Monoclonal antibody
- 2. Monoclonal Antibodies Dr. Ashutosh Tiwari M.D. Pharmacology 1st yr. stud. SAIMS Indore 26/12/2013
- 3. Seminar layout Antibody Polyclonal Antibody Monoclonal Antibody Hybridoma technique Production of Monoclonal Antibody Evolution of Monoclonal Antibody Nomenclature of Monoclonal Antibody Types of Monoclonal Antibody Pharmacokinetics & Adverse Effects Therapeutic Potentials of Monoclonal Antibody
- 4. What are antibodies? An antibody is a protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects like bacteria and viruses. Each antibody recognizes a specific antigen unique to its target. Monoclonal antibodies (mAb) are antibodies that are identical because they were produced by one type of immune cell, all clones of a single parent cell. Polyclonal antibodies are antibodies that are derived from different cell lines. They differ in amino acid sequence. Immunoglobulin (Ig) are structurally related glycoproteins that function as antibodies
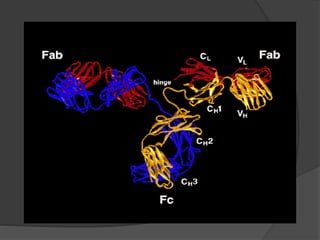
- 5. The Structure of an Antibody 2 identical light chains (~220 amino acids long) Variable domain: VL Constant domain: CL 2 identical heavy chains (~440 amino acids long) Variable domain: VH 3 Constant domains: CH1, CH2, CH3 Covalent, disulfide bonds between cysteine residues Flexible “hinge region”
- 6. Antibodies have two major functions: • Recognize and bind antigen • Induce immune responses after binding The variable region mediates binding • Affinity for a given antigen is determined by the variable region • The variable region confers absolute specificity for an antigen The constant region mediates immune response after binding • Different classes of constant regions generate different isotypes • Different isotypes of antibody have differing properties Antibody Function Constant region Variable region
- 7. Antibodies as Drugs Antibodies are naturally occurring Discovery of their innate properties hinted at great therapeutic potential High-specificity in binding Already present in the body Can activate and couple components of the immune system Modification to structure and refinement in production methods have made antibodies a viable modern drug
- 8. History 1975 : Hybridoma Technology George Kohler and Cesar Milstein devised a method to obtain large amounts of a mAb 1988 : The Nobel Prize for Medicine - In 1988, Greg Winter et al pioneered the techniques to humanize monoclonal antibodies
- 9. History 1986 first monoclonal antibody reached the market – Muromonab-CD3 2003 First fully human monoclonal antibody – Adalimumab
- 10. Polyclonal antibodies are a mixture of antibodies with different antigen binding sites that may bind to different epitopes or antigens of the immunizing agent with varying affinities. Produced by immunizing an animal with the appropriate antigen - wide array of B cells will be stimulated to produce anti-protein antibodies. Antibodies may be made to a number of different epitopes of the protein. Even antibodies that bind to the same epitope may have different antigen-binding sites and bind the epitope with different affinity. Polyclonal Antibodies
- 11. The serum obtained from an immunized animal is referred to as a polyclonal antiserum. Contains antibody to different epitopes and different antigens that were present in the immunizing inoculum The immunized animal’s serum is collected. Antibodies can then be purified from the serum. Since one antigen induces the production of many antibodies the result is a ‘polyclonal’ mixture of antibodies. ATG ( Anti thymocyte globulin) ALG ( Anti lymphocyte globulin, Lymphocyte immune globulin)
- 12. Monoclonal Antibodies • A class of highly specific antibodies produced by the clones of a single hybrid cell • Produced by fusing a B cell secreting the desired antibody with a tumour cell (myeloma cell) capable of growing indefinitely • Fused cell called hybridoma • Monoclonal antibodies all have identical antigen- binding sites • bind to the same epitope with same affinity • same antibody class (isotype)
- 13. Antibodies Polyclonal Monoclonal Produced by: Many B cell clones A single B cell clone Bind to: Multiple epitopes of all antigens used in the immunization A single epitope of a single antigen Antibody class: A mixture of different Ab classes (isotypes) All of a single Ab class Ag-binding sites: different antigen- binding sites All Abs have the same antigen binding site
- 14. Antibodies Polyclonal Monoclonal Cost Less expensive More expensive Yield Limited supply Infinite supply Ease Easily, rapidly produced Time consuming, more technical skill Potential for cross- reactivity High Low
- 17. PRODUCTION OF MONOCLONAL ANTIBODY Step 1: - Immunization Of Mice & Selection Of Mouse Donor For Generation Of Hybridoma cells HYBRIDOMA TECHNOLOGY ANTIGEN ( Intact cell/ Whole cell membrane/ micro-organisms ) + ADJUVANT (emulsification) Ab titre reached in Serum Spleen removed (source of cells)
- 18. PRODUCTION OF MONOCLONAL ANTIBODY Step 2: - Screening Of Mice For Antibody Production HYBRIDOMA TECHNOLOGY After several weeks of immunization Serum Antibody Titre Determined (Technique: - ELISA / Flow cytometery) Titre too low BOOST (Pure antigen) Titre High BOOST (Pure antigen) 2 weeks
- 19. PRODUCTION OF MONOCLONAL ANTIBODY Step 3: - Preparation of Myeloma Cells HYBRIDOMA TECHNOLOGY Immortal Tumor Of Lymphocytes + 8 - Azaguanine Myeloma Cells High Viability & Rapid Growth HGPRT- Myeloma Cells
- 20. PRODUCTION OF MONOCLONAL ANTIBODY Step 4: - Fusion of Myeloma Cells with Immune Spleen Cells & Selection of Hybridoma Cells HYBRIDOMA TECHNOLOGY FUSION PEG MYELOMA CELLSSPLEEN CELLS HYBRIDOMA CELLS ELISA PLATE Feeder Cells Growth Medium HAT Medium 1. Plating of Cells in HAT selective Medium 2. Scanning of Viable Hybridomas
- 21. PRODUCTION OF MONOCLONAL ANTIBODY Step 4: - Cloning of Hybridoma Cell Lines by “ Limiting Dilution” or Expansion HYBRIDOMA TECHNOLOGY A. Clone Each +ve Culture B. Test Each Supernatant for Antibodies C. Expand +ve Clones Mouse Ascites Method Tissue Culture Method
- 22. Myeloma cells have been genetically engineered such that they can not use hypoxanthine, aminopterin, and thymidine (HAT medium) as a source for nucleic acid biosynthesis and will die in culture (lack HGPRT enzyme) Spleen cells (B cells) have limited life span Only B cells that have fused with the engineered myeloma cells will survive in culture when grown in HAT medium. Hybridoma Selection The “HAT Trick”
- 24. Conventional production of mAbs The hybridoma technology: spleen cells from immunized mice are fused with the murine myeloma cells. The several process had been developed at large scale. According to the different cell culture methods, it can calisifed into four fields 1. Robottle cell culture process. 2. Membrane binded cell culture process 3. Microcarrier cell culture process 4. Suspended cell culture process
- 25. Production in animals ( In-vivo ) Mouse ascites method •Hybridoma cells injected in mouse •Produce ascites •Fluid contains high concentration of Ab’s •No further concentration required •Purification required •Easy and inexpensive •Animal mortality
- 26. Ethical issues: Freund’s complete adjuvant (FCA) (to enhance the immune response): painful lesions at the injection site. Pristane as a "priming" agent - granulomatous reactions Respiratory distress: due to ascites. Shock - rapid fluid loss FCA and pristane should not be used where it is possible to use no adjuvant or less irritant adjuvants. FCA should not be used more than once in individual mice. The volume of FCA and pristane used should not exceed 0.1ml and 0.2ml respectively. Individual mice should not be inoculated with adjuvant more than 3 times. A priming agent should not be used in individual mice more than once. Ascites fluid should only be harvested once at the time of euthanasia.
- 27. Production in cell culture ( In-vitro) Batch tissue culture method: • Grow hybridoma cells in batches • Purify Mabs from the culture media • Fetal bovine serum commonly used • low concentration • denaturation during concentration Semi permeable membrane based system : • A barrier – hollow fibre or a membrane • Larger compartment containing culture media • Smaller chamber to isolate cells and Mabs • High concentrations • Method of choice for large scale production
- 28. Origin First generation Murine, rabbit or rat proteins purified after immunisation with antigen Abs to these proteins (Ag) generated in patients: human antimurine antibody (HAMA) Block effectiveness of therapy Adverse events serum sickness or anaphylaxis
- 29. Origin Second generation DNA technology or genetic engineering used to construct hybrids composed of human Abs regions with murine Chimeric Abs Humanized Human
- 30. EVOLUTION OF MONOCLONAL ANTIBODY 1. TRANSGENIC 2. LIBRARIES a.BACTERIOPHAGE b. mRNA c. Cell Surface Ist generation mab 2nd generation mab Daclizumab
- 31. Types of mAbs Purple denotes human component orange murine component
- 33. Murine Derived from mice Patients treated with murine mAbs develop a human antimouse antibody (HAMA) response Rapid clearance of the mAb Poor tumour penetration Hypersensitivity reactions 90Y-ibritumomab 131I -Tositumomab
- 34. Chimeric Abs Antigen binding parts (variable region) of mouse with effector parts (constant region) of human Infliximab Abciximab Rituximab
- 35. Humanized Human Ab with complimentary determining region (CDR) or hypervariable region from non human source Daclizumab Trastuzumab
- 36. Human Abs Recombinant DNA technology: Genes for variable Fab portion of human Abs is inserted in genome of bacteriophages & replicated Mixed with Ag & complementary Ab producing phages selected e.g. Adalimumab
- 37. Human mAbs Transgenic Mice Phage Display
- 38. Human Abs Even human Ab can provoke anti-idiotype responses HACA (human antichimera antibodies) HAHA (human antihuman antibodies) Plant Derived Mabs - Plant Genetic Engineering - Transgenic Plants - Transgenic tobacco, soyabeen, alfalfa etc. Lack of animal pathogenic contaminants Low production cost Ease of agricultural scale up
- 39. Nomenclature of Monoclonal Antibodies Prefix Target Source Suffix variable -o(s)- bone -u- human -mab -vi(r)- viral -o- mouse -ba(c)- bacterial -a- rat -li(m)- immune -e- hamster -le(s)- infectious lesions -i- primate -ci(r)- cardiovascular -xi- chimeric -mu(l)- musculoskeletal -zu- humanized -ki(n)- interleukin -axo- rat/murine hybrid -co(l)- colonic tumor -me(l)- melanoma -ma(r)- mammary tumor -go(t)- testicular tumor -go(v)- ovarian tumor -pr(o)- prostate tumor -tu(m)- miscellaneous tumor -neu(r)- nervous system -tox(a)- toxin as target
- 40. Nomenclature Suffix Human: -umab Humanized: -zumab Murine: -momab Chimeric: -ximab
- 41. Examples ab- + -ci- + -xi- + -mab: chimeric monoclonal antibody used on the cardiovascular system. tras- + -tu- + -zu- + -mab: humanized monoclonal antibody used against a tumor. Pali- + -vi- + -zu- + -mab humanized mab used against a virus (RSV)
- 42. Types of Monoclonal Antibody Naked Monoclonal Antibody: those without any drug or radioactive material attached to them Mark the cells for the immune system Attach to receptors – block binding of growth factors E.g.1. Trastuzumab - For advanced breast cancer (HER-2) 2. Rituximab - For B cell non Hodgkin lymphoma (CD 20) 3. Cetuximab - For advanced colorectal cancer ( HER-1) 4. Bevacizumab - For metastatic colorectal cancer (VEGF) 5. Alemtuzumab - For B cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. (CD 52)
- 43. Types of Monoclonal antibodies Conjugated/loaded/labeled Mabs : Coupled with drugs / toxins / radioatiactive atoms Chemo-labeled antibodies: ○ MAbs conjugated with chemotherapeutic agents e.g. brentuximab vedotin and ado-trastuzumab emtansine. ○ Brentuximab vedotin, attached to a chemo drug (MMAE) targets the CD30 antigen (present on T and B-cells) in treatment of Hodgkin lymphoma and non-responding anaplastic large cell lymphoma. ○ Ado-trastuzumab emtansine, attached to DM1 chemo drug, targets the HER2 protein antigen used for curing advanced breast cancer patients.
- 44. Types of Monoclonal antibodies Immune-toxins: conjugated with toxins e.g. Denileukin diftitox ○ used to treat some cancers (cutaneous T-cell lymphoma and many others) ○ consists of IL-2 protein attached to a toxin (derived from the germ causing diphtheria). ○ IL-2 normally attaches to cells that express the CD25 antigen and thus helps in delivering the toxin to these cells. Radio-immune Abs: e.g. Ibritumomab, ○ an MAb against the CD20 antigen on B cells (and lymphomas), ○ conjugated to either the radioactive isotope indium-111 (111In) or yttrium-90 (90Y) for treatment of lymphoma patients
- 45. Pharmacokinetics: mAbs Routes of administration: Subcutaneously (Rituximab, Trastuzumab, Adalimumab) Intramuscularly (Palivizumab) Intravenously IV route: preferred because of 100% bioavailability Route for elimination of antibodies Via uptake & catabolism by reticuloendothelial system & target tissue.
- 46. P/K: mAbs Half-life Chimeric : 4 –15 days Humanized: 3 - 24 days Recombinant human: 11– 24 days Human antimouse antibody (HAMA) response develops 7–10 days following exposure to murine antibody
- 47. Adverse Effect of Mabs Related to three mechanism: Xenogenetic nature of Mab used Suppression of physiological function Activation of inflammatory cells or mediators after binding of Mab to its target
- 48. Adverse Effect of Mabs Naked Mabs : Mild ; often allergic reaction on 1st infusion Cytokine release syndrome infusion toxicity, cytopenias Conjugated Mabs: More A/E’s ; depend on substances attached Antilymphocytes Mabs Immunosupression increase risk of infection Cancer Anti TNF-α Mab reactivation of tuberculosis lymphomas
- 49. Mechanisms of Action 1. Blocking action of molecular targets Can work antagonistically by binding a receptor to prevent activation Can also bind the antigen and prevent activation 2. “Magic Bullet” Compound with target specificity is coupled with various effector groups ○ Toxins, radionuclei, enzymes, DNA 3. Signal molecules Coupled to mediators of apoptosis, cell division, etc.
- 50. Pharmaceutical Antibodies The fastest growing segment of the biopharmaceutical market $65 billion in sales for 2012 there are 5 antibody drugs listed in the top 10 best selling drugs of 2012 The antibody drugs featured in the top 10 in the year 2012: #8 = Roche’s Avastin (bevacizumab), with sales of US$6.260 billion #7 = Johnson & Johnson’s Remicade (infliximab), with sales of US$6.139 billion #5 = Roche’s Hereceptin (trastuzumab), with sales of US$6.397 billion #3 = Roche’s Rituxan (rituximab), with sales of US$7.285 billion #1 = AbbVie’s Humira (adalimumab), with sales of US$9.265 billion. therapeutic antibody drugs are in high demand and are playing a significant role in the generation of revenue for drug companies Many of the leading pharmaceutical companies have entered the mAb sector, attracted by quicker and less costly development, higher success rates, & premium pricing
- 53. Therapeutic uses Immunosuppression Autoimmune diseases Malignancies Antiplatelet therapy Infectious diseases Asthma Osteoporosis
- 54. Autoimmune disease mAB Target immune cells: remove them, block their function decrease cytokine levels
- 55. Cancer Strategies for the Mabs in Cancer: Immune reaction directed destruction of cancer cells Interference with the growth & differentiation of malignant cells Antigen epitope directed transport of anticancer agents to malignant cells Anti idiotype vaccines Variety of agents conjugated to Mabs for selective delivery to cancer cells
- 56. Applications of mABs Diagnostic tools in research and laboratory Different technologies in which MAbs are used include Western blot, immunodot blot, ELISA, radioimmuno assay (RIA), flow cytometry, immunohistochemistry, fluorescence microscopy, electron microscopy, confocal microscopy
- 57. Applications of mABs Diagnostic applications MAb is used to detect pregnancy as early as a week or two after conception by reacting with human chorionic gonadotrophin HIV diagnostic kits Rapid diagnosis of hepatitis, influenza, herpes, streptococcal & chlamydia infections Identification & characterization of tumor specific antigen: classification of cancer Imaging: Localization of cancer ○ Arcitumomab : colorectal carcinoma ○ Nofetumomab : small cell lung cancer
- 58. Future Applications Fight against bioterrorism Inhalational anthrax (potent biological terrorism) is caused by breathing the bacterial spores of Bacillus anthracis Raxibacumab injection is used to treat infectious inhalational anthrax when alternative therapies have failed
- 59. Future aspects Zanolimumab : Cutaneous T cell lymphoma Tremelimumab : Advanced melanoma Ruplizumab : Lupus nephritis Efungumab : Invasive Candida Infection Panobacumab : Pseudomonas Infection Solanezumab : Alzheimer’s Disease 60
- 60. Limitations of MAbs The typical doses of MAb drugs needed for treatment are significantly higher than those required for other drugs (or products). The huge demand to increase production of these drugs and the drive to lower the cost of these expensive medicines is a continuous challenge to the present industry.
- 61. Interesting Variations Small antibody fragments (Fv or Fab) are also effective in blocking cytokines Benefit: More readily penetrate tissue Coupling of antibody fragments to form dimers and tetramers Increases avidity and cross-linking Engineered Diabodies (Bispecific mABs) Two different antigen specificities ○ One against the target ○ The other against effectors Can cross-link effector cells
- 62. Nanobodies A Nanobody/single-domain antibody is a peptide chain of about 110 amino acids long, comprising one variable domain (VH) of a heavy-chain antibody, or of a common IgG 1989 - Raymond Hamers Discovered in camels Completely lack the light chain! Same antigen affinity as their four- chain counterparts Structure makes them more resistant to heat and pH May lead to development of oral nanobody pills Orally available single-domain antibodies against E. coli-induced diarrhoea in piglets have been developed and successfully tested Other diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, such as inflammatory bowel disease and colon cancer, are also possible targets for orally available sdAbs
- 63. TO SUMMARISE : MAbs are highly specific Abs produced by a clone of single hybrid cells formed by fusion of B cell with the tumor cell. The hybridoma formed yields higher amount of MAbs. MAbs can be produced in vitro and in vivo . Animals are utilized to produce MAbs, but these antibodies are associated with immunogenicity and ethical problems. Recombinant DNA technology, genetic engineering and transgenic animals are used to produce humanized MAbs or pure human MAbs, with fewer ADRs Used for treatment of cancer, autoimmune disorders, graft rejections, infections, asthma etc.
- 64. Finally, the dreams of Paul Ehrlich who considered antibodies a magic bullets have become reality. Monoclonal antibodies have established themselves as the most important and rapidly expanding class of drugs in oncology. Paul Ehrlich (1854-1915)
