocean Group Additional data: USGS EROS Data Center (topography); USGS Terrestrial Remote Sensing Flagstaff Field Center (Antarctica); Defense Meteorological Satellite Program (city lights).This spectacular “blue marble” image is the most detailed true-color image of the entire Earth to date. Using a collection of satellite-based observations, scientists and visualizers stitched together months of observations of the land surface, oceans, sea ice, and clouds into a seamless, true-color mosaic of every square kilometer (.386 square mile) of our planet. These images are freely available to educators, scientists, museums, and the public.Much of the information contained in this image came from a single remote-sensing device-NASA’s Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer, or MODIS. Flying over 700 km above the Earth onboard the Terra satellite, MODIS provides an integrated tool for observing a variety of terrestrial, oceanic, and atmospheric features of the Earth. The land and coastal ocean portions of these images are based on surface observations collected from June through September 2001 and combined, or composited, every eight days to compensate for clouds that might block the sensor’s view of the surface on any single day. Two different types of ocean data were used in these images: shallow water true color data, and global ocean color (or chlorophyll) data. Topographic shading is based on the GTOPO 30 elevation dataset compiled by the U.S. Geological Survey’s EROS Data Center. MODIS observations of polar sea ice were combined with observations of Antarctica made by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s AVHRR sensor—the Advanced Very High Resolution Radiometer. The cloud image is a composite of two days of imagery collected in visible light wavelengths and a third day of thermal infra-red imagery over the poles. Global city lights, derived from 9 months of observations from the Defense Meteorological Satellite Program, are superimposed on a darkened land surface map.
- Narrative: These next generation blue marbles are based on a variety of imaging technologies and months of observations. Much of the data came from the MODIS device on the Terra satellite, which is in orbit 435 miles above the planet.Source: NASAURL: http://visibleearth.nasa.gov/view.php?id=57723Notes: NASA Goddard Space Flight Center Image by Reto Stöckli (land surface, shallow water, clouds). Enhancements by Robert Simmon (ocean color, compositing, 3D globes, animation). Data and technical support: MODIS Land Group; MODIS Science Data Support Team; MODIS Atmosphere Group; MODIS Ocean Group Additional data: USGS EROS Data Center (topography); USGS Terrestrial Remote Sensing Flagstaff Field Center (Antarctica); Defense Meteorological Satellite Program (city lights).This spectacular “blue marble” image is the most detailed true-color image of the entire Earth to date. Using a collection of satellite-based observations, scientists and visualizers stitched together months of observations of the land surface, oceans, sea ice, and clouds into a seamless, true-color mosaic of every square kilometer (.386 square mile) of our planet. These images are freely available to educators, scientists, museums, and the public.Much of the information contained in this image came from a single remote-sensing device-NASA’s Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer, or MODIS. Flying over 700 km above the Earth onboard the Terra satellite, MODIS provides an integrated tool for observing a variety of terrestrial, oceanic, and atmospheric features of the Earth. The land and coastal ocean portions of these images are based on surface observations collected from June through September 2001 and combined, or composited, every eight days to compensate for clouds that might block the sensor’s view of the surface on any single day. Two different types of ocean data were used in these images: shallow water true color data, and global ocean color (or chlorophyll) data. Topographic shading is based on the GTOPO 30 elevation dataset compiled by the U.S. Geological Survey’s EROS Data Center. MODIS observations of polar sea ice were combined with observations of Antarctica made by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s AVHRR sensor—the Advanced Very High Resolution Radiometer. The cloud image is a composite of two days of imagery collected in visible light wavelengths and a third day of thermal infra-red imagery over the poles. Global city lights, derived from 9 months of observations from the Defense Meteorological Satellite Program, are superimposed on a darkened land surface map.
- Narrative: Here are both images together.Source: NASAURL: http://visibleearth.nasa.gov/view.php?id=57723Notes: NASA Goddard Space Flight Center Image by Reto Stöckli (land surface, shallow water, clouds). Enhancements by Robert Simmon (ocean color, compositing, 3D globes, animation). Data and technical support: MODIS Land Group; MODIS Science Data Support Team; MODIS Atmosphere Group; MODIS Ocean Group Additional data: USGS EROS Data Center (topography); USGS Terrestrial Remote Sensing Flagstaff Field Center (Antarctica); Defense Meteorological Satellite Program (city lights).This spectacular “blue marble” image is the most detailed true-color image of the entire Earth to date. Using a collection of satellite-based observations, scientists and visualizers stitched together months of observations of the land surface, oceans, sea ice, and clouds into a seamless, true-color mosaic of every square kilometer (.386 square mile) of our planet. These images are freely available to educators, scientists, museums, and the public.Much of the information contained in this image came from a single remote-sensing device-NASA’s Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer, or MODIS. Flying over 700 km above the Earth onboard the Terra satellite, MODIS provides an integrated tool for observing a variety of terrestrial, oceanic, and atmospheric features of the Earth. The land and coastal ocean portions of these images are based on surface observations collected from June through September 2001 and combined, or composited, every eight days to compensate for clouds that might block the sensor’s view of the surface on any single day. Two different types of ocean data were used in these images: shallow water true color data, and global ocean color (or chlorophyll) data. Topographic shading is based on the GTOPO 30 elevation dataset compiled by the U.S. Geological Survey’s EROS Data Center. MODIS observations of polar sea ice were combined with observations of Antarctica made by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s AVHRR sensor—the Advanced Very High Resolution Radiometer. The cloud image is a composite of two days of imagery collected in visible light wavelengths and a third day of thermal infra-red imagery over the poles. Global city lights, derived from 9 months of observations from the Defense Meteorological Satellite Program, are superimposed on a darkened land surface map.
- Narrative: The blue marble project also makes high-resolution images of Earth available. Here’s a close-up of the West on February 1, 2004. Source: NASAURL: http://visibleearth.nasa.gov/view.php?id=57723Notes: NASA Goddard Space Flight Center Image by Reto Stöckli (land surface, shallow water, clouds). Enhancements by Robert Simmon (ocean color, compositing, 3D globes, animation). Data and technical support: MODIS Land Group; MODIS Science Data Support Team; MODIS Atmosphere Group; MODIS Ocean Group Additional data: USGS EROS Data Center (topography); USGS Terrestrial Remote Sensing Flagstaff Field Center (Antarctica); Defense Meteorological Satellite Program (city lights).This spectacular “blue marble” image is the most detailed true-color image of the entire Earth to date. Using a collection of satellite-based observations, scientists and visualizers stitched together months of observations of the land surface, oceans, sea ice, and clouds into a seamless, true-color mosaic of every square kilometer (.386 square mile) of our planet. These images are freely available to educators, scientists, museums, and the public.Much of the information contained in this image came from a single remote-sensing device-NASA’s Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer, or MODIS. Flying over 700 km above the Earth onboard the Terra satellite, MODIS provides an integrated tool for observing a variety of terrestrial, oceanic, and atmospheric features of the Earth. The land and coastal ocean portions of these images are based on surface observations collected from June through September 2001 and combined, or composited, every eight days to compensate for clouds that might block the sensor’s view of the surface on any single day. Two different types of ocean data were used in these images: shallow water true color data, and global ocean color (or chlorophyll) data. Topographic shading is based on the GTOPO 30 elevation dataset compiled by the U.S. Geological Survey’s EROS Data Center. MODIS observations of polar sea ice were combined with observations of Antarctica made by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s AVHRR sensor—the Advanced Very High Resolution Radiometer. The cloud image is a composite of two days of imagery collected in visible light wavelengths and a third day of thermal infra-red imagery over the poles. Global city lights, derived from 9 months of observations from the Defense Meteorological Satellite Program, are superimposed on a darkened land surface map.
- Narrative: The preceding slides have shown the Earth with the north pole up and south pole down. By accident, I flipped the image and was struck by how different it looked. North America seems more like an island on a planet that is 71 percent ocean.Source: NASAURL: http://visibleearth.nasa.gov/view.php?id=57723Notes: NASA Goddard Space Flight Center Image by Reto Stöckli (land surface, shallow water, clouds). Enhancements by Robert Simmon (ocean color, compositing, 3D globes, animation). Data and technical support: MODIS Land Group; MODIS Science Data Support Team; MODIS Atmosphere Group; MODIS Ocean Group Additional data: USGS EROS Data Center (topography); USGS Terrestrial Remote Sensing Flagstaff Field Center (Antarctica); Defense Meteorological Satellite Program (city lights).This spectacular “blue marble” image is the most detailed true-color image of the entire Earth to date. Using a collection of satellite-based observations, scientists and visualizers stitched together months of observations of the land surface, oceans, sea ice, and clouds into a seamless, true-color mosaic of every square kilometer (.386 square mile) of our planet. These images are freely available to educators, scientists, museums, and the public.Much of the information contained in this image came from a single remote-sensing device-NASA’s Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer, or MODIS. Flying over 700 km above the Earth onboard the Terra satellite, MODIS provides an integrated tool for observing a variety of terrestrial, oceanic, and atmospheric features of the Earth. The land and coastal ocean portions of these images are based on surface observations collected from June through September 2001 and combined, or composited, every eight days to compensate for clouds that might block the sensor’s view of the surface on any single day. Two different types of ocean data were used in these images: shallow water true color data, and global ocean color (or chlorophyll) data. Topographic shading is based on the GTOPO 30 elevation dataset compiled by the U.S. Geological Survey’s EROS Data Center. MODIS observations of polar sea ice were combined with observations of Antarctica made by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s AVHRR sensor—the Advanced Very High Resolution Radiometer. The cloud image is a composite of two days of imagery collected in visible light wavelengths and a third day of thermal infra-red imagery over the poles. Global city lights, derived from 9 months of observations from the Defense Meteorological Satellite Program, are superimposed on a darkened land surface map.
- Narrative: Here’s the other view inverted.Source: NASAURL: http://visibleearth.nasa.gov/view.php?id=57723Notes: NASA Goddard Space Flight Center Image by Reto Stöckli (land surface, shallow water, clouds). Enhancements by Robert Simmon (ocean color, compositing, 3D globes, animation). Data and technical support: MODIS Land Group; MODIS Science Data Support Team; MODIS Atmosphere Group; MODIS Ocean Group Additional data: USGS EROS Data Center (topography); USGS Terrestrial Remote Sensing Flagstaff Field Center (Antarctica); Defense Meteorological Satellite Program (city lights).This spectacular “blue marble” image is the most detailed true-color image of the entire Earth to date. Using a collection of satellite-based observations, scientists and visualizers stitched together months of observations of the land surface, oceans, sea ice, and clouds into a seamless, true-color mosaic of every square kilometer (.386 square mile) of our planet. These images are freely available to educators, scientists, museums, and the public.Much of the information contained in this image came from a single remote-sensing device-NASA’s Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer, or MODIS. Flying over 700 km above the Earth onboard the Terra satellite, MODIS provides an integrated tool for observing a variety of terrestrial, oceanic, and atmospheric features of the Earth. The land and coastal ocean portions of these images are based on surface observations collected from June through September 2001 and combined, or composited, every eight days to compensate for clouds that might block the sensor’s view of the surface on any single day. Two different types of ocean data were used in these images: shallow water true color data, and global ocean color (or chlorophyll) data. Topographic shading is based on the GTOPO 30 elevation dataset compiled by the U.S. Geological Survey’s EROS Data Center. MODIS observations of polar sea ice were combined with observations of Antarctica made by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s AVHRR sensor—the Advanced Very High Resolution Radiometer. The cloud image is a composite of two days of imagery collected in visible light wavelengths and a third day of thermal infra-red imagery over the poles. Global city lights, derived from 9 months of observations from the Defense Meteorological Satellite Program, are superimposed on a darkened land surface map.
- Narrative: NASA has also created some interesting images from unusual vantage points. This one shows the Arctic region and high latitudes.Source: NASAURL: http://visibleearth.nasa.gov/view_cat.php?categoryID=1484Notes: Image by Norman Kuring, NASA/GSFC/Suomi NPP. Caption by Michael Carlowicz. Suomi NPP is the result of a partnership between NASA, NOAA and the Department of Defense.There have been many images of the full disc of Earth from space—a view often referred to as “the Blue Marble”—but few have looked quite like this. Using natural-color images from the Visible/Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) on the recently launched Suomi-NPP satellite, a NASA scientist has compiled a new view showing the Arctic and high latitudes.Ocean scientist Norman Kuring of NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center pieced together this composite image of Europe, Asia, North Africa, and the entire Arctic. It was compiled from 15 satellite passes made by Suomi-NPP on May 26, 2012. The spacecraft circles the Earth from pole to pole at an altitude of 824 kilometers (512 miles), so it takes multiple passes to gather enough data to show an entire hemisphere without gaps in the view.Kuring stitched the image swaths together and then set up this view looking down from 70 degrees North, 60 degrees East. (That is, the view is artificial, as the satellite does not see the full disc at one time.) He was able to show the Arctic in this image because northern hemisphere spring spreads enough sunlight over the North Pole to allow a natural-light view. VIIRS is a scanning radiometer that acquires data in 22 spectral bands, covering visible, near-infrared, and thermal infrared regions of the electromagnetic spectrum. It was designed to extend and improve upon the measurements of land masses, oceans, ice, and the atmosphere made over the past two decades by the Advanced Very High Resolution Radiometer (AVHRR) and the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS).
- Narrative: In some of the views, Earth looks more like the black marble. Here we can see night lights in the Western hemisphere. Source: NASAURL: http://visibleearth.nasa.gov/view.php?id=79787Notes:NASA Earth Observatory image by Robert Simmon, using Suomi NPP VIIRS data provided courtesy of Chris Elvidge (NOAA National Geophysical Data Center). Suomi NPP is the result of a partnership between NASA, NOAA, and the Department of Defense. Caption by Mike Carlowicz.This image of North and South America at night is a composite assembled from data acquired by the Suomi NPP satellite in April and October 2012. The new data was mapped over existing Blue Marble imagery of Earth to provide a realistic view of the planet.The nighttime view was made possible by the new satellite’s “day-night band” of the Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite. VIIRS detects light in a range of wavelengths from green to near-infrared and uses filtering techniques to observe dim signals such as city lights, gas flares, auroras, wildfires, and reflected moonlight. In this case, auroras, fires, and other stray light have been removed to emphasize the city lights.“Artificial lighting is a excellent remote sensing observable and proxy for human activity,” says Chris Elvidge, who leads the Earth Observation Group at NOAA’s National Geophysical Data Center. Social scientists and demographers have used night lights to model the spatial distribution of economic activity, of constructed surfaces, and of populations. Planners and environmental groups have used maps of lights to select sites for astronomical observatories and to monitor human development around parks and wildlife refuges. Electric power companies, emergency managers, and news media turn to night lights to observe blackouts.Named for satellite meteorology pioneer Verner Suomi, NPP flies over any given point on Earth's surface twice each day at roughly 1:30 a.m. and p.m. The polar-orbiting satellite flies 824 kilometers (512 miles) above the surface, sending its data once per orbit to a ground station in Svalbard, Norway, and continuously to local direct broadcast users distributed around the world. The mission is managed by NASA with operational support from NOAA and its Joint Polar Satellite System, which manages the satellite's ground system.Learn more about the VIIRS day-night band and nighttime imaging of Earth in our new feature story: Out of the Blue and Into the Black.
- Narrative: Here’s the entire world at night.Source: NASAURL: http://visibleearth.nasa.gov/view.php?id=55167Notes:Data courtesy Marc Imhoff of NASA GSFC and Christopher Elvidge of NOAA NGDC. Image by Craig Mayhew and Robert Simmon, NASA GSFC.This image of Earth’s city lights was created with data from the Defense Meteorological Satellite Program (DMSP) Operational Linescan System (OLS). Originally designed to view clouds by moonlight, the OLS is also used to map the locations of permanent lights on the Earth’s surface.The brightest areas of the Earth are the most urbanized, but not necessarily the most populated. (Compare western Europe with China and India.) Cities tend to grow along coastlines and transportation networks. Even without the underlying map, the outlines of many continents would still be visible. The United States interstate highway system appears as a lattice connecting the brighter dots of city centers. In Russia, the Trans-Siberian railroad is a thin line stretching from Moscow through the center of Asia to Vladivostok. The Nile River, from the Aswan Dam to the Mediterranean Sea, is another bright thread through an otherwise dark region.Even more than 100 years after the invention of the electric light, some regions remain thinly populated and unlit. Antarctica is entirely dark. The interior jungles of Africa and South America are mostly dark, but lights are beginning to appear there. Deserts in Africa, Arabia, Australia, Mongolia, and the United States are poorly lit as well (except along the coast), along with the boreal forests of Canada and Russia, and the great mountains of the Himalaya.The Earth Observatory article Bright Lights, Big City describes how NASA scientists use city light data to map urbanization
- Narrative: And here’s the continental United States.Source: NASAURL: http://visibleearth.nasa.gov/view.php?id=55167Notes:Data courtesy Marc Imhoff of NASA GSFC and Christopher Elvidge of NOAA NGDC. Image by Craig Mayhew and Robert Simmon, NASA GSFC.This image of Earth’s city lights was created with data from the Defense Meteorological Satellite Program (DMSP) Operational Linescan System (OLS). Originally designed to view clouds by moonlight, the OLS is also used to map the locations of permanent lights on the Earth’s surface.The brightest areas of the Earth are the most urbanized, but not necessarily the most populated. (Compare western Europe with China and India.) Cities tend to grow along coastlines and transportation networks. Even without the underlying map, the outlines of many continents would still be visible. The United States interstate highway system appears as a lattice connecting the brighter dots of city centers. In Russia, the Trans-Siberian railroad is a thin line stretching from Moscow through the center of Asia to Vladivostok. The Nile River, from the Aswan Dam to the Mediterranean Sea, is another bright thread through an otherwise dark region.Even more than 100 years after the invention of the electric light, some regions remain thinly populated and unlit. Antarctica is entirely dark. The interior jungles of Africa and South America are mostly dark, but lights are beginning to appear there. Deserts in Africa, Arabia, Australia, Mongolia, and the United States are poorly lit as well (except along the coast), along with the boreal forests of Canada and Russia, and the great mountains of the Himalaya.The Earth Observatory article Bright Lights, Big City describes how NASA scientists use city light data to map urbanization
- Narrative: And the American West.Source: NASAURL: http://visibleearth.nasa.gov/view.php?id=55167Notes:Data courtesy Marc Imhoff of NASA GSFC and Christopher Elvidge of NOAA NGDC. Image by Craig Mayhew and Robert Simmon, NASA GSFC.This image of Earth’s city lights was created with data from the Defense Meteorological Satellite Program (DMSP) Operational Linescan System (OLS). Originally designed to view clouds by moonlight, the OLS is also used to map the locations of permanent lights on the Earth’s surface.The brightest areas of the Earth are the most urbanized, but not necessarily the most populated. (Compare western Europe with China and India.) Cities tend to grow along coastlines and transportation networks. Even without the underlying map, the outlines of many continents would still be visible. The United States interstate highway system appears as a lattice connecting the brighter dots of city centers. In Russia, the Trans-Siberian railroad is a thin line stretching from Moscow through the center of Asia to Vladivostok. The Nile River, from the Aswan Dam to the Mediterranean Sea, is another bright thread through an otherwise dark region.Even more than 100 years after the invention of the electric light, some regions remain thinly populated and unlit. Antarctica is entirely dark. The interior jungles of Africa and South America are mostly dark, but lights are beginning to appear there. Deserts in Africa, Arabia, Australia, Mongolia, and the United States are poorly lit as well (except along the coast), along with the boreal forests of Canada and Russia, and the great mountains of the Himalaya.The Earth Observatory article Bright Lights, Big City describes how NASA scientists use city light data to map urbanization
- Narrative: Some of the most captivating views of Earth show the juxtaposition with the moon. The Galileo spacecraft captured this image from nearly 4 million miles away.Source: NASA/JPLURL: http://www.planetary.org/multimedia/space-images/earth/gal_earth_moon.htmlNotes: On December 16, 1992, eight days after its encounter with Earth, the Galileo spacecraft looked back from a distance of about 6.2 million kilometers to capture this remarkable view of the Moon in orbit about Earth.The composite photograph was constructed from images taken through visible (violet, red) and near-infrared (1.0-micron) filters. The Moon is in the foreground; its orbital path is from left to right. Brightly colored Earth contrasts strongly with the Moon, which reacts only about one-third as much sunlight as our world. To improve the visibility of both bodies, contrast and color have been computer enhanced. At the bottom of Earth's disk, Antarctica is visible through clouds. The Moon's far side can also be seen. The shadowy indentation in the Moon's dawn terminator -- the boundary between its dark and lit sides -- is the South Pole-Aitken Basin, one of the largest and oldest lunar impact features.
- Narrative: Here’s an animation of planet, over a 25-hour period, as the Galileo spacecraft departed in 1990 for Jupiter.Source: NASA/JPL/Doug EllisonURL: http://www.planetary.org/multimedia/space-images/earth/all_gal_e1_1hr.htmlNotes: As Galileo receded from its first flyby of Earth on December 11 and 12, 1990, it took images of Earth in six different filters almost every minute over a 25-hour period. The animation here includes images taken once an hour, representing about a tenth of the full number of frames.
- Narrative: Other space probes, such as Cassini, have also pointed their cameras back toward Earth. In this image, released earlier this year, the Earth and moon are visible as a tiny dot beneath Saturn’s rings.Source: NASA/JPL/SSIURL: http://www.planetary.org/multimedia/space-images/earth/the-day-the-earth-smiled.htmlNotes:In this rare image taken on July 19, 2013, the wide-angle camera on NASA's Cassini spacecraft has captured Saturn's rings and our planet Earth and its Moon in the same frame. This is only one footprint in a mosaic of 33 footprints covering the entire Saturn ring system (including Saturn itself). At each footprint, images were taken in different spectral filters for a total of 323 images: some were taken for scientific purposes and some to produce a natural color mosaic. This is the only wide-angle footprint that has the Earth-Moon system in it.The dark side of Saturn, its bright limb, the main rings, the F ring, and the G and E rings are clearly seen; the limb of Saturn and the F ring are overexposed. The "breaks" in the brightness of Saturn's limb are due to the shadows of the rings on the globe of Saturn, preventing sunlight from shining through the atmosphere in those regions. The E and G rings have been brightened for better visibility.Earth, which is 898 million miles (1.44 billion kilometers) away in this image, appears as a blue dot at center right; the moon can be seen as a fainter protrusion off its right side.
- Narrative: The Deep Impact spacecraft, launched in 2005 to study comets, sent back stunning images of the moon transiting the Earth.Source: NASA/JPL/UMD, color composite by Gordan UgarkovicURL: http://www.planetary.org/multimedia/space-images/earth/moon-transiting-earth-deep-impact-sequence.htmlAs part of its EPOXI mission, Deep Impact spent 24 hours over May 28 and 29, 2008, watching Earth from a distance of 50 million kilometers. During that time, the Moon transited Earth as seen from the spacecraft. The view was captured using Deep Impact's High Resolution Imager, which had a serious blurring problem; efforts to reduce the blurring have introduced some other artifacts, like the concentric rings on the Moon. These eight images were captured about half an hour apart, so the whole sequence spans about 3.5 hours.
- Narrative: Here’s the animation, captured from a distance of about 31 million miles.Source: NASA/JPL/UMDURL: http://www.planetary.org/multimedia/space-images/earth/moon-transiting-earth-deep-impact-animation.htmlNotes: As part of its EPOXI mission, Deep Impact spent 24 hours over May 28 and 29, 2008, watching Earth from a distance of 50 million kilometers. During that time, the Moon transited Earth as seen from the spacecraft. The view was captured using Deep Impact's High Resolution Imager, which had a serious blurring problem; efforts to reduce the blurring have introduced some other artifacts, like the concentric rings on the Moon. The full sequence covers 24 hours, a full rotation of Earth.
- Narrative: Finally, here’s an intriguing shot of a solar eclipse on Earth, as viewed by the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter in 2012. Source: NASA / GSFC / ASUURL: http://www.planetary.org/multimedia/space-images/sun/a-solar-eclipse-as-viewed.htmlNotes: Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter performed a challenging feat, catching the Moon's shadow crossing the full Earth's disk a total of four times during the May 12, 2012 solar eclipse. Click here for an animation of all four images. Visit the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter Camera website to learn more about how it was taken. Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter turned toward Earth to catch a view of the Moon's shadow passing across the Aleutian Islands during the May 12, 2012 solar eclipse. The Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter Camera team explained some of the challenge inherent in the acquisition of this image on their website:The LROC NAC cannot easily acquire images of the Earth, and acquiring Earth views requires a significant amount of planning. The NAC is a line scanner, meaning that it has only one row of 5064 pixels per camera. Instead of snapping a single frame, an image is built up by the motion of the spacecraft in orbit about the Moon (about 1600 meters per second). To obtain an image of the Earth the spacecraft is turned 180° to face the Earth, then the spacecraft is pitched as quickly as possible (one-tenth of a degree per second), so that the image is built up line by line. You can see that two of the frames in the animated image below are slightly clipped, because LRO's timing wasn't perfect and the NAC ran out of lines before completing the scan (the NAC buffer is filled up after 52,240 lines, which is 256 Mbytes of data).Because it was an annular eclipse, the shadow isn't totally dark; some sunlight still made it down to viewers of the eclipse as it passed over.
